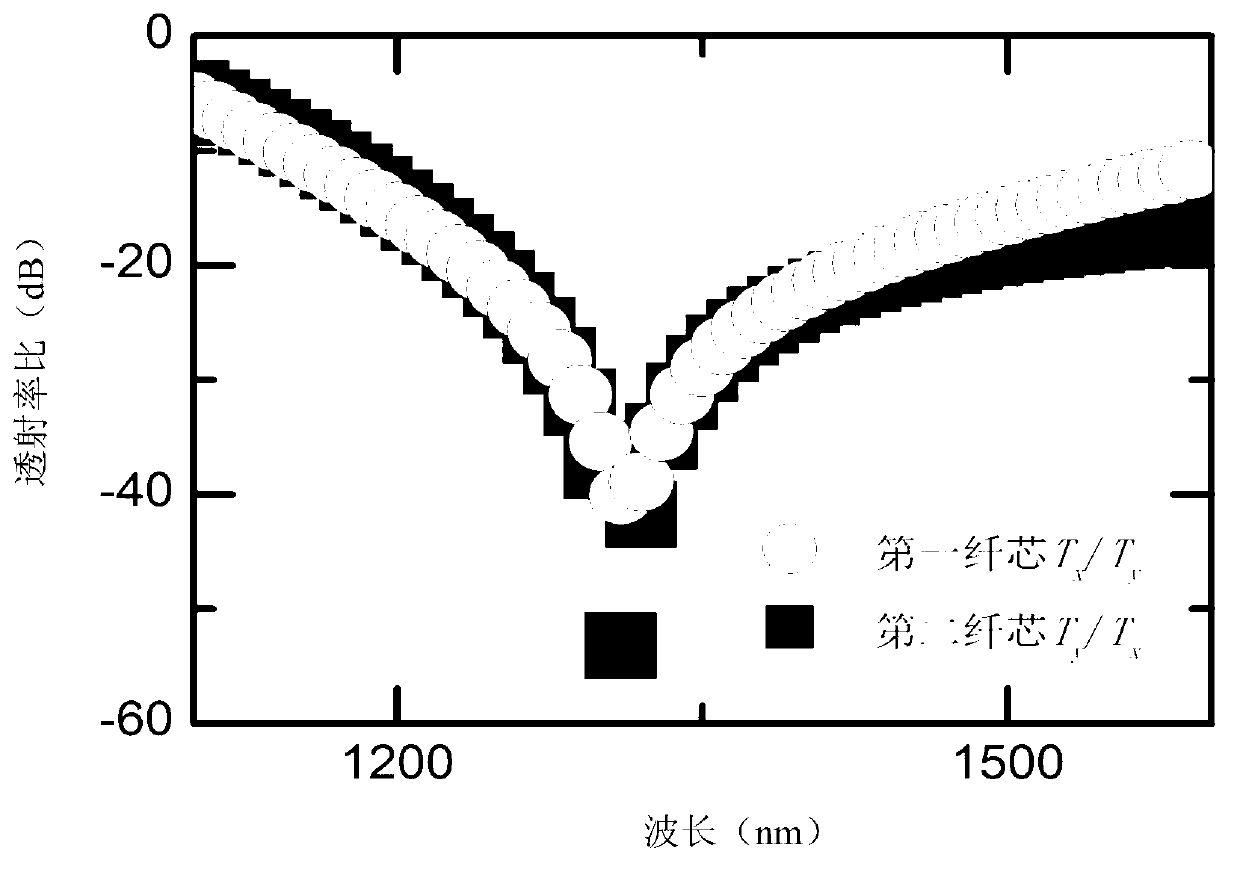
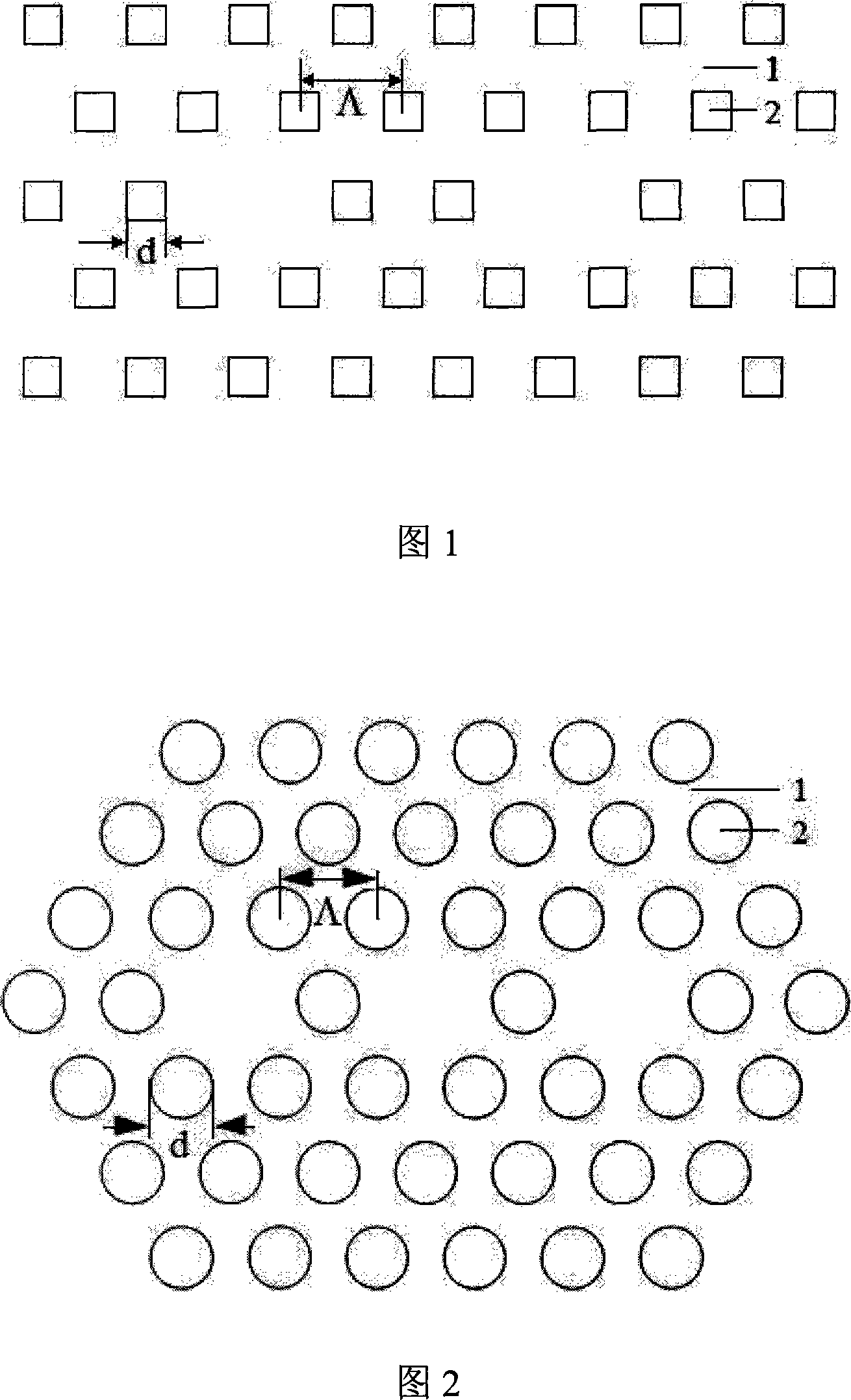
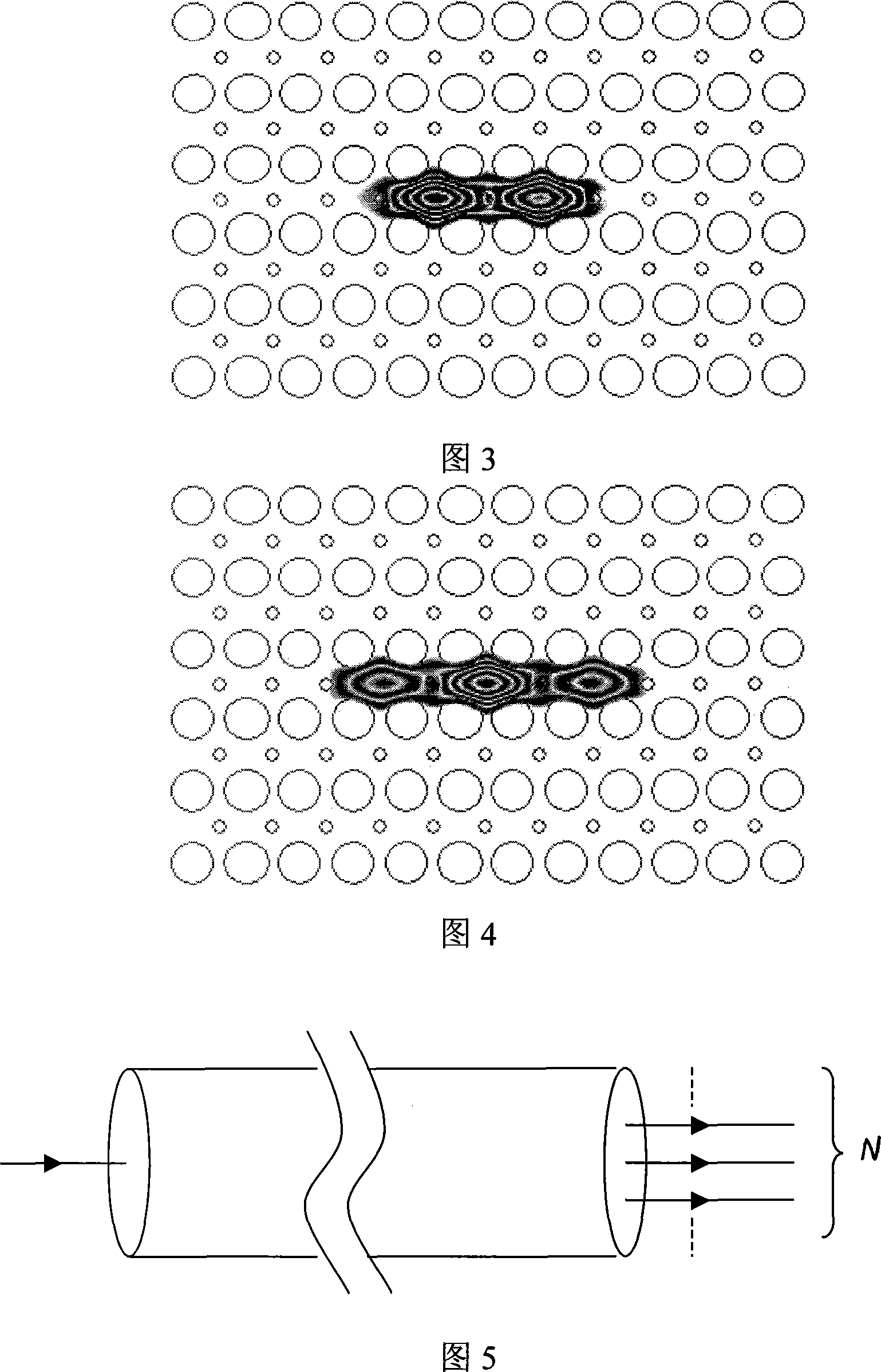
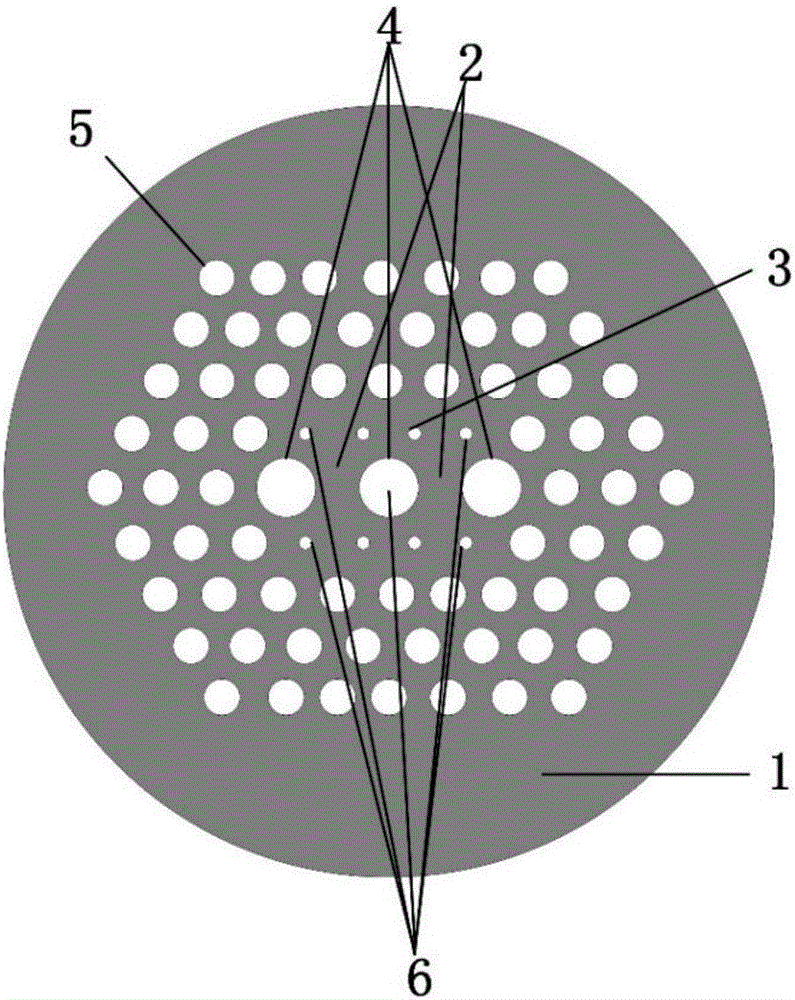
Patents
Literature
122 results about "Coupling length" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
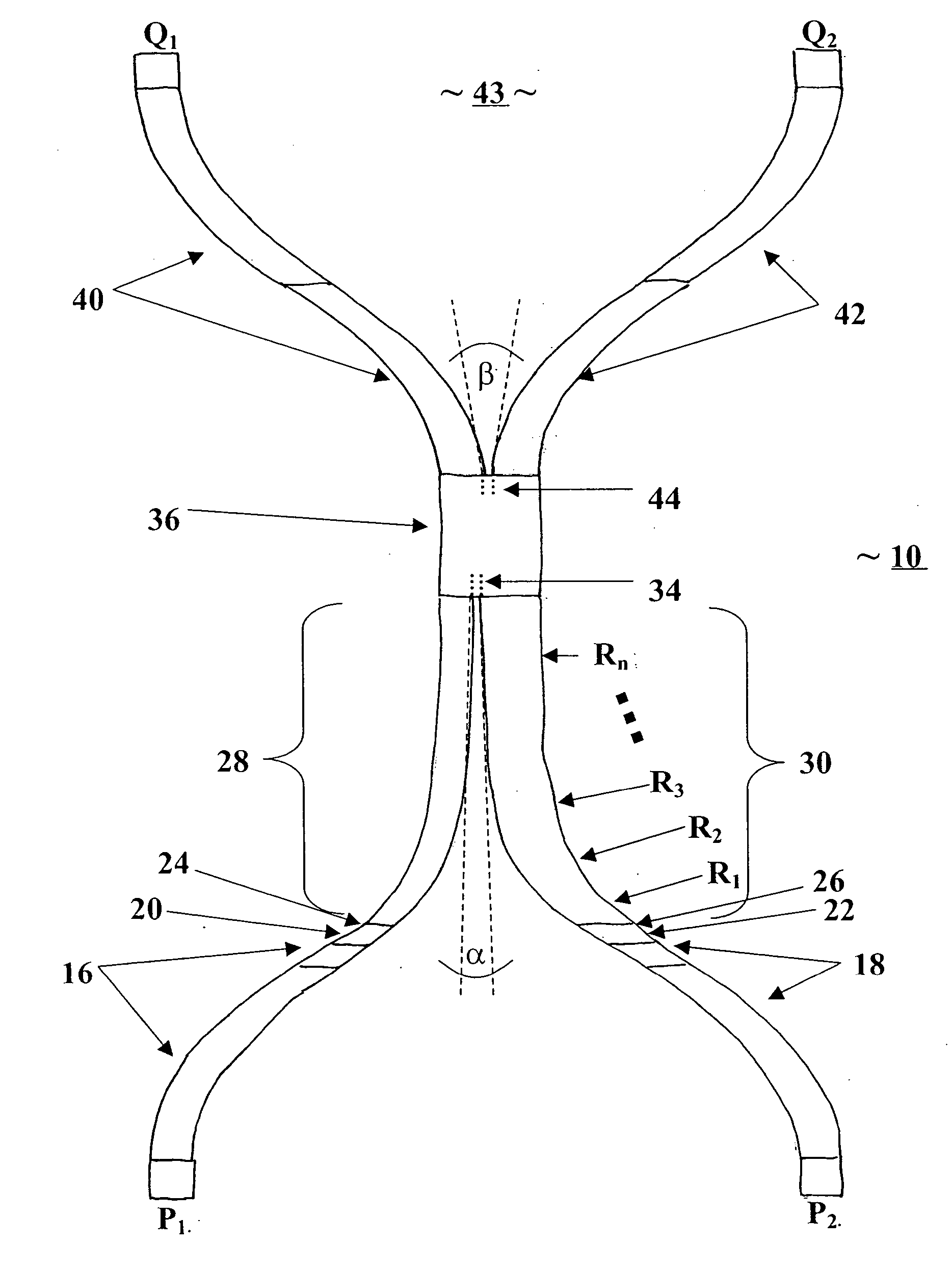
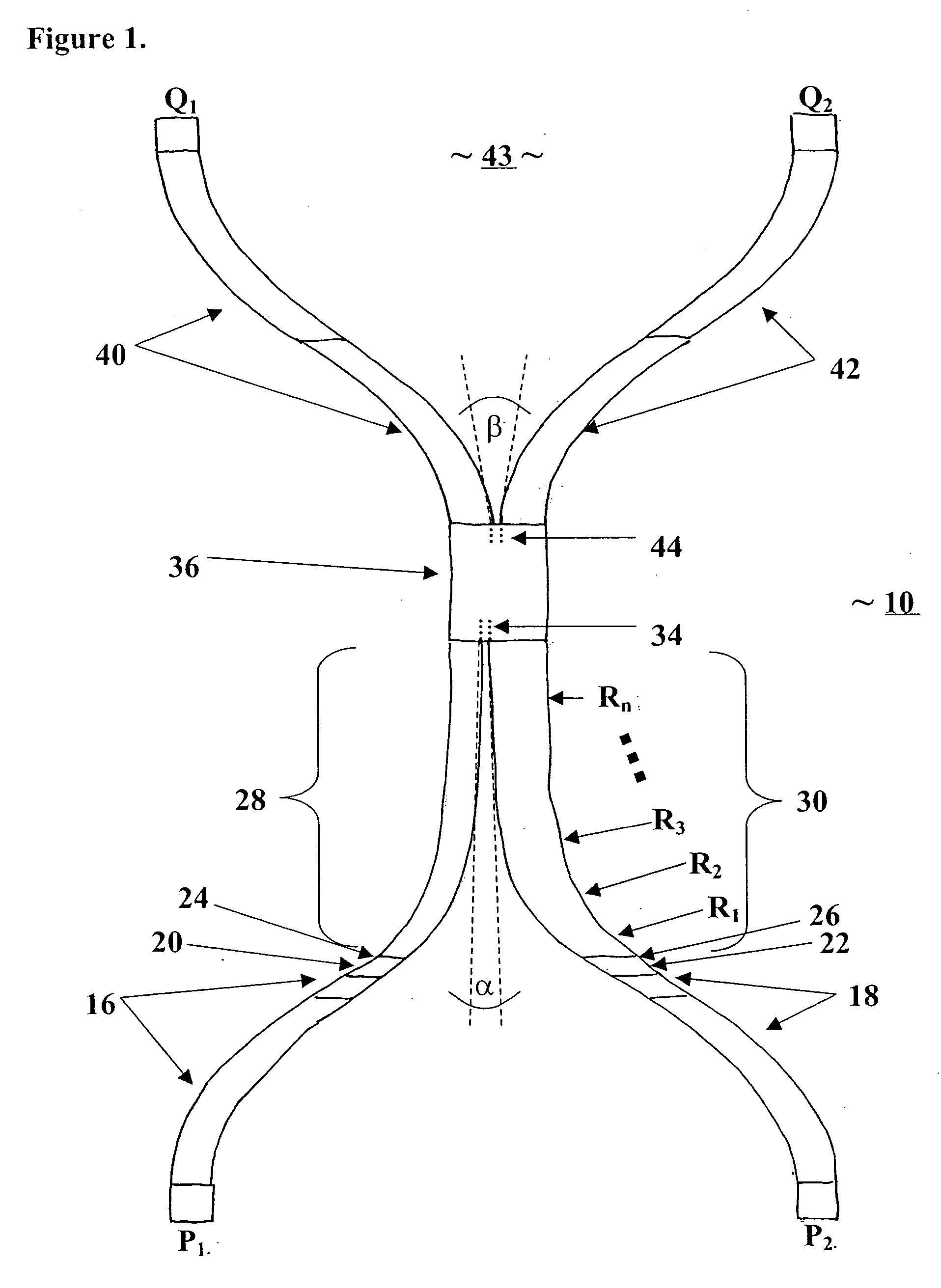
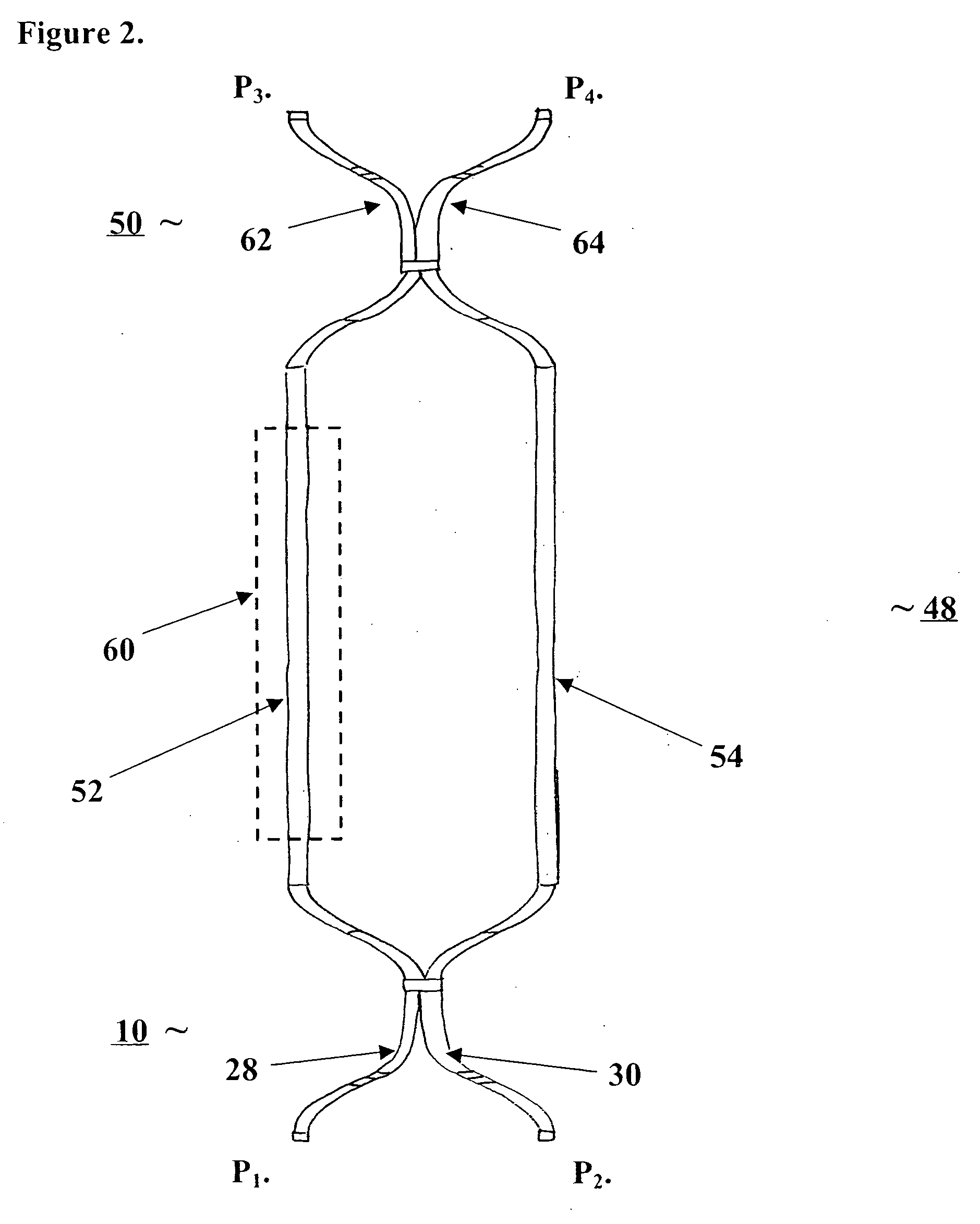
Electrical metallic tube, coupling, and connector apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050006122A1Shorten the timeEliminates time-consuming complexitySubstation/switching arrangement detailsRigid pipesCouplingBiomedical engineering
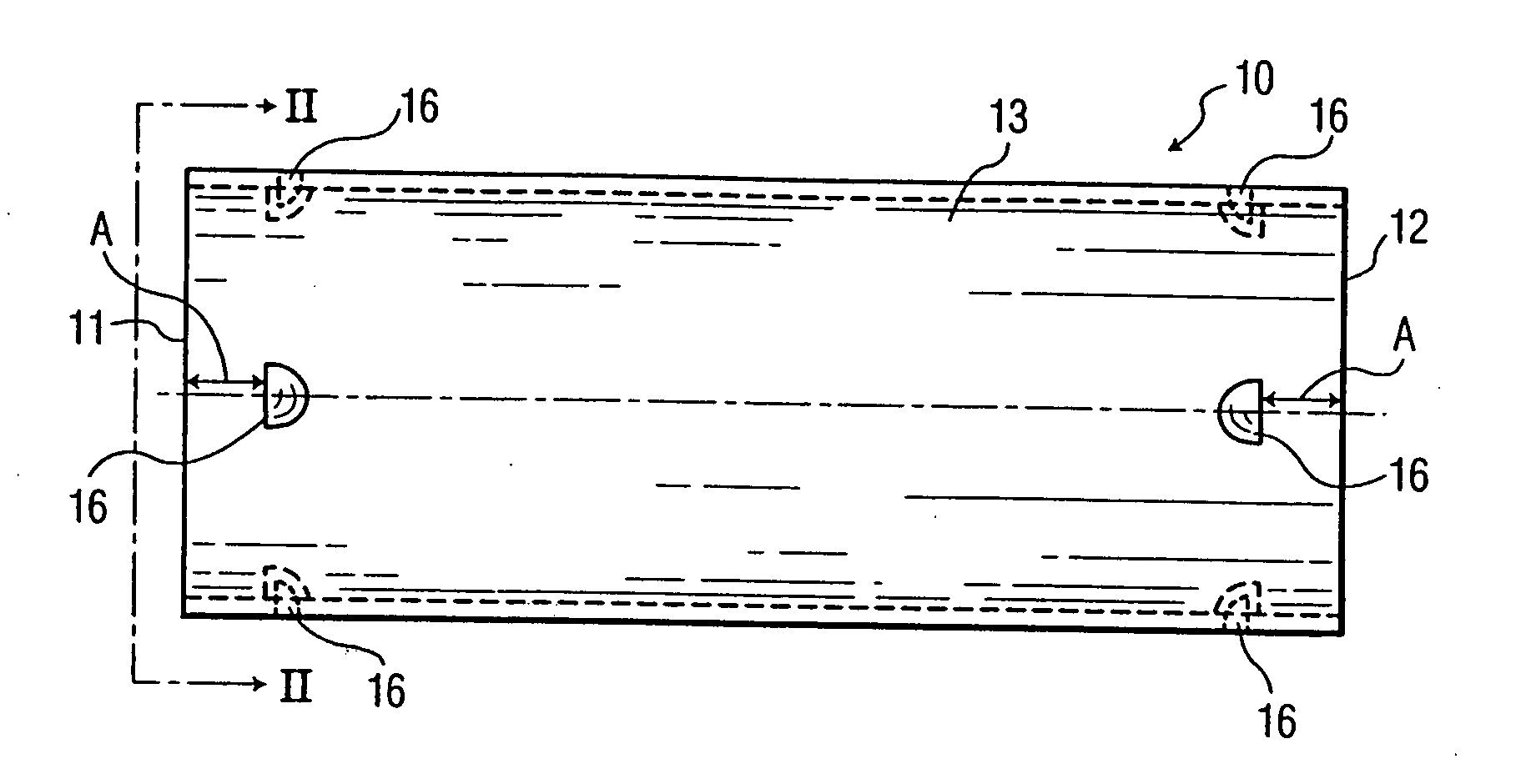
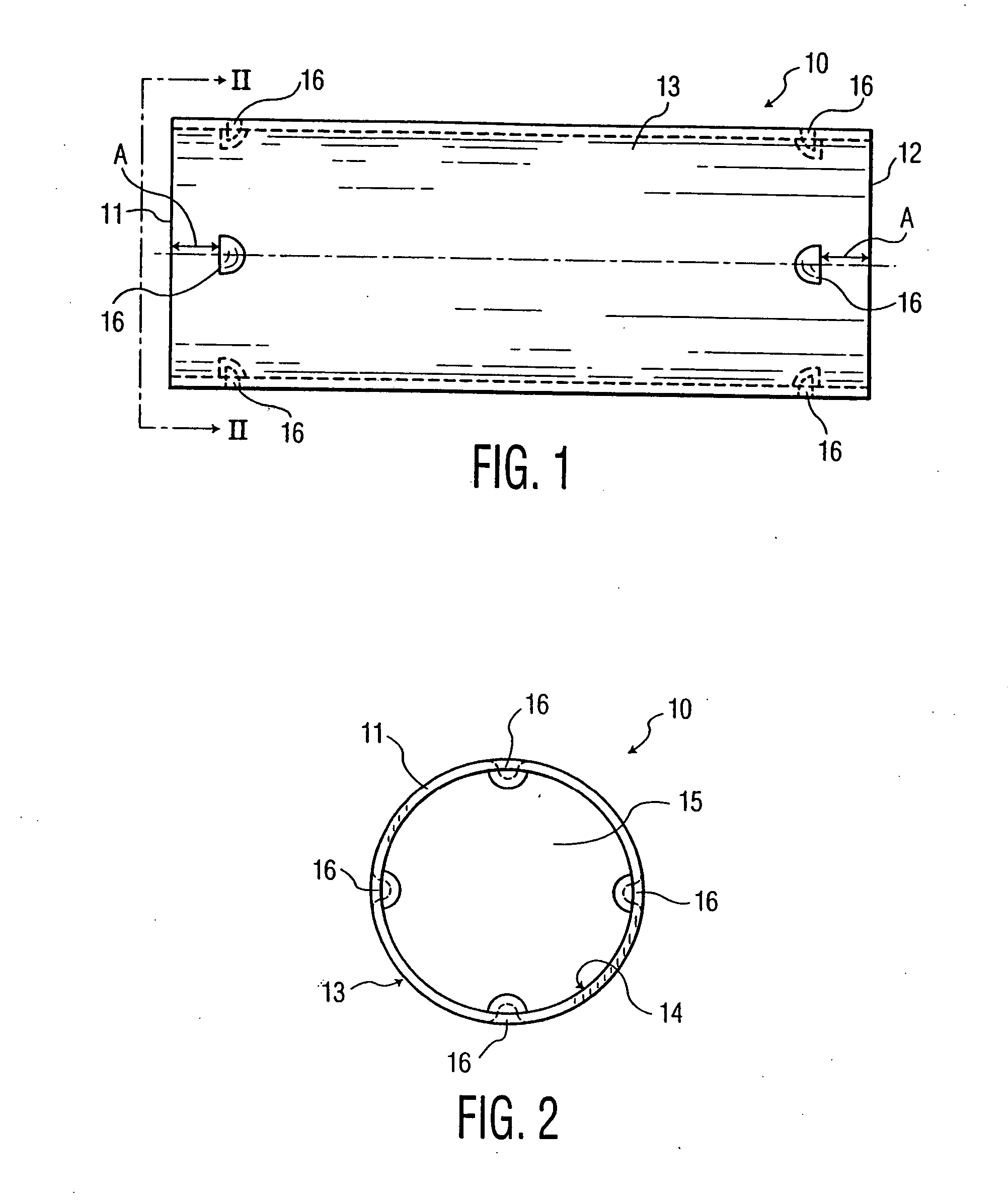
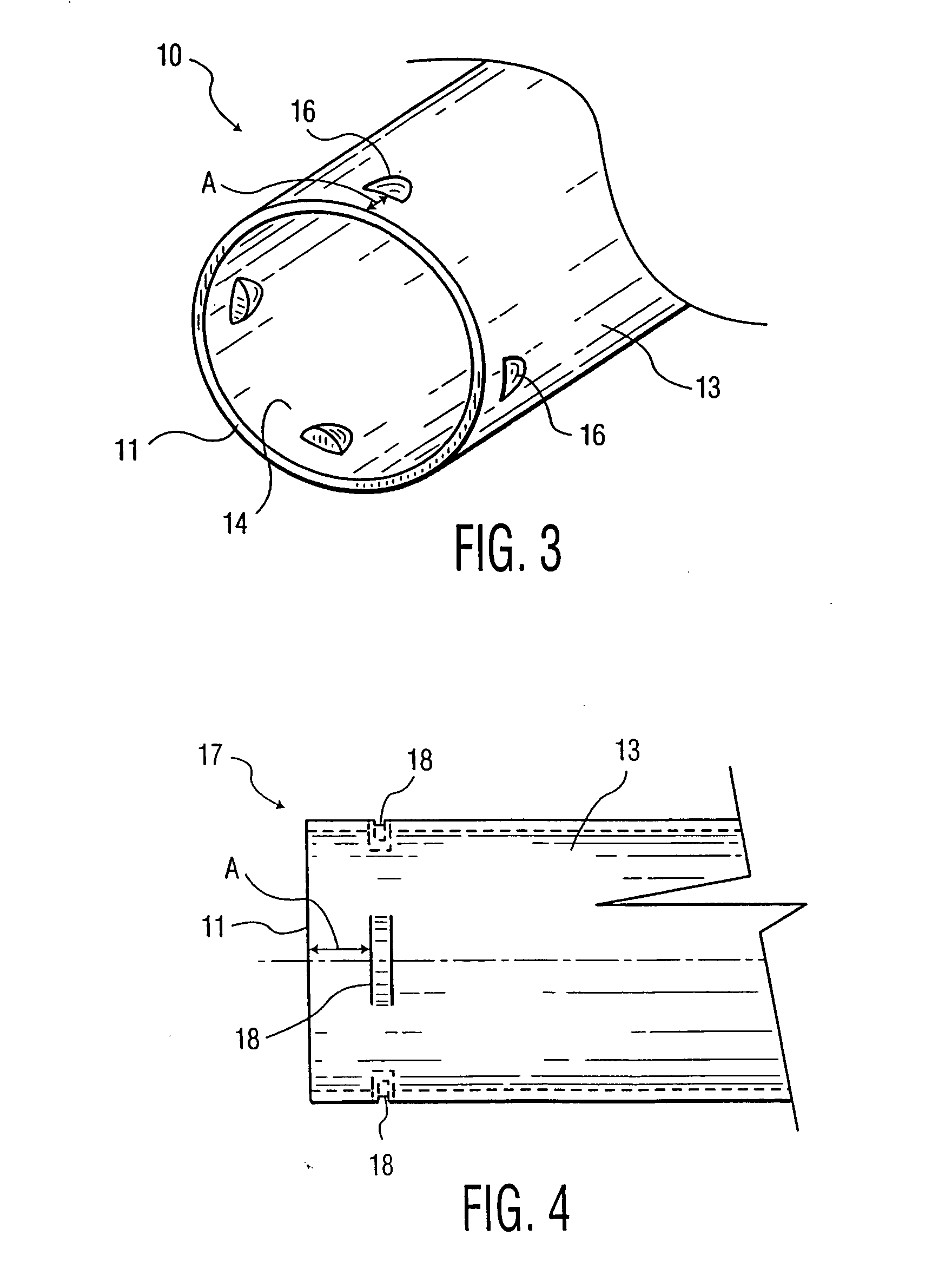
A labor saving system, method, and apparatus for connecting or coupling lengths of electric metallic tubing (“EMT”). The invention uses couplings / connectors that have barbs that are designed to engage corresponding indentations on EMT to ensure proper installation. In one aspect, the invention is an EMT having: an EMT inner surface forming an EMT cavity; an EMT outer surface; an EMT first end; and at least one indentation in the EMT outer surface at or near the EMT first end, the indentation adapted to receive a corresponding barb from a sleeve device. In another aspect, the invention is a sleeve device comprising; a sleeve inner surface forming a sleeve cavity adapted to receive an end of an EMT; a sleeve outer surface; a first sleeve end; at least one barb on the sleeve inner surface at or near the first sleeve end, the barb adapted to engage a corresponding indentation on the EMT.
Owner:JOHN MANEELY
Threaded and coupled connection for improved fatigue resistance
InactiveUS6609735B1Reduce horizontal sizeReduce stress concentrationDrilling rodsFluid pressure sealed jointsCouplingEngineering
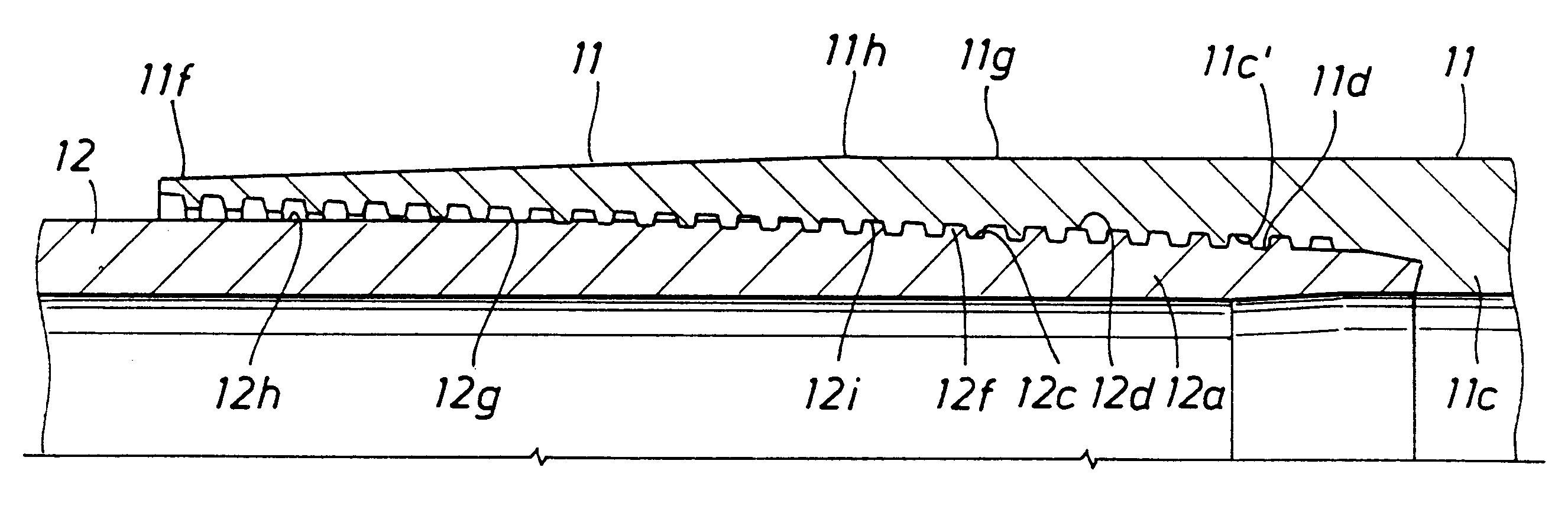
Threaded and coupled pipe connections are provided with a number of design features that increase resistance of the connection to fatigue failure from cyclical side loading. The features acting alone or in combination include the provision of a pin thread that is formed along a single taper and that vanishes at the surface of the pipe. The coupling engages the pin such that the threaded area of the coupling engages all of the pin threads and extends beyond the vanish point of the pin threads at the optimum coupling makeup position. The threads of the coupling and pipe may engage along both the stab and load flanks to distribute the side loading. The external surface of the coupling may be tapered from the center toward each coupling end to reduce the stiffness ratio of the connection, and the ends or faces of the coupling may be reduced in radial thickness to prevent coupling splitting. The coupling length may be extended to exceed standard coupling lengths to provide the additional threaded area and / or taper areas and / or reduced stiffness ratios.
Owner:DEUT BANK TRUST COMPANY AMERICAS
Tile with wide coupling configuration and method for the same
A method and apparatus providing a tile configured to form a modular floor covering including an array of substantially identical tiles. The tile includes a top surface, bottom side, front and rear sides and first and second lateral sides. The top surface includes an elongated shape and the bottom side includes a support grid. The front and rear sides are defined along a longitudinal length of the elongated shape. The front side includes at least one first hinge member and the rear side includes at least one complementary second hinge member configured to be engageable with the at least one first hinge member of an adjacently positioned tile. The first and second lateral sides define a width of the elongated shape with the first and second lateral sides including a respective tab and slot coupling portion each having a coupling length at least one-third the width of the elongated shape.
Owner:CONNOR SPORT COURT INT
High-tolerance broadband-optical switch in planar lightwave circuits
InactiveUS20040151423A1Reduce lossHigh extinction ratioCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsMach–Zehnder interferometerWaveguide
Broadband optical switches based on adiabatic couplers having a pair of asymmetric waveguides with variable curvature sections include in a 2x2 configuration based on a Mach-Zehnder interferometer two such adiabatic couplers, and in a 1x2 or 2x1 configuration an adiabatic coupler and an Y-splitter. Each adiabatic coupler includes two waveguide branches of different but constant widths having curved sections with varying radii, separated over a coupling length by a changing spacing therebetween and blending in an asymmetric intersection area, and two symmetric branches. In the 2x2 switch, the two adiabatic couplers face each other with their respective symmetric branches, and are connected by the two identical arms along a main propagation axis in a mirror image. The utilization of the variable curvature adiabatic couplers in silica MZI switches on a silicon substrate provides switches with an exceptional broadband range (1.2-1.7 mum), very high extinction ratios (>35 dB), low fabrication sensitivity and polarization independent operation. The switches are significantly smaller than known broadband switches, have significantly smaller excess loss, faster switching time and low power consumption.
Owner:LYNX PHOTONIC NETWORKS
Photon crystal wave-guide polarization beam splitter
