Quantitative determination method for reversible lithium precipitation of lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery, quantitative determination technology, applied in the direction of measuring electrical variables, measuring electricity, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of inability to evaluate the severity of lithium precipitation, inability to detect the amount of lithium precipitation, etc., to achieve the effect of non-destructive evaluation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] S1. Take the lithium-ion battery to be tested after constant capacity. The battery capacity is 1.1Ah. Under the condition of -20°C, first apply a current of 1C to the battery for constant current charging, charge to 50% SOC, and measure the voltage value 3.78V, then apply a voltage of 3.78V to the battery for constant voltage charging to 70% SOC;
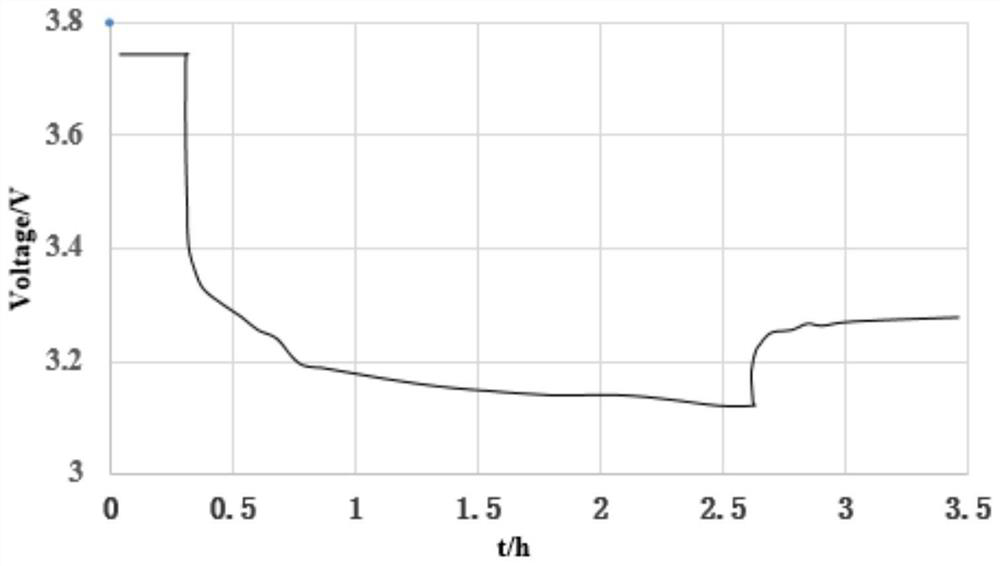
[0025] S2. Apply a small current of 1 / 20C to the charged battery for constant current discharge, record the voltage change with time during the discharge period, and obtain the V ~ t curve, such as figure 1 shown;
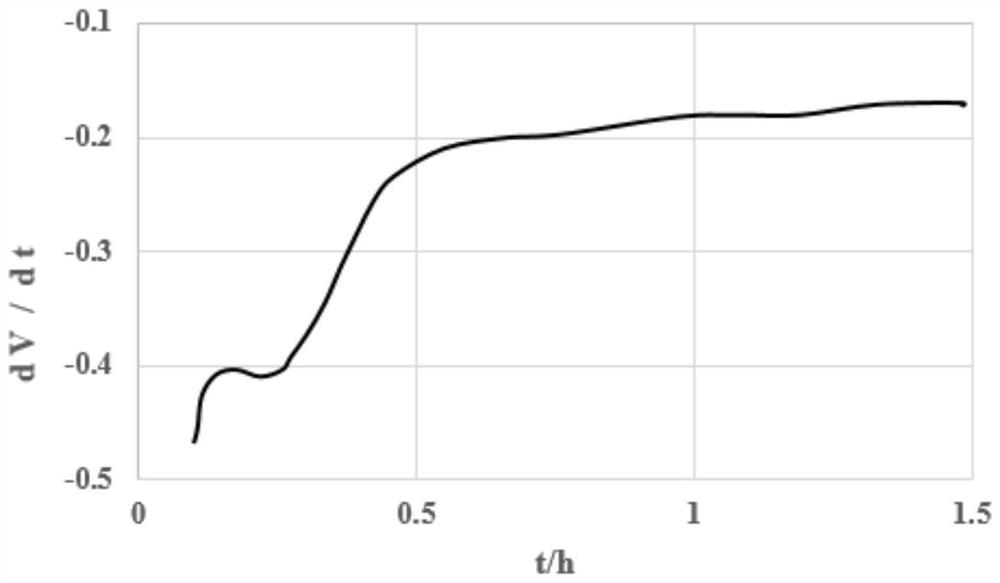
[0026] S3. Perform second-order differential processing on the V~t curve to obtain the dV / dt~t curve, such as figure 2 As shown, the time to record the inflection point of the curve is 0.24h;
[0027] S4. Calculate the reversible lithium amount of the battery during the charging process, the reversible lithium amount Q=(1.1 / 20)A×0.24h=13.2mAh.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com