A hydrophilic modification method for polyglycidyl methacrylates or copolymers thereof and materials obtained by modification
A technology of polymethacrylic acid and methacrylic acid, which is applied in the field of hydrophilic modification of polyglycidyl methacrylate or its copolymers, and the modified materials can solve the problem that the coating layer is easy to loosen.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
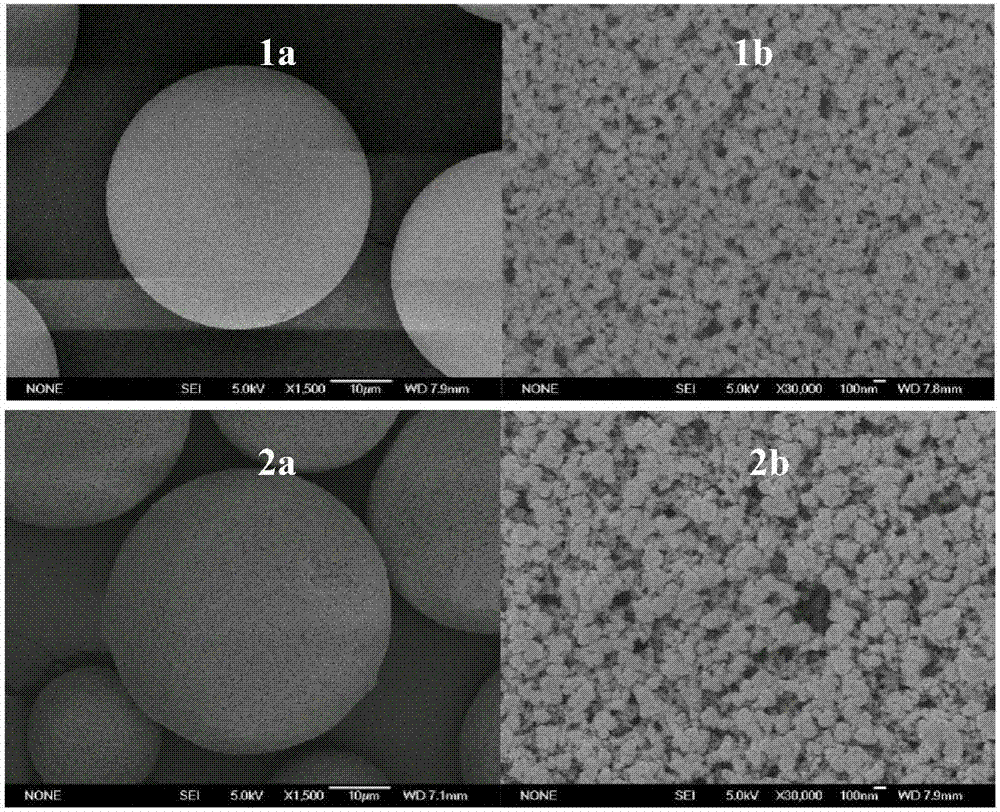
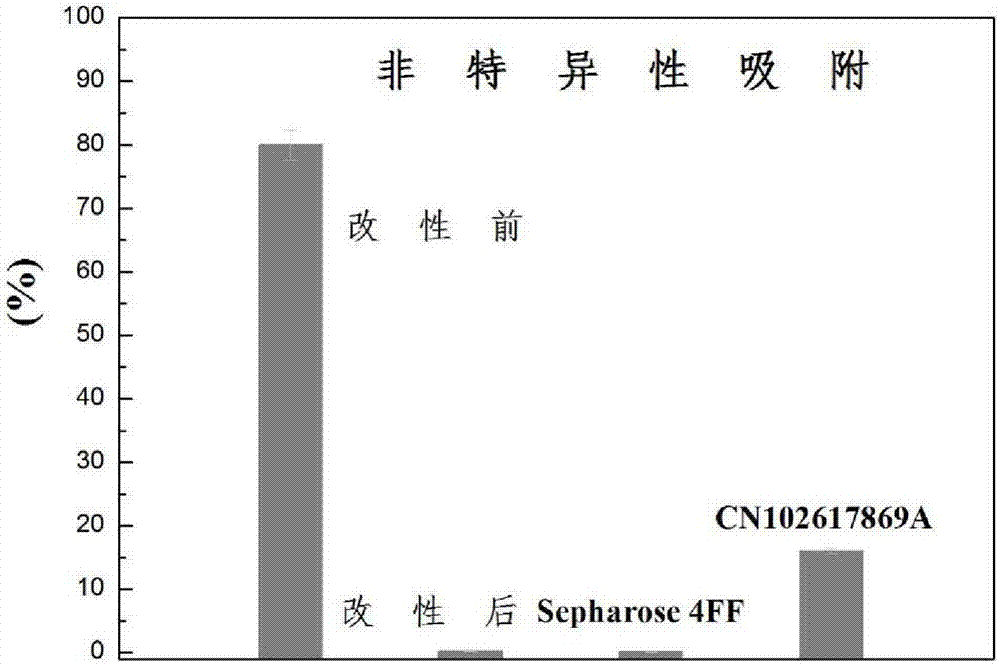
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
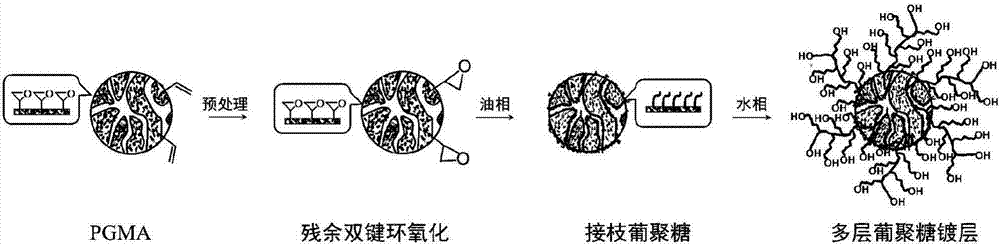
[0067] Preparation and pretreatment of embodiment 1 polyglycidyl methacrylate (PGMA) linear powder
[0068] Since the epoxy group of glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) is prone to ring-opening reaction at high temperature, the atom transfer radical polymerization of GMA is carried out in this embodiment under low temperature conditions. Add GMA monomer 6.6mL (50mmol) in the 100mL reactor of polytetrafluoroethylene liner, CuBr 2 55mg (0.25mmol), 2,2'-bipyridine (bpy) 78.1mg (0.5mmol), initiator azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) 2mL, THF 15mL, pass into N 2 to remove O from the reaction system 2 , placed in an oven, and reacted at the set temperature for 8h (take out the ice bath to cool to terminate the reaction). With tetrahydrofuran (THF) or CH 2 Cl 2 As a solvent, methanol or n-hexane as a precipitant to purify the polymer, and vacuum-dried at 45°C for 24 hours to obtain PGMA as a white powder. Such as figure 1 The residual double bond treatment method shown is to take 10 g of t...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Preparation and pretreatment of embodiment 2 cross-linked polyglycidyl methacrylate (PGMA-DVB) microspheres
[0070] Add a certain proportion of GMA monomer, crosslinking agent (DVB), diluent, surfactant and initiator (BPO) into the beaker to form an oil phase, and stir until the BPO is completely dissolved. A certain amount of stabilizer (PVA), anhydrous Na 2 SO 4 , SDS and HQ were dissolved in deionized water to form a water phase, and the oil phase was dispersed in the water phase under stirring (200r / min) to form an O / W emulsion. After passing nitrogen for 1 hour, the temperature was raised to 75° C., and polymerization was carried out under nitrogen atmosphere for 20 hours. The obtained polymer microspheres were washed three times with water and ethanol, respectively. Unpolymerized substances in the microspheres, such as surfactants, diluents, etc., were removed with acetone extraction for 24 hours. After vacuum drying at room temperature, PGMA microspheres were ...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Embodiment 3 graft monolayer dextran
[0072] Under normal temperature, 30L dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is injected in the 50L reactor, start stirring, 100rpm, then take by weighing 1kg dextran powder and 12g 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) powder and put into large beaker, by Pour the beaker directly into the kettle, and keep stirring until it is completely dissolved and transparent. It takes 4 hours; after it is completely dissolved, add 2 kg of dried PGMA microspheres prepared in Example 2 to the reaction kettle, stir at room temperature for 1 hour, and then set at 100 rpm; Start to heat up to 37 degrees, start timing after the temperature rise, and keep the reaction for 3 days. During the reaction, the color of the reaction solution will deepen to 12h and become dark yellow, and the color will not change until the end of the reaction. After discharging, after filtering, wash the coated microspheres with deionized water. Cross-linked reinforced coating: prepare water p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com