Full wave rectifier circuit and voltage converter
A full-wave rectification circuit and circuit technology, applied in the direction of conversion equipment without intermediate conversion to AC, can solve problems such as high cost, complicated control, and affecting the efficiency of rectification circuits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
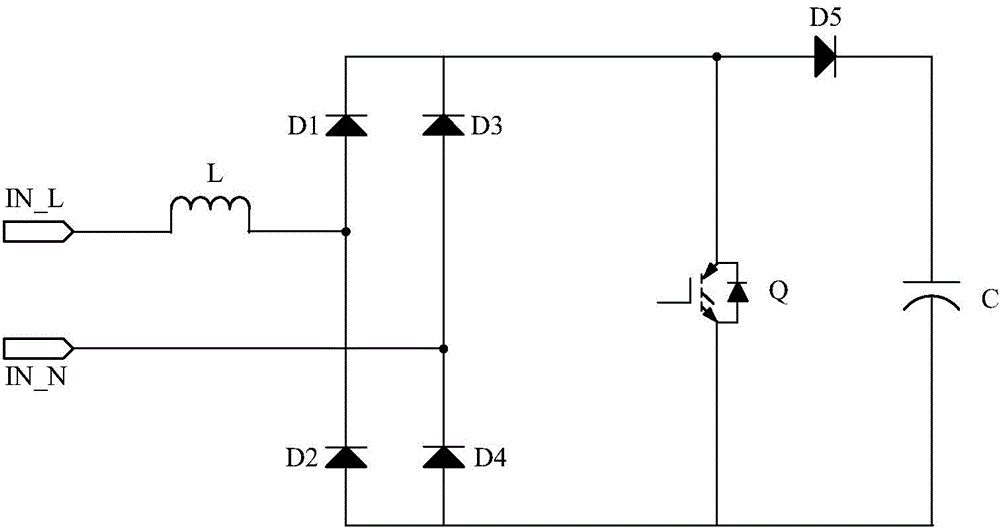
[0074] figure 2 Shown is the full-wave rectifier circuit provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, including a capacitor C, an inductor L, a MOS transistor Q, a first rectifier diode D1, a second rectifier diode D2, a third rectifier diode D3, a fourth rectifier diode D4 and Freewheeling diode D5, where:
[0075] The first rectifier diode D1 and the second rectifier diode D2 are connected in series to form the first branch, the third rectifier diode D3 and the fourth rectifier diode D4 are connected in series to form the second branch, and the first branch and the second branch are connected in parallel to form the third branch The third branch is connected with the inductor L and the MOS transistor Q in series to form a loop;
[0076] The terminal between the inductor L and the drain of the MOS transistor Q is connected to the anode of the freewheeling diode D5, and the cathode of the freewheeling diode D5 is connected to the positive electrode of the capacitor C; ...
Embodiment 2
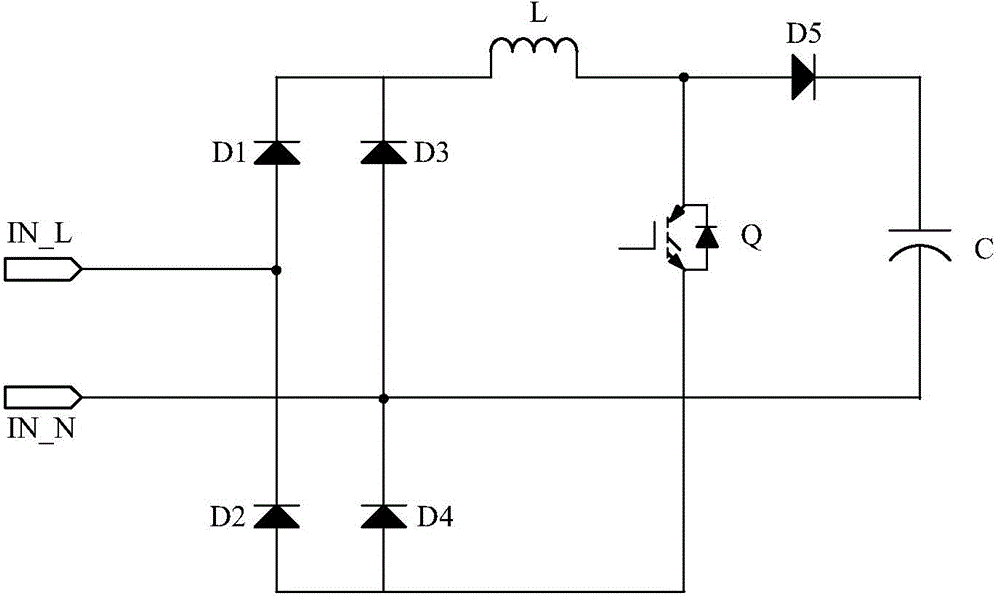
[0086] image 3 Shown is a full-wave rectifier circuit provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention, including a capacitor C, an inductor L, a MOS transistor Q, a first rectifier diode D1, a second rectifier diode D2, a third rectifier diode D3, a fourth rectifier diode D4 and Freewheeling diode D5, where:
[0087] The first rectifier diode D1 and the second rectifier diode D2 are connected in series to form the first branch, the third rectifier diode D3 and the fourth rectifier diode D4 are connected in series to form the second branch, and the first branch and the second branch are connected in parallel to form the third branch The third branch is connected with the MOS transistor Q and the inductor L in series to form a loop;
[0088] The terminal between the inductor L and the source of the MOS transistor Q is connected to the cathode of the freewheeling diode D5, and the anode of the freewheeling diode D5 is connected to the negative electrode of the capacitor C;
...
Embodiment 3
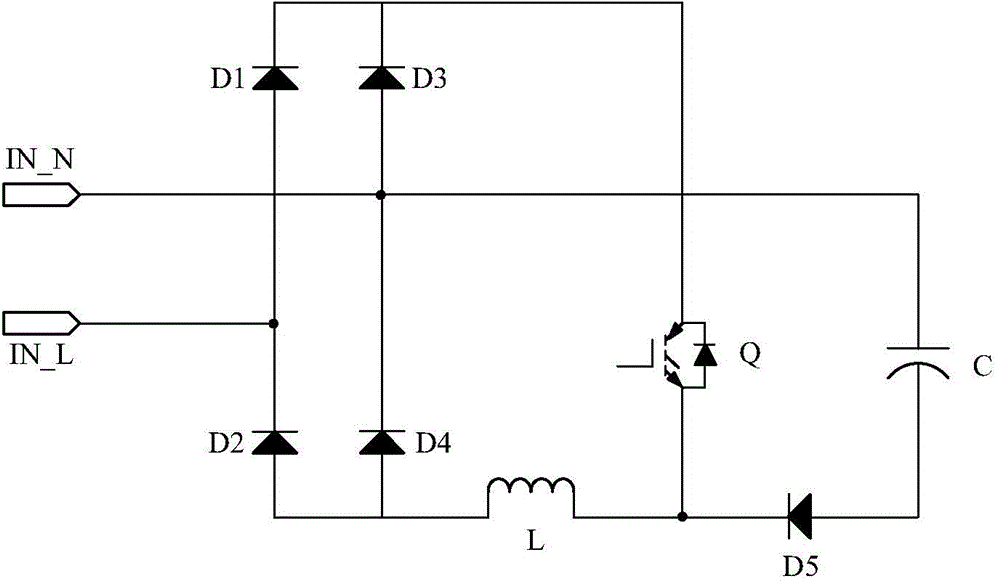
[0098] Figure 4 Shown is the full-wave rectifier circuit provided by Embodiment 3 of the present invention, which is compared with the full-wave rectifier circuit provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention. figure 2 In the full-wave rectifier circuit shown, a soft-start unit is added to the live wire terminal IN_L side of the AC input power supply, and the terminal between the first rectifier diode D1 and the second rectifier diode D2 in the first branch is connected to the output of the soft-start unit. terminal, the input terminal of the soft-start unit is used as the live wire terminal IN_L of the AC input power supply.
[0099] The soft-start unit may specifically include a parallel-connected current-limiting diode D6 and a switch S; one end corresponding to the cathode of the current-limiting diode D6 in the soft-start unit is used as the input end of the soft-start unit, and the anode of the current-limiting diode D6 in the soft-start unit corresponds to One en...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com