A Linux-based non-interrupted wire-speed packet receiving and sending method and device
A wire-speed, device technology, applied in the field of uninterrupted wire-speed packet sending and receiving based on LINUX, can solve the problem of low performance of sending and receiving packets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
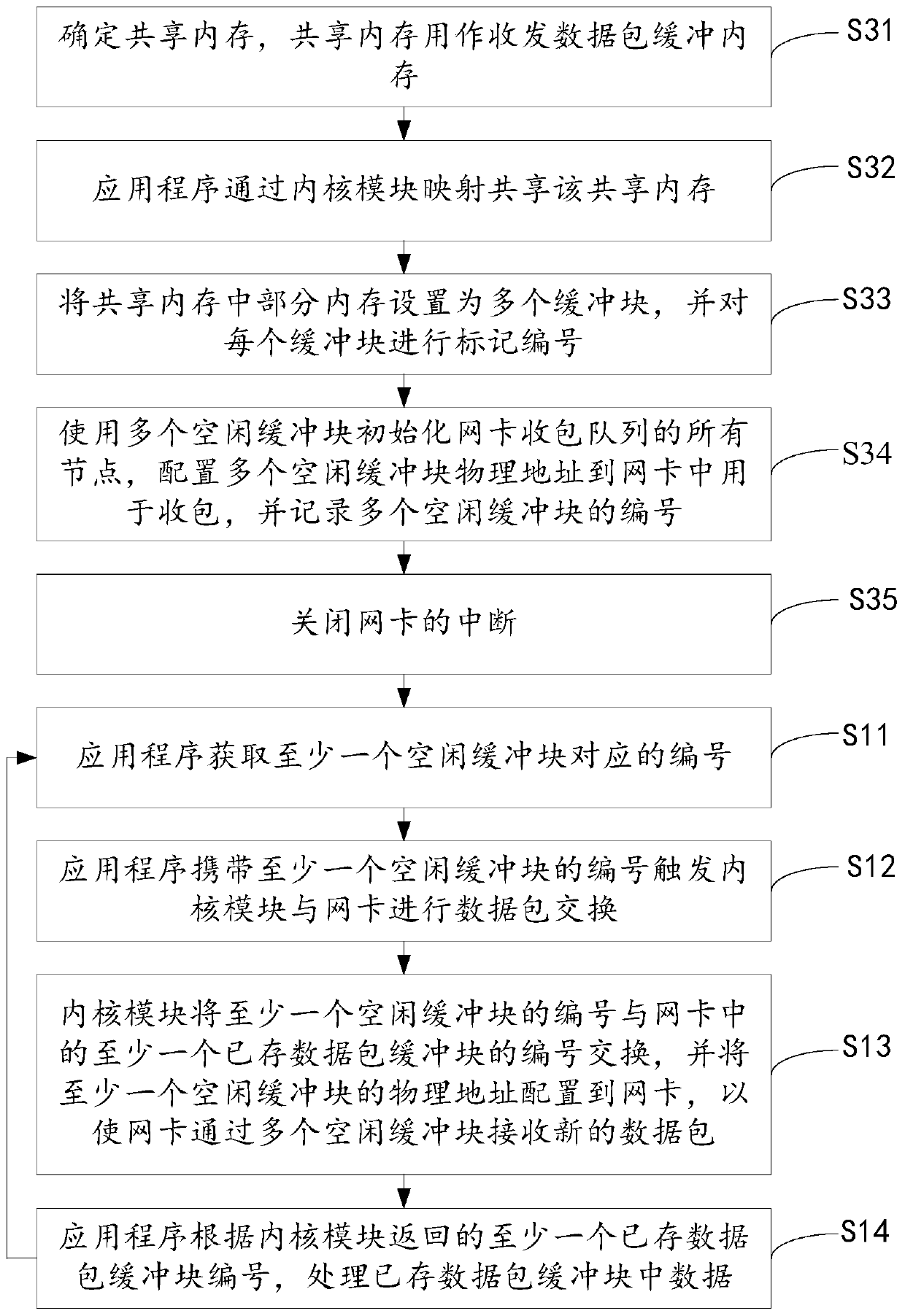
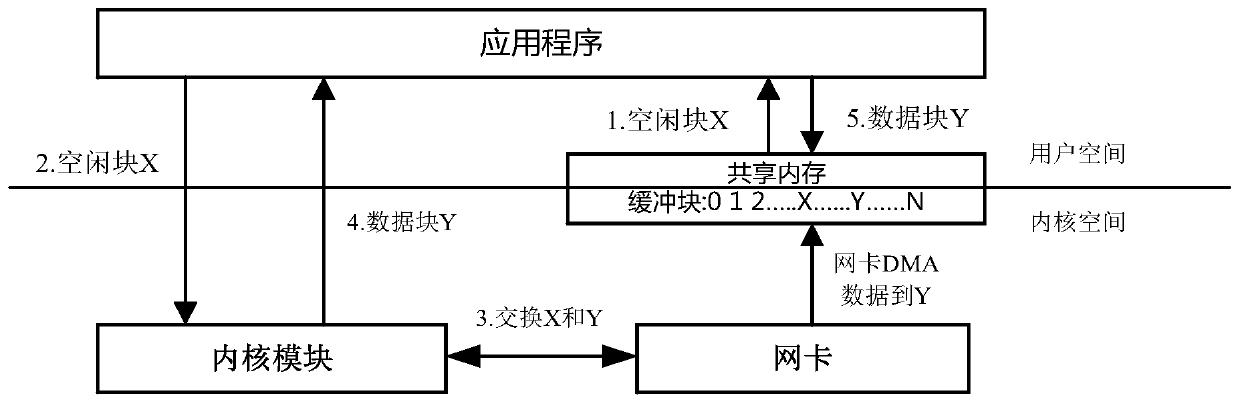
[0080] The embodiment of the present invention provides a kind of uninterrupted wire-speed packet receiving method based on LINUX, refer to figure 1 As shown, the method flow includes:
[0081] S11. The application program obtains the serial number corresponding to at least one free buffer block.
[0082] S12. The application program carries the number of at least one free buffer block to trigger the kernel module to exchange data packets with the network card.
[0083] Specifically, this step includes:
[0084] The application program carries at least one free buffer block number through the packet receiving function, and sends at least one free buffer block number to the kernel module;
