Cube unit deformation decomposition method meeting complete orthogonality and mechanical equilibrium conditions
A technology with complete orthogonal and balanced conditions, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
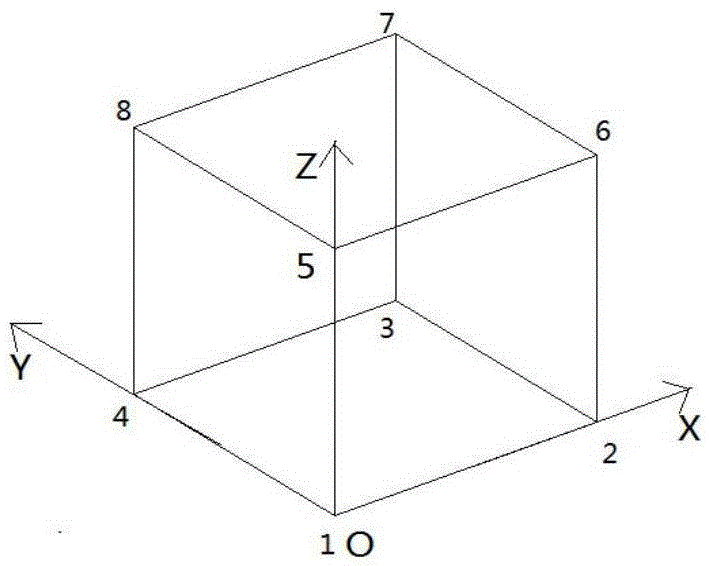
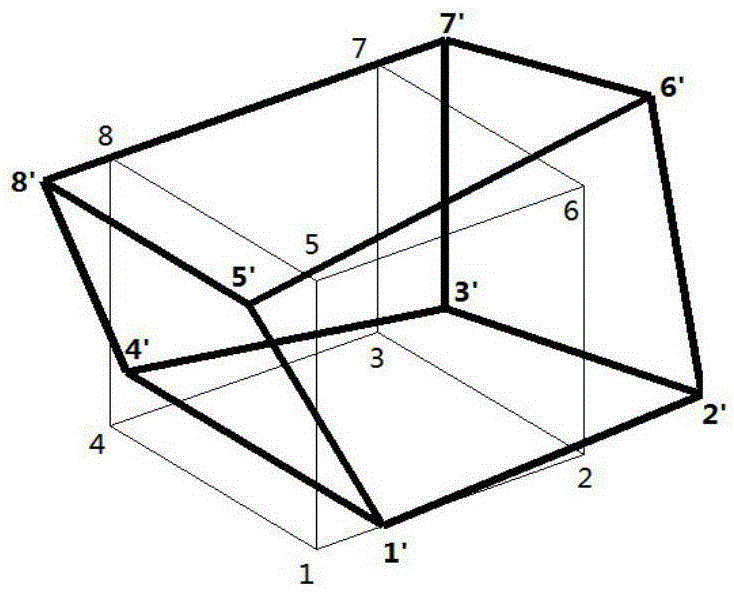
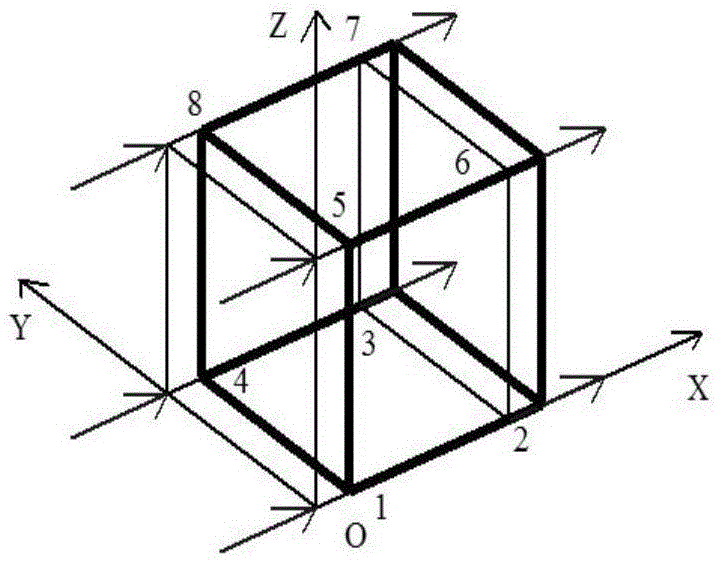
[0131] Theoretical derivation of the invention: Williams [1] etc. think that the motion and deformation of the block can be regarded as the superposition of the motion and deformation of the rigid body of the block under certain conditions. Zhang Canhui [2] It is pointed out that in the case of small deformation, the spatial deformation of the eight-node square element can be decomposed into 3 rigid body linear displacements, 3 rigid body rotational displacements, 3 tension and compression deformations, 6 bending deformations, 3 shear deformations, 3 There are 24 basic forms of reverse bending deformation and 3 torsional shear deformations.
[0132] references:
[0133] [1] Williams JR, Hocking G, Mustoe GGW. The theoretical basis of the discrete element method [C]. Proceeding of the Numeta 1985 Conference, 1985: 897-906.
[0134] [2] Canhui Zhang, Suong V. Hoa. A systematic and quantitative method to determine the optimal assumed stress fields for hybrid stress finite elem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com