A method for non-destructive evaluation of damage performance of optical components
A technology for optical components and performance, applied in the field of non-destructive evaluation of optical components, can solve problems such as small scale, laser output improvement, optical component damage, etc., to achieve the effect of damage performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
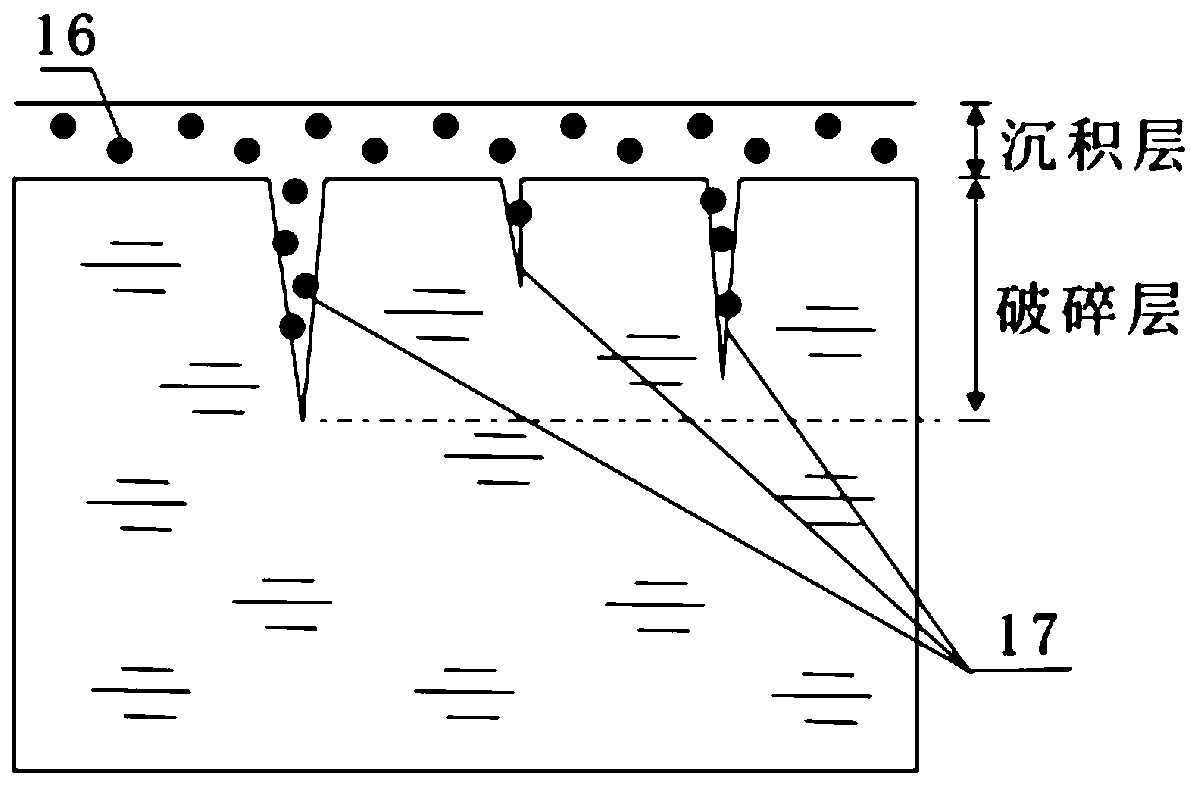
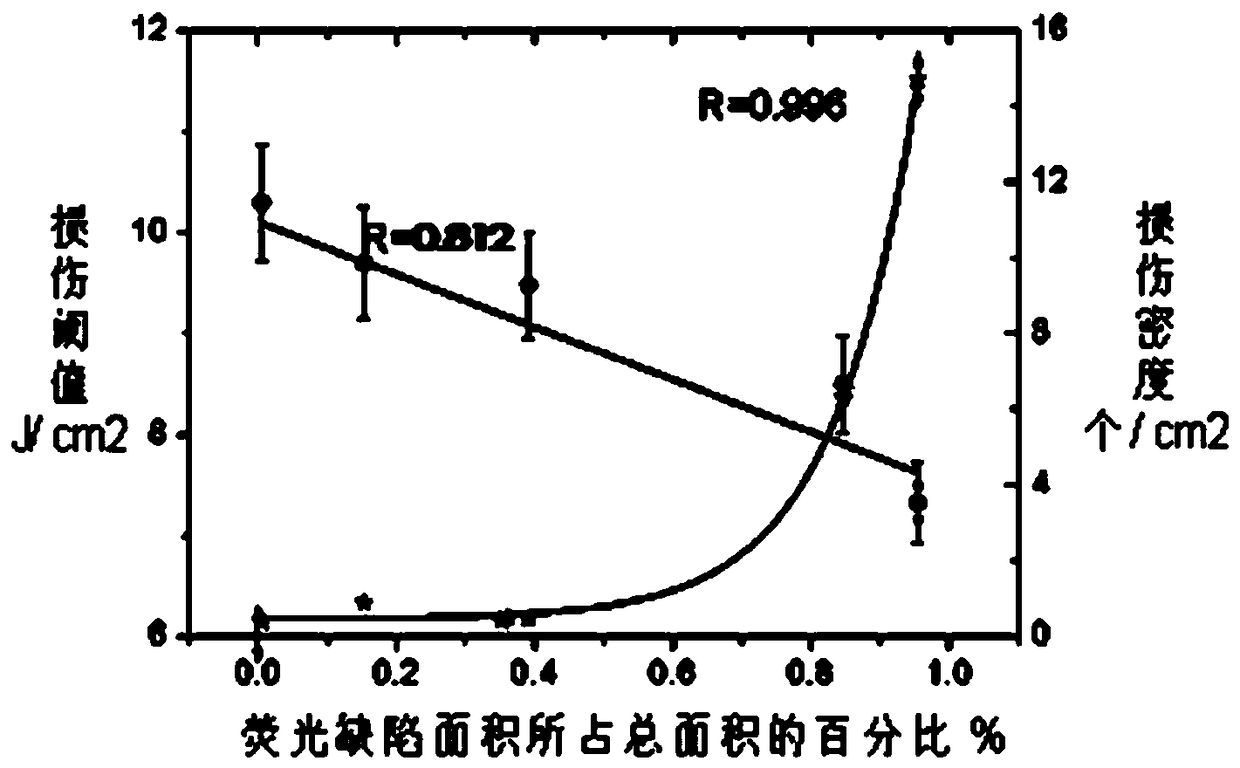
[0029] Embodiment 1: see figure 1 , the surface of sample 5 is divided into a sedimentary layer and a broken layer. The surface of the sedimentary layer is polished, and there are many microcracks 17 in the broken layer below it. Both the sedimentary layer and the broken layer contain impurities 