[0085] The packet receiving function in the kernel module is called to trigger the kernel module to exchange data packets with the network card according to at least one free buffer block number.
[0086] S13. The kernel module exchanges the number of at least one free buffer block with t...
Embodiment 2
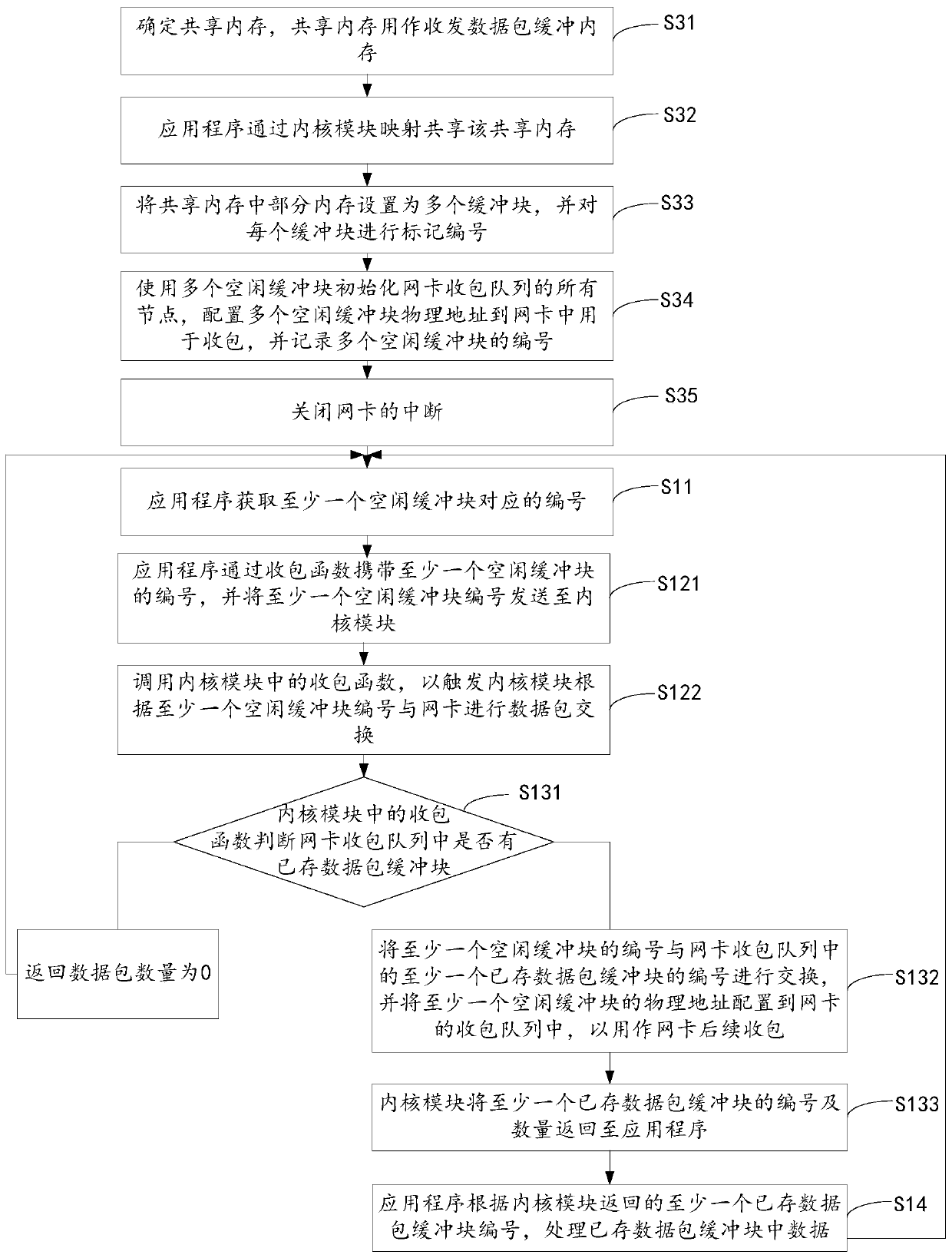
[0106] The embodiment of the present invention provides a kind of uninterrupted wire-speed packet receiving method based on LINUX, refer to figure 2 As shown, the method flow includes:
[0107] S31. Determine the shared memory, where the shared memory is used as a buffer memory for transmitting and receiving data packets.
[0108] Specifically, the kernel module applies for a memory of a certain size as a shared memory; the user can also preset a memory of a certain size through the kernel module. In addition, the shared memory can also be determined in other ways. The embodiment of the present invention is specific to the method Not limited.
[0109] Among them, the size of the shared memory is at least greater than 2M, and the size of the shared memory can also be set according to the overall size of the device memory space and the size of the interaction with network data; the size of the shared memory can also be set according to other settings, such as device performanc...
Embodiment 3
[0161] The embodiment of the present invention provides a method for sending packets at a line speed without interruption based on LINUX, referring to Figure 4 As shown, the method flow includes:
[0162] S41. Determine the shared memory, where the shared memory is used as a buffer memory for transmitting and receiving data packets.
[0163] S42. The application programs share the shared memory through kernel module mapping.
[0164] S43. Set part of the memory in the shared memory as a plurality of buffer blocks, and mark and number each buffer block.
[0165] Wherein, the plurality of buffer blocks are idle buffer blocks when no data packets are stored.
[0166] S44. Initialize all nodes of the packet receiving queue of the network card using multiple free buffer blocks, configure physical addresses of the multiple free buffer blocks to the network card for packet receiving, and record numbers of the multiple free buffer blocks.
[0167] S45. Turn off the interruption of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com