A multi-terminal traveling wave ranging method for t-junction lines based on the distribution characteristics of fault traveling waves along the line
A technology of traveling wave distance measurement and distribution characteristics, which is applied to the location of faults, detecting faults according to conductor types, and measuring electrical and other directions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
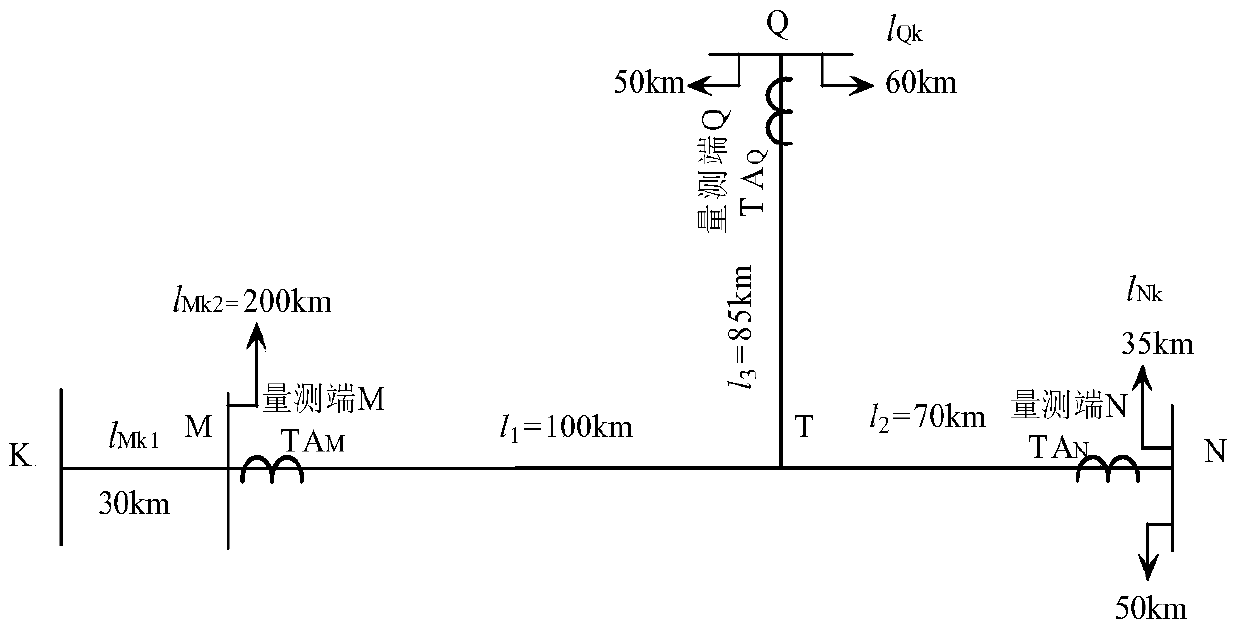
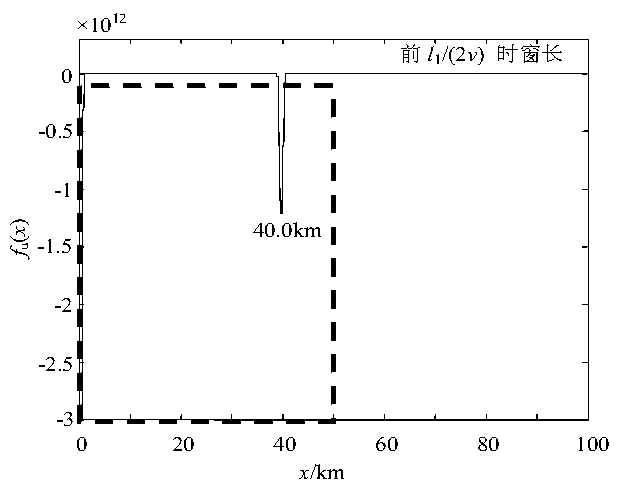
[0106] Embodiment 1: with figure 1 Take the transmission line shown as an example, assuming that the MT branch is 40km away from the M terminal and a phase A ground fault occurs.
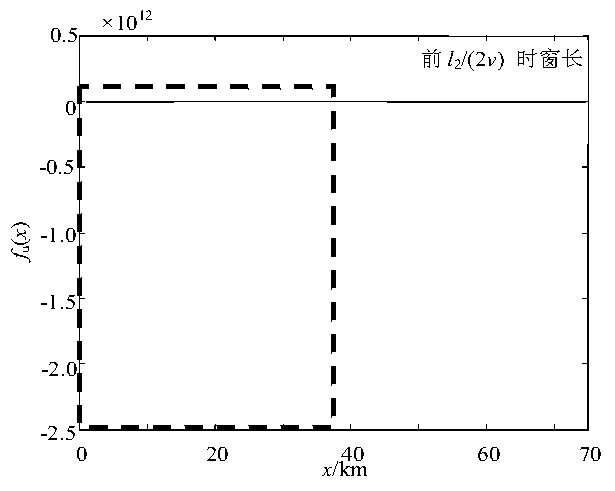
[0107] According to step 1 and step 2 in the instruction manual, the ranging function f of the measuring terminal M, measuring terminal N and measuring terminal Q of the ranging function is obtained Mu (x), f Nu (x) and f Qu (x). Get f according to step 3 Mu =[40.0],f Nu = φ (represents the empty set), f Qu =[39.8]. by f Nu = φ, it can be seen that the fault is not located in the NT branch, then use the data of the measuring terminal N to calculate [t 0 ,t 0 +l 3 / (2v)] The ranging function in the time window is along l 3 The mutation distribution f' in the range of line length Nu =[40.0]. It can be seen that x M1 =x' N1 ≈x Q1 , and sgn(x M1 )&sgn(x N )=0, sgn(x M )&sgn(xQ )=0, and sgn(x N )&sgn(x Q )=1. It can be seen that the fault is located in the MT branch, and the distanc...
Embodiment 2
[0108] Embodiment 2: with figure 1 The transmission line shown is taken as an example, assuming that the NT branch is 25km away from the T node, and a phase A ground fault occurs.
[0109] According to step 1 and step 2 in the instruction manual, the ranging function f of the measuring terminal M, measuring terminal N and measuring terminal Q of the ranging function is obtained Mu (x), f Nu (x) and f Qu (x). Get f according to step 3 Mu =[24.7 44.9],f Nu =[24.7], f Qu =[24.7], it can be seen that x M1 =x N1 =x Q1 , and sgn(x M )&sgn(x N )=0, sgn(x M )&sgn(x Q )=1, and sgn(x N )&sgn(x Q )=0. It can be seen that the fault is located in the NT branch, and the distance from the J node is 24.7km.
Embodiment 3
[0110] Embodiment 3: with figure 1 Take the transmission line shown as an example, assuming that the phase A ground fault occurs at the point where the QT branch is 20km away from the T node.
[0111] According to step 1 and step 2 in the instruction manual, the ranging function f of the measuring terminal M, measuring terminal N and measuring terminal Q of the ranging function is obtained Mu (x), f Nu (x) and f Qu (x). Get f according to step 3 Mu =[20.0],f Nu =[20.0],f Qu =[20.0], it can be seen that x M1 =x N1 =x Q1 , and sgn(x M )&sgn(x N )=1, sgn(x M )&sgn(x Q )=0, and sgn(x N )&sgn(x Q )=0. It can be seen that the fault is located in the QT branch and is 20.0km away from the J node.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com