Spatial analysis method for influence between carbon dioxide emission elements under condition of precise temporal and spatial scales
A carbon dioxide and emission space technology, applied in the field of urban and ecological environment, can solve the problems such as the inability to objectively reveal the characteristics of the carbon dioxide emission process, the inability to effectively identify the source, and the lack of solutions.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] The details of the present invention can be understood more clearly with reference to the accompanying drawings and the description of specific embodiments of the present invention. However, the specific embodiments of the present invention described here are only for the purpose of explaining the present invention, and should not be construed as limiting the present invention in any way. Under the teaching of the present invention, the skilled person can conceive any possible modification based on the present invention, and these should be regarded as belonging to the scope of the present invention.
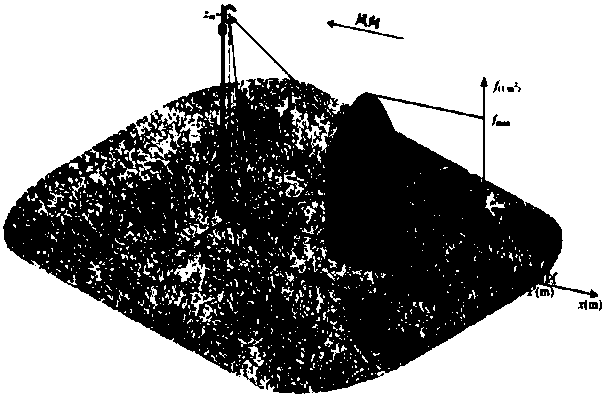
[0042] figure 1 It is the flow chart of the method in the embodiment of the present invention, as figure 1 As shown, the applicant proposes a spatial analysis method for the influence of carbon dioxide emission elements on a fine spatio-temporal scale, which includes the following steps:
[0043] Step 1: Obtain remote sensing images of the target area, set the observati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com