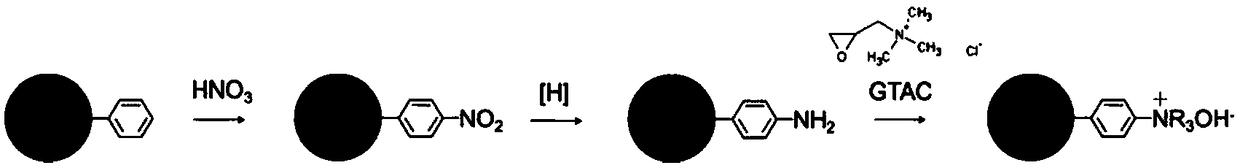
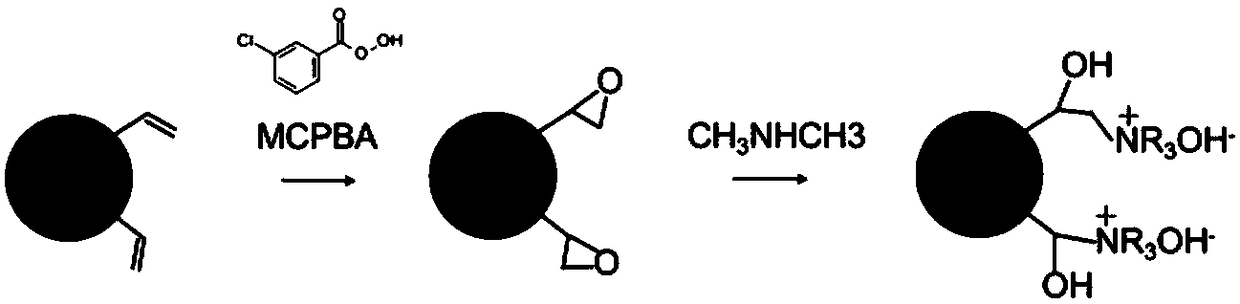
A kind of hydrophilic modification method of polystyrene material and product thereof
A polystyrene-based, hydrophilic modification technology, applied in the field of polymer material modification, can solve the problems of difficulty in hydrophilic modification, inconspicuous shielding of non-specific adsorption, and difficulty in modification and further grafting. achieve the effect of reducing hydrophobicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] Example 1 Preparation of polystyrene (PSt) microspheres
[0080] After mixing 2g methyl styrene (MST), 2g styrene and 1g divinylbenzene (DVB), add 2g n-heptane (HP) and 0.3g dibenzoyl peroxide (BPO) to dissolve Later as the dispersed phase. In 100 mL of deionized water, 2 g of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and 0.0015 g of dodecyl sulphuric acid (SDS) were added and dissolved as a continuous phase. Use conventional membrane emulsification technology (3.5μm membrane pores) to uniformly disperse the dispersed phase in the continuous phase to form a uniform oil / water emulsion. Then the prepared emulsion was moved into a reactor with a condenser, a stirring rod, and a nitrogen conduit, and after the oxygen was replaced by nitrogen, the polymerization reaction was carried out at 70° C. for 10 hours to obtain a microsphere polymerization suspension. After the polymerization, the microsphere product was obtained by suction filtration with a Buchner funnel. After repeated washing wit...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Example 2 Preparation of polystyrene (PSt) microspheres Prepare
[0082] Weigh 10g ethyl styrene (EST), 10g divinylbenzene (DVB), 0.5g potassium persulfate (KPS) and mix and dissolve as the oil phase; add 1.9g PVA, 0.0001g SDS and 0.0045 to 150mL deionized water g Na 2 SO 4 After being completely dissolved, it is used as the water phase. Using rapid membrane emulsification technology (membrane pores of 2.8μm), the oil-water phase mixture was quickly pressed through the microporous membrane tube and circulated and emulsified 4 times to obtain a uniform emulsion. Then the prepared emulsion was moved into a reactor equipped with a condenser, a stirring rod, and a nitrogen conduit. After the oxygen was replaced by nitrogen, the polymerization reaction was carried out at 85° C. for 20 hours to obtain a microsphere polymerization suspension. After the polymerization, the microsphere product was obtained by centrifugation at 8000 rpm with a centrifuge. After repeated centrifug...
Embodiment 3
[0083] Example 3 Preparation of polystyrene (PSt) microspheres
[0084] Weigh 4.5g of styrene (St), 5.5g of DVB, 0.28g of azoamidine (V65), 3g of hexadecane (HD) and 3g of n-hexanol (HA), mixed and dissolved as the oil phase; add 300mL of deionized water 3.5g PVA, 0.0008g SDS and 0.009gNa 2 SO 4 After being completely dissolved, it is used as the water phase. Using conventional membrane emulsification technology (membrane pores of 5.2 μm), the oil phase is evenly dispersed in the water phase to form a uniform oil / water emulsion. Then the prepared emulsion was moved into a reactor with a condenser, a stirring rod, and a nitrogen conduit, and after oxygen was replaced by nitrogen, the polymerization reaction was carried out at 80° C. for 20 hours to obtain a microsphere polymerization suspension. After the polymerization, the microsphere product was obtained by suction filtration with a Buchner funnel. After repeated washing with deionized water and ethanol, the product is dried...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com