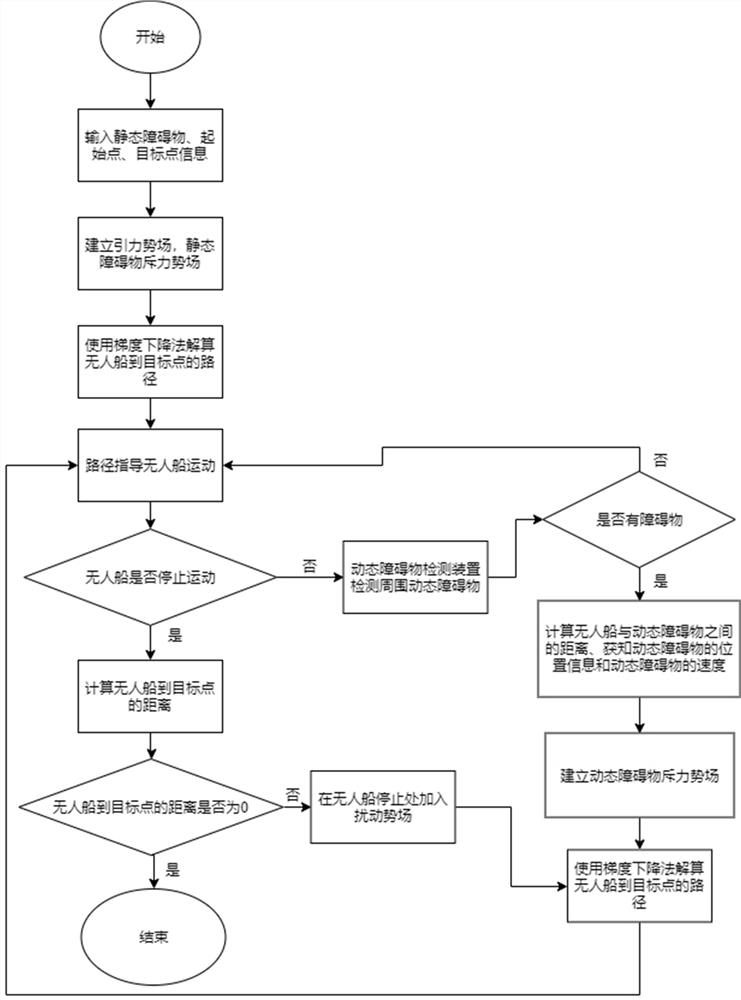
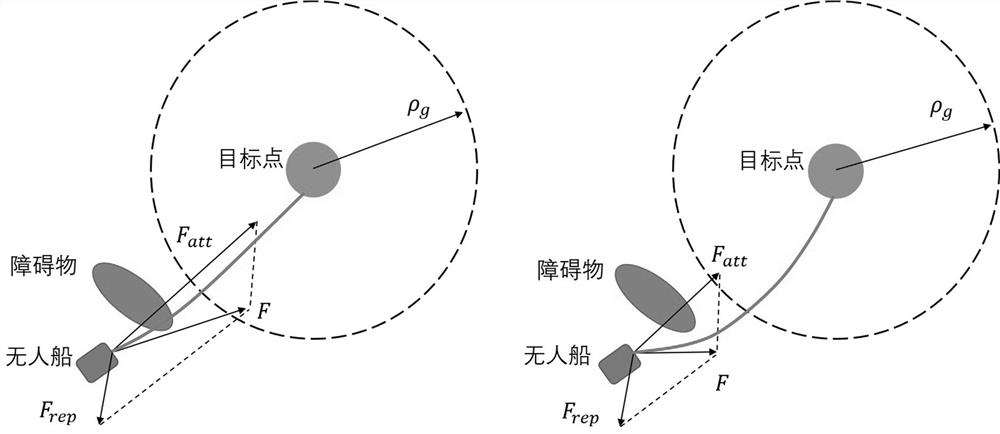
An intelligent unmanned ship path planning method based on improved artificial potential field
A path planning and artificial potential field technology, applied in two-dimensional position/channel control, vehicle position/route/height control, instruments, etc., can solve target unreachable, energy consumption loss, unmanned ships and obstacles increased risk of collision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
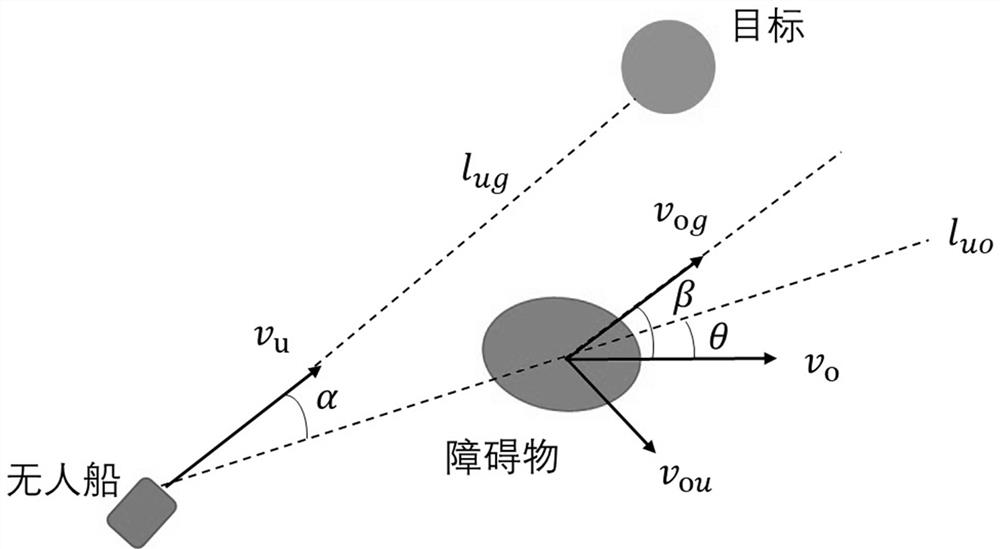
[0080] In the above embodiment, in addition to eliminating the interference that the dynamic obstacle is not in the threat area, the influence of the relative position and relative running speed between the dynamic obstacle and the unmanned ship on the obstacle avoidance path planning of the unmanned ship should also be considered. v u and v o are the moving speeds of the unmanned ship and the obstacle, respectively; l ug is the straight-line path from the unmanned ship to the target, and the direction is the same as v u the same; l uo is the straight path from the unmanned ship to the obstacle, and the direction is from the unmanned ship to the obstacle; v ou and v og are respectively the moving speed v of the obstacle o Components, where v ou means v o in vertical l ug Component in direction, v og means v o in v u Components in the direction; α, β, θ represent v respectively u Direction and unmanned ship and obstacle connection l uo angle, v og direction and v ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com