Process and apparatus to reduce declared capacity of storage device by conditionally trimming
A storage device and capacity technology, which is applied in the field of storage systems and can solve problems such as device wear and tear
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
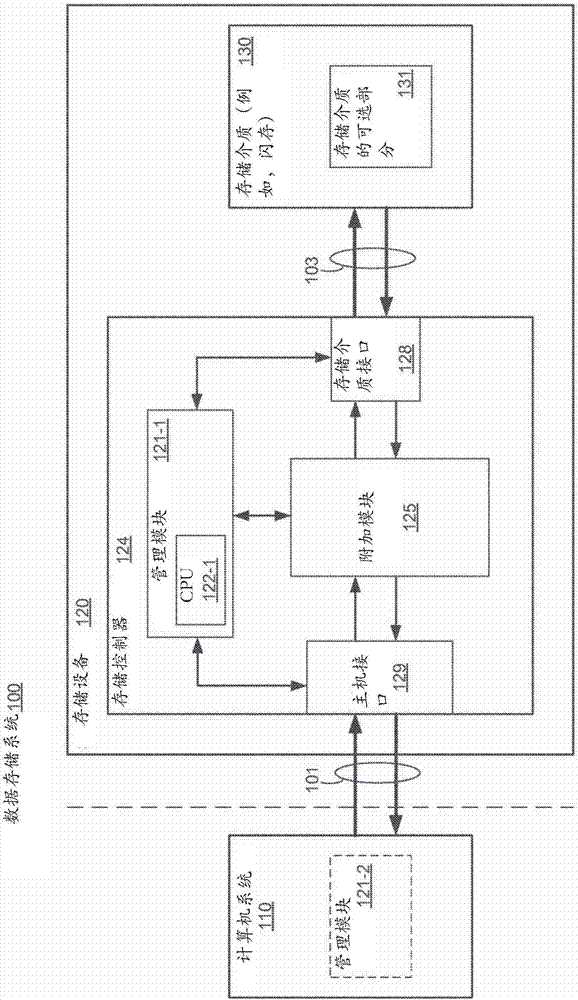
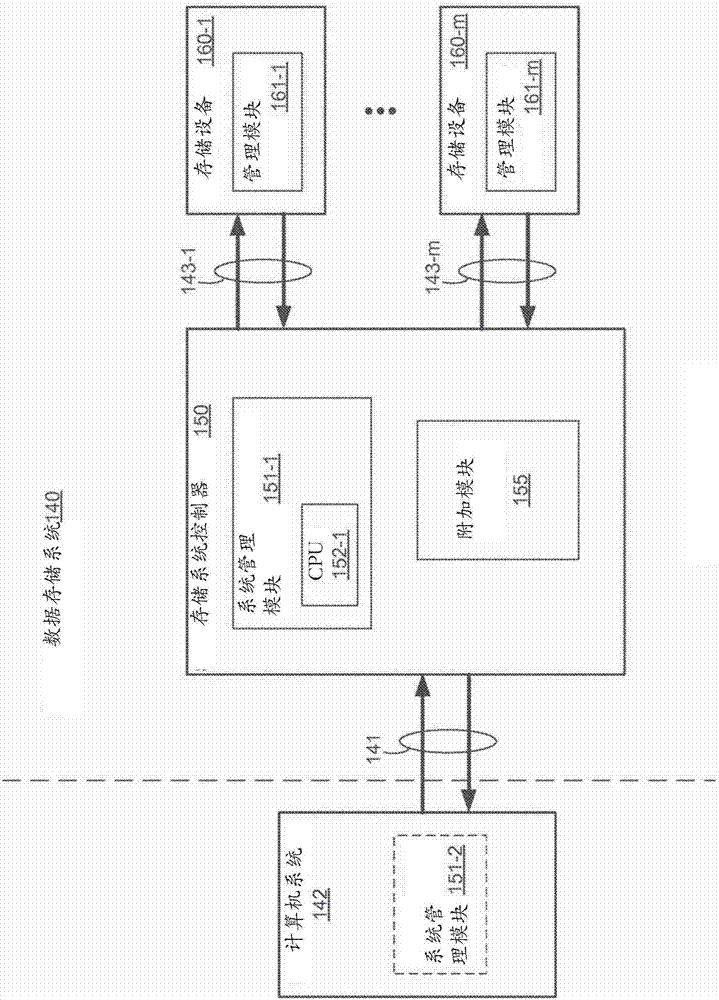
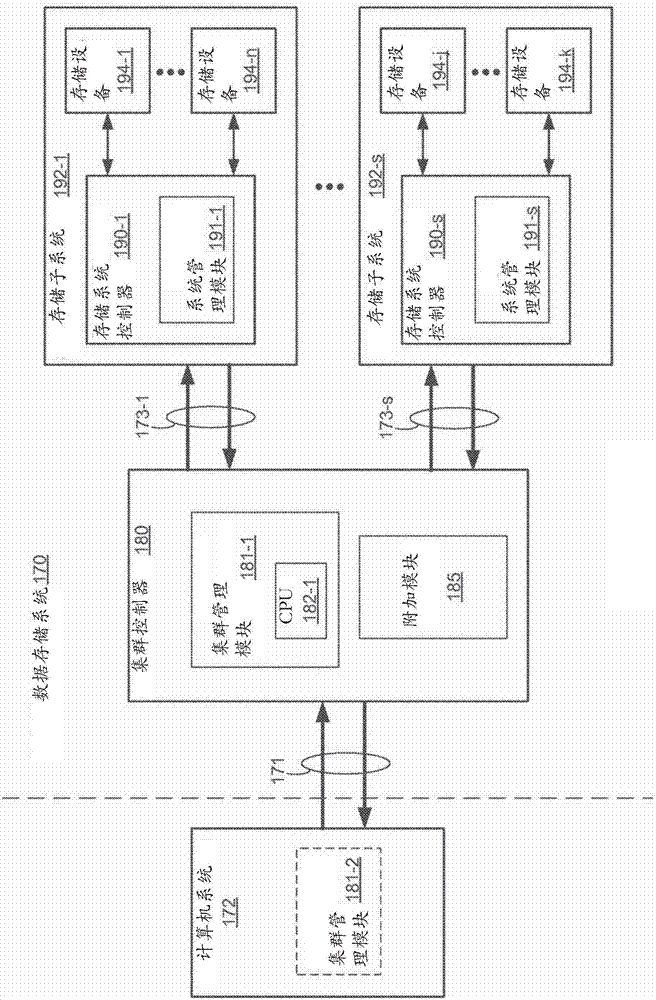
[0025] When a multi-level flash memory cell has reached its wear limit, it typically still has sufficient charge retention to store a reduced amount of charge. It is often the case that most erase and reprogram cycles can be performed on wear-limited multi-level flash cells with full recovery of stored data, provided that a reduced amount of charge is used and desired. For example, a flash memory device operating in 3 bits per cell mode (TLC) can typically perform 500 to 1500 erase and reprogram cycles before it is considered worn out. However, at that point in time, there will typically still be enough charge storage capacity to operate in single-bit-per-cell mode (SLC) for an additional 10,000 to 20,000 erases and reprograms before the SLC wear limit is reached cycle. Thus, the lifetime of a flash memory device can be extended if the flash memory device is allowed to store less data. Currently, storage systems have difficulty taking advantage of this expanded capability be...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap