Design method of telescopic support rod, passive telecentric mechanism and support rod thereof
A technology of telescopic support rods and design methods, applied in the field of medical equipment, can solve problems such as difficult operation, unbalance, and constant size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
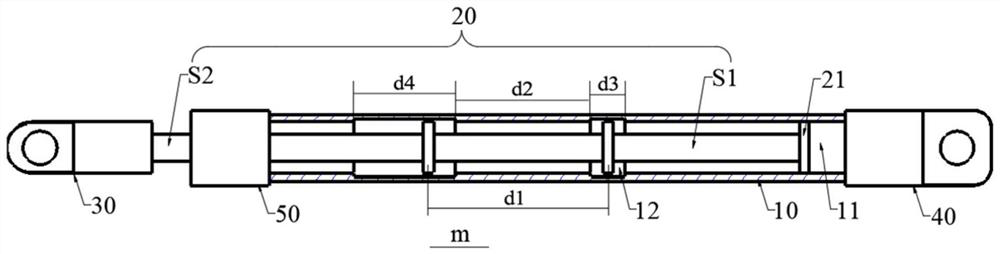
[0031] figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of an exemplary telescopic support rod of the present invention.
[0032] refer to figure 1 As shown, the exemplary telescopic support rod m of the present invention includes a first support rod 10 and a second support rod 20 that are socketed and can slide relative to each other. A telescopic channel 11 is axially provided in the first support rod 10, and the telescopic channel 11 An accommodating groove 12 is provided in the inner cavity, and the second support rod 20 has opposite first end S1 and second end S2. The first end S1 is provided with a friction block 21, and the first end S1 extends into the telescopic channel 11 to enable The friction block 21 is in frictional contact with the inner wall of the telescopic channel 11, and the second end S2 extends out of the first pole 10. During the relative sliding process of the first pole 10 and the second pole 20, the friction block 21 breaks away from or enters the accom...
Embodiment 2
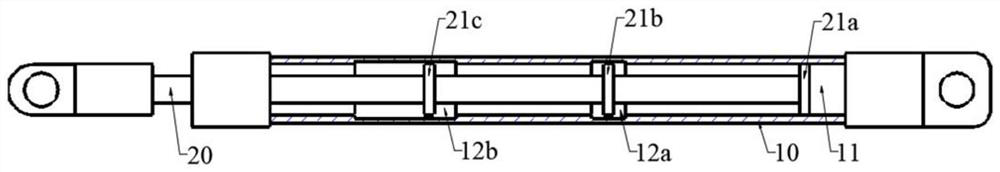
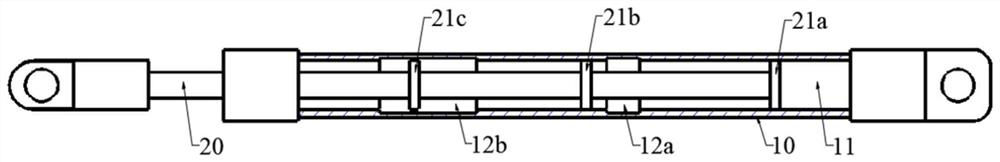
[0039] This embodiment proposes a specific implementation based on the telescopic support rod m of Embodiment 1, as shown in FIG. 2 , Figure 2(a) ~ Figure 2(c) It is a schematic diagram of the relative sliding process of the first pole and the second pole in the telescopic support pole of this embodiment.
[0040] Specifically, as shown in FIG. 2(a), two accommodating grooves 12 are arranged at intervals along the axial direction of the first strut 10 in this embodiment, which are respectively the first accommodating groove 12a and the second accommodating groove 12b, and The lengths of the first accommodating groove 12a and the second accommodating groove 12b increase sequentially. Three friction blocks 21 are provided at intervals along the axial direction of the second support rod 20 , which are respectively a first friction block 21 a , a second friction block 21 b and a third friction block 21 c .
[0041] Continuing to refer to Fig. 2 (a), when the first strut 10 and t...
Embodiment 3
[0046] This embodiment provides a passive telecentric mechanism including the telescopic support rod in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 above, image 3 It is a schematic structural diagram of an exemplary passive telecentric mechanism in this embodiment.
[0047] refer to image 3 As shown, the passive telecentric mechanism of this embodiment includes a frame 1, a rotating arm group 2, a moving arm group 3, an imaging device 4, and the telescopic support rod m in the above-mentioned embodiment 1 or embodiment 2. The rotating arm group 2 includes connecting rod a and connecting rod b arranged in parallel, and the moving arm group 3 includes connecting rod c and connecting rod d arranged in parallel, and one end of connecting rod a and connecting rod b is respectively at hinge point A and hinge point C It is hinged with the frame 1, and the other end is hinged with the connecting rod c and the connecting rod d at the same time, wherein the connecting rod d forms hinge point B and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com