16. Based on the damage mechanism of the optical element, that is, the subsurface microcracks 17 embedded in the polluting impurities 16 are easy to absorb high-flux laser energy to cause damage under laser irradiation. For the buried polluting impurities 16, the corresponding fluorescent defects are obtained by detecting the fluorescence emitted by them.
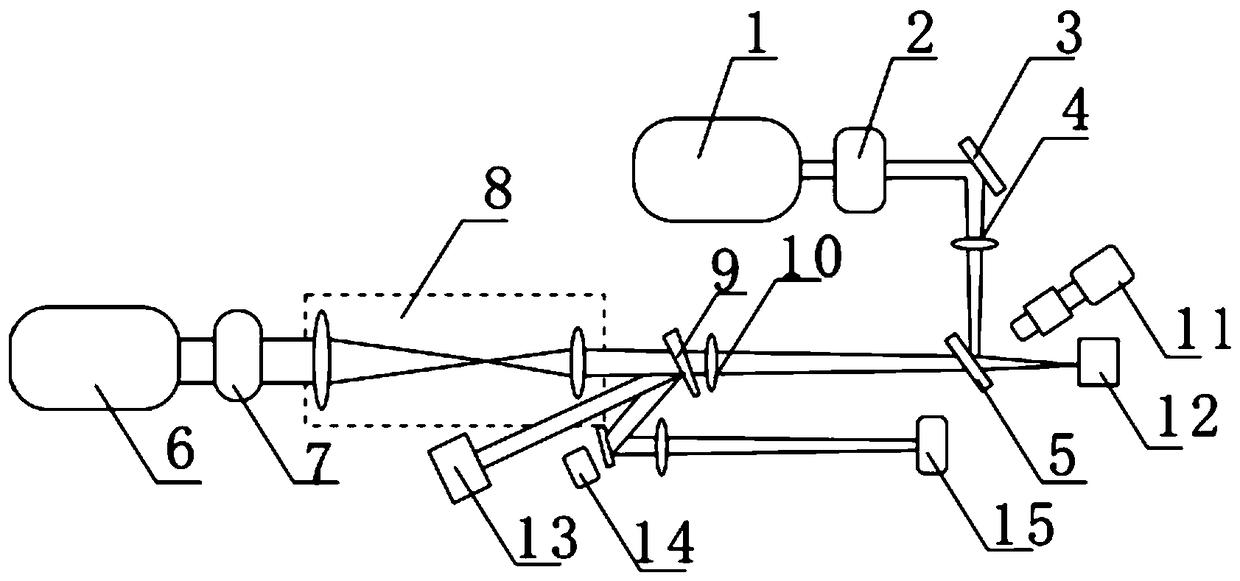
[0030] see figure 2 and image 3 , in order to test, must use optical path system, we construct a kind of optical path system for the present invention, described optical path system comprises continuous laser 1, pulsed laser 6, sample stage, microscopic imaging system 11, sample stage can move three-dimensionally And the sample...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com