Method and system for estimating future average power consumption and remaining driving range of electric automobile
An average power consumption, electric vehicle technology, applied in electric vehicles, electric traction, electric devices, etc., can solve the problem of unreliable remaining driving range value of electric vehicles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
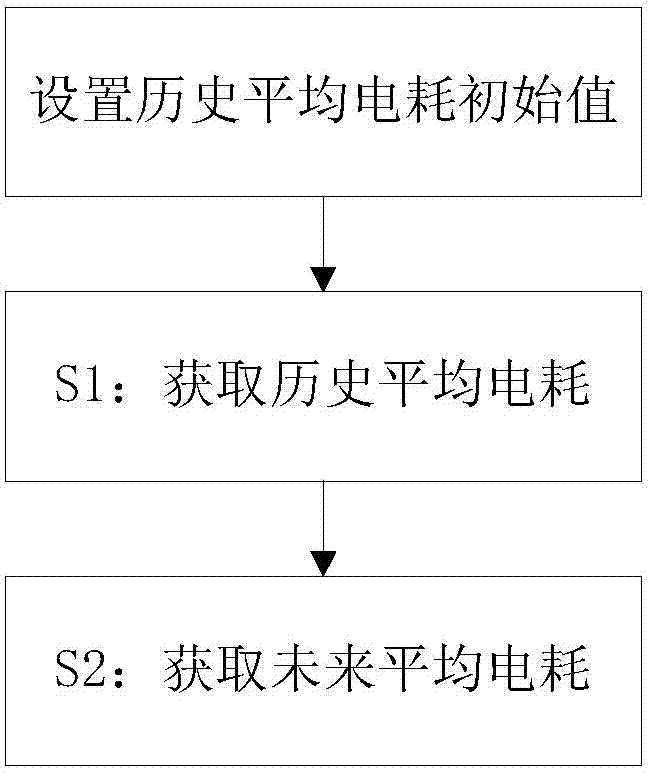
[0066] This embodiment provides a method for estimating future average power consumption, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0067] S1: Get historical average power consumption.
[0068] S2: Obtain future average power consumption according to the historical average power consumption.
[0069] In the step S1:
[0070] The historical average power consumption and the future average power consumption are distinguished by using the current moment as a time node. What is obtained before the current moment is the historical average power consumption, and what is obtained after the current moment is the future average power consumption. The historical average power consumption may be the historical average power consumption in a past period of time, or the historical average power consumption accumulated since the first operation of the electric vehicle until now. Regardless of the historical average power consumption at any stage, it can be calculated by u...
Embodiment 2
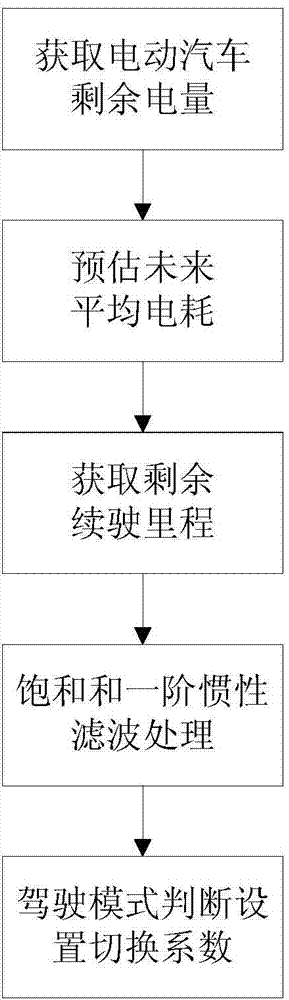
[0091] This embodiment provides a method for estimating the remaining driving range of an electric vehicle, such as figure 2 shown, including the following steps:
[0092] W1: Obtain the remaining power of the electric vehicle.
[0093] W2: Using the method for estimating the future average power consumption of the electric vehicle described in Embodiment 1, the future average power consumption of the electric vehicle is obtained.
[0094] W3: Obtain the remaining mileage of the electric vehicle S = remaining power / future average power consumption.
[0095] Wherein, in the step W1, the remaining power is obtained directly from the BMS (Battery Management System); or the rated voltage U of the power battery is obtained from the BMS 0 , rated capacity C 0 , SOC (State of Charge) value, battery health status SOH (State Of Health), the minimum discharge SOC value allowed by BMS SOC low , use the following formula to obtain the remaining power Q:
[0096] Q=U 0 ×C 0 ×(SOC-S...
Embodiment 3
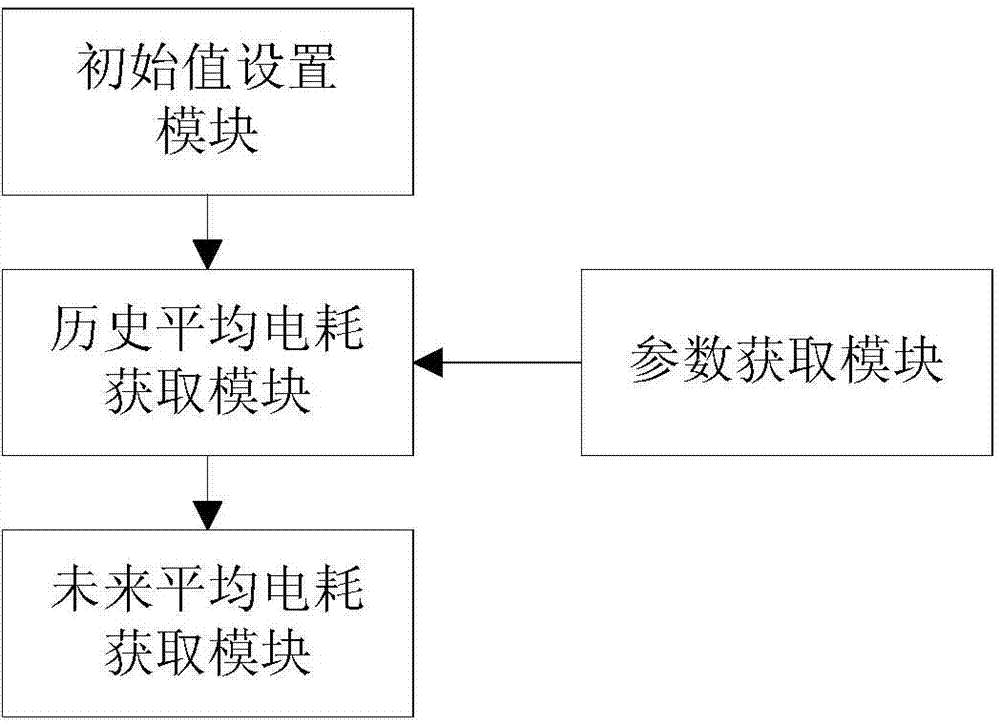
[0104] This embodiment provides a system for estimating the future average power consumption of electric vehicles, such as image 3 shown, including:
[0105] The historical average power consumption obtaining module is used to obtain the historical average power consumption.
[0106] The future average power consumption acquisition module acquires the future average power consumption according to the historical average power consumption obtained by the historical average power consumption acquisition module.
[0107] In this embodiment, in the historical average power consumption acquisition module, the following methods are used to obtain n historical average power consumptions of the latest n segments of mileage in real time, where n is a natural number:
[0108] Real-time acquisition of n historical average power consumption of the latest n segments of mileage, where the calculation method of the historical average power consumption of each segment of mileage is:
[0109...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com