Polarization-insensitive directional coupler structure and method
A directional coupler and polarization-insensitive technology, applied in the coupling of optical waveguides, instruments, light guides, etc., can solve the problems of polarization insensitivity, birefringence, etc., and achieve easy implementation, less stringent process requirements, and broadband transmission characteristics Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example Embodiment
[0050] Example 1
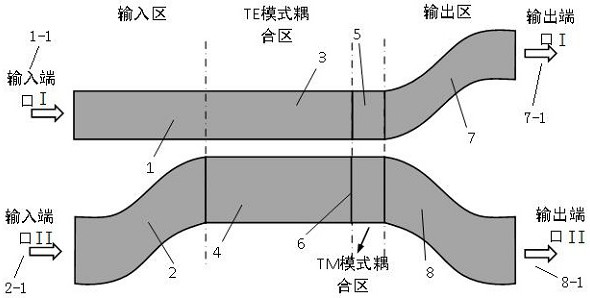
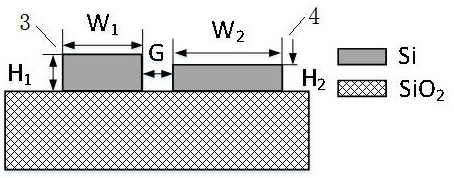
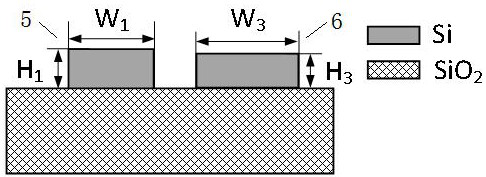
[0051] The structure of a polarization-insensitive directional coupler is as follows figure 1 shown. The cross-sectional structure of the waveguide structure in the TE mode coupling region and the TM mode coupling region is as follows: figure 2 and image 3 shown. Both the TE mode coupling region and the TM mode coupling region are asymmetric directional coupler structures. The width and height of the coupling waveguide I3 in the TE mode coupling region are W1=400nm, H1=220nm, the width and height of the coupling waveguide II4 are W2=575nm, H2=159.3nm, and the coupling spacing G=200nm. The width and height of the coupling waveguide III 5 in the TM mode coupling region are W1=400nm, H1=220nm, the height of the coupling waveguide IV 6 is H3=202.5nm, the width W3=575nm, and the coupling spacing G=200nm. The length of the curved waveguide in the output region along the beam propagation direction is 30 μm.
[0052] First, we use the beam propagation method...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com