ANTI-PD-1 antibodies, activatable ANTI-PD-1 antibodies, and methods of use thereof
A PD-1 and antibody technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, antibodies, antibody medical components, etc., can solve problems such as deterioration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0905] Example 1. Generation of mouse antibodies of embodiments that bind to human PD-1 and block hPD-L1 and hPD-L2 binding to human PD-1
[0906] This example demonstrates that mouse antibodies of the invention that bind to human PD-1 can be isolated from hybridomas derived from mice immunized with recombinant human PD-1 protein, and that such binding can inhibit PD-1 binding to PDL1 and PDL2.
[0907] Six NZBWF1 / J female mice (Jackson Laboratories, Sacramento, CA; cat. no. 100008) were immunized on the right side with recombinant human PD-1 (Sino Biological, Beijing, P.R. China; cat. no. ABIN2181605) on days 0, 7, and 21 ). Sera were taken from immunized mice on day 28 and binding to HEK293-hPD-1 (cells transfected with an expression vector encoding human PD-1 (Origene, cat. no. SC117011)) was measured. All six mice showed positive binding. Splenocytes were isolated from mice 1, 3, and 6 and fused with SPO mouse B cells; similarly, splenocytes were isolated from mice 2, 4,...
Embodiment 2
[0920] Example 2. Purification and testing of humanized anti-PD-1 antibodies
[0921] This example demonstrates that mouse antibodies of the invention that bind human PD-1 can be converted into humanized IgG antibodies that retain PD-1 binding and inhibition of PDL1 and PDL2 binding to PD-1.
[0922] The variable domains of mouse anti-PD-1 antibodies generated as described in Example 1 were humanized and expressed as full-length hIgG4 / hκ antibodies. Fully human IgG anti-PD-1 antibodies were expressed from transiently transfected HEK-293 cells and purified from culture supernatants by protein A chromatography.
[0923] The humanized antibody sequences used in the studies presented here are as follows:
[0924]
[0925]
[0926]
[0927]
[0928]
[0929]
[0930]
[0931]
[0932]
[0933]
[0934]
[0935] These variable heavy chain regions (VH) and variable light chain regions (VL) can be used in various combinations to generate anti-PD-1 ant...
Embodiment 3
[0937] Example 3: Anti-PD-1 antibodies show specificity in binding
[0938] Example 3 shows that humanized anti-PD-1 antibody groups A1 and C1 of the present invention specifically bind hPD-1 by plate ELISA.
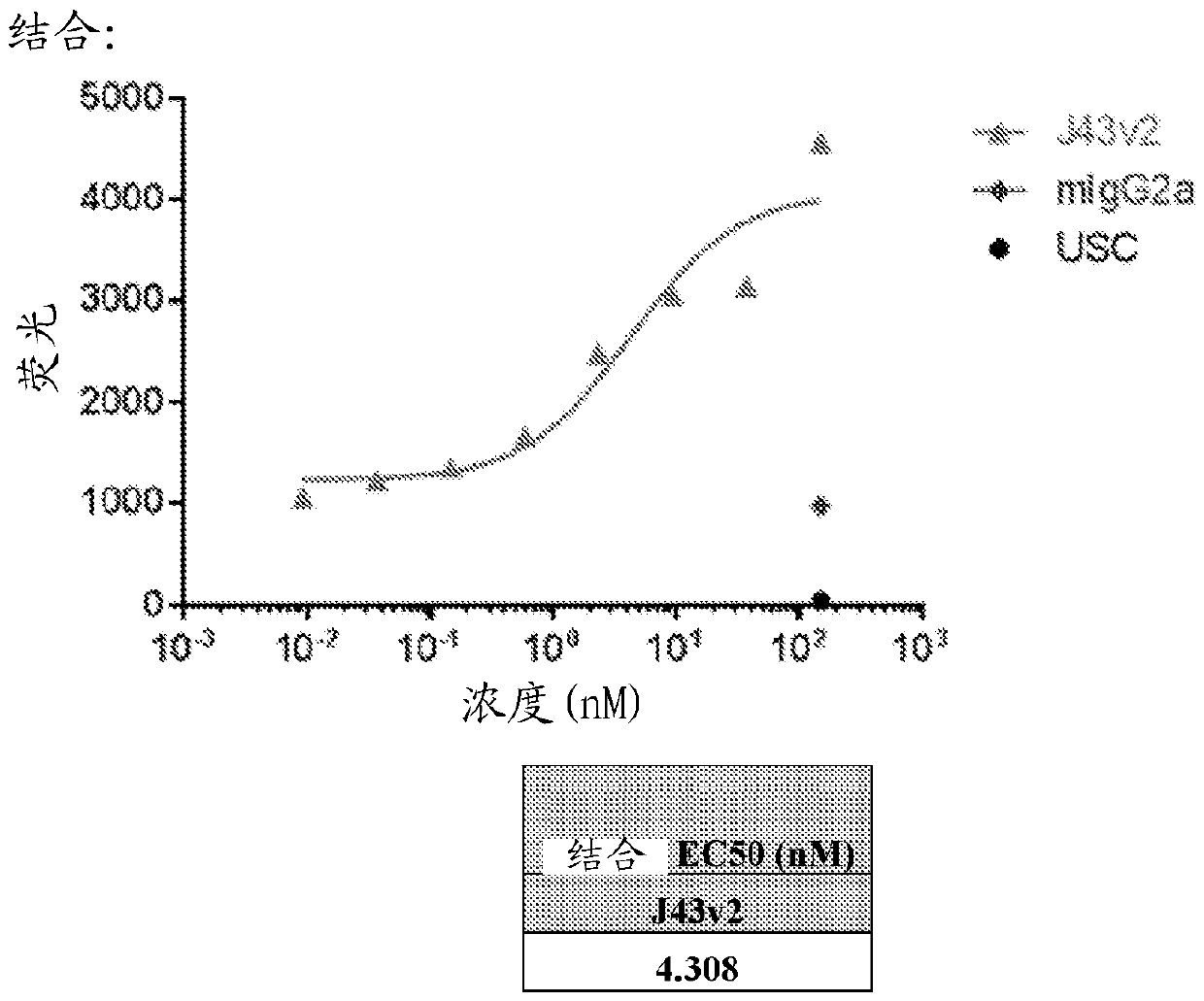
[0939]Binding of the anti-PD-1 antibody A1.5 of the present invention is highly specific for hPD-1-Fc against a panel of numerous human and mouse proteins in a standard ELISA ( Figure 10 ). Binding of anti-PD-1 A1.5 was detected with an anti-human IgG-HRP conjugate (specific for FAb) (Sigma, StLouis, MO) and visualized with the chromogenic substrate TMB (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL). Plot in Prizm (Sigma Plot) and fit the data to a model for single site saturation binding.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com