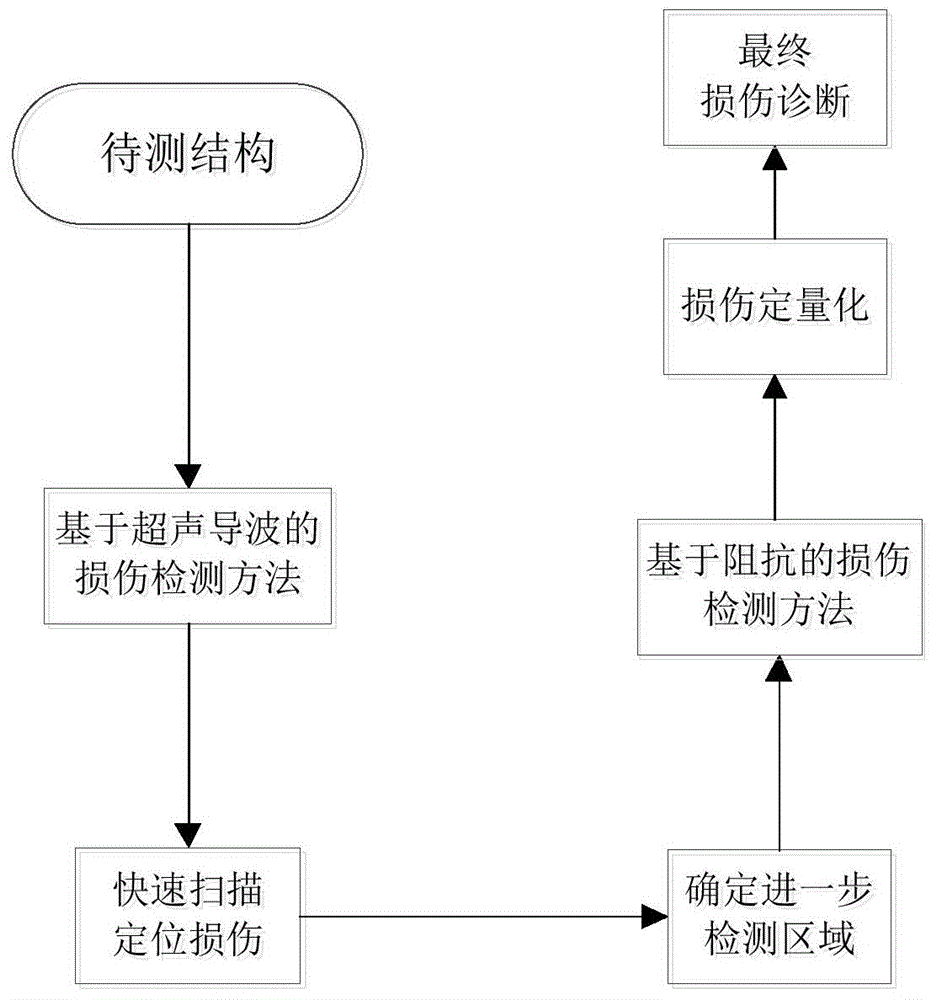
Ultrasonic guided wave and electromechanical impedance-based mobile damage detection method
An electromechanical impedance and ultrasonic guided wave technology, applied in material impedance and other directions, can solve the problems of damage location, the difficulty and disadvantage of quantitative damage detection, achieve flexible detection and diagnosis, and improve damage detection capabilities.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
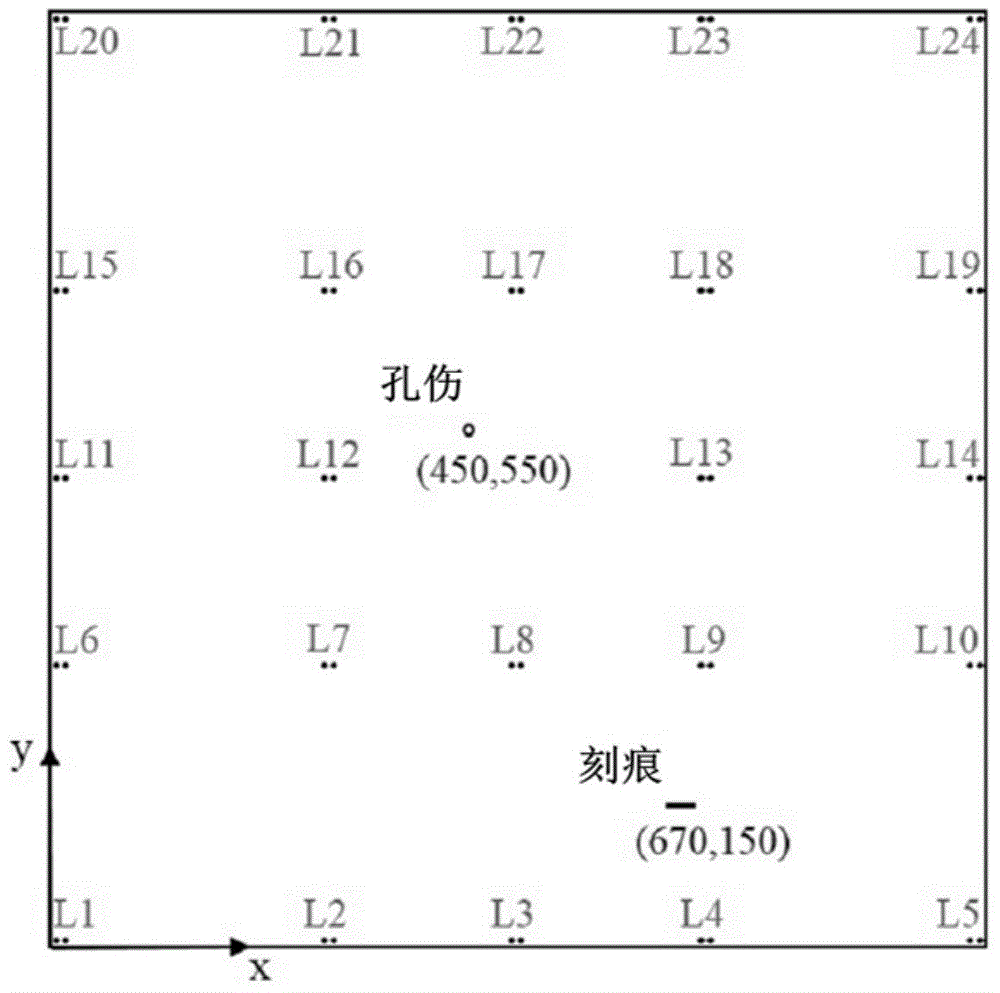
[0039] Step 1: Take a piece such as figure 2 The shown aluminum plate specimen (dimensions: 1000mm×1000mm×3mm), respectively set a hole and a notch on it, and the coordinates of the two are as follows: figure 2 shown. Among them, the diameter of the hole is 20mm, while the length of the notch is 30mm and the width is 1.5mm. Select N (24 in this example) different positions (L1, L2, ..., L24) on the aluminum plate as detection points, and their distribution is as follows figure 2 shown;
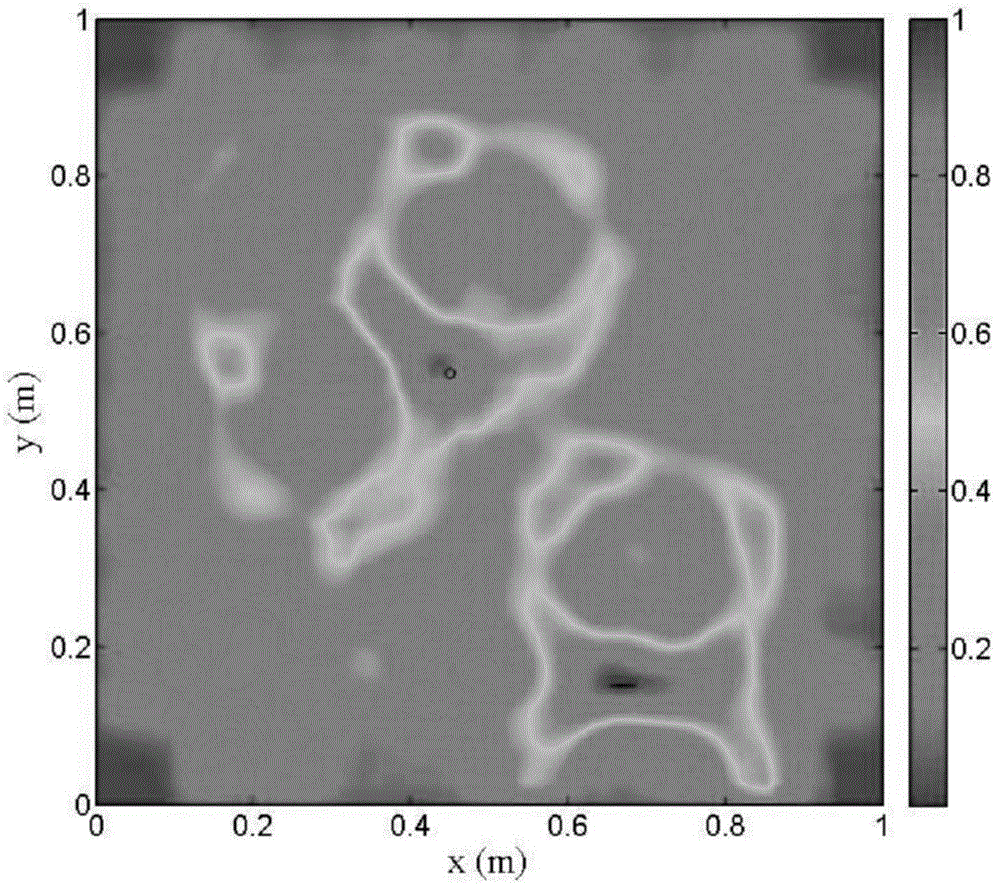
[0040] Step 2: According to the embodiment steps in the Chinese invention patent (application number 201410020701.1) applied by the inventor, a large-area structural damage detection method based on Lamb wave, the image of the test result of the guided wave method of the test piece is obtained, as shown in image 3 shown;
[0041] Step 3: According to the image of the damage diagnosis result of the guided wave, adjust the threshold and select the area E to be detected as the fine inspec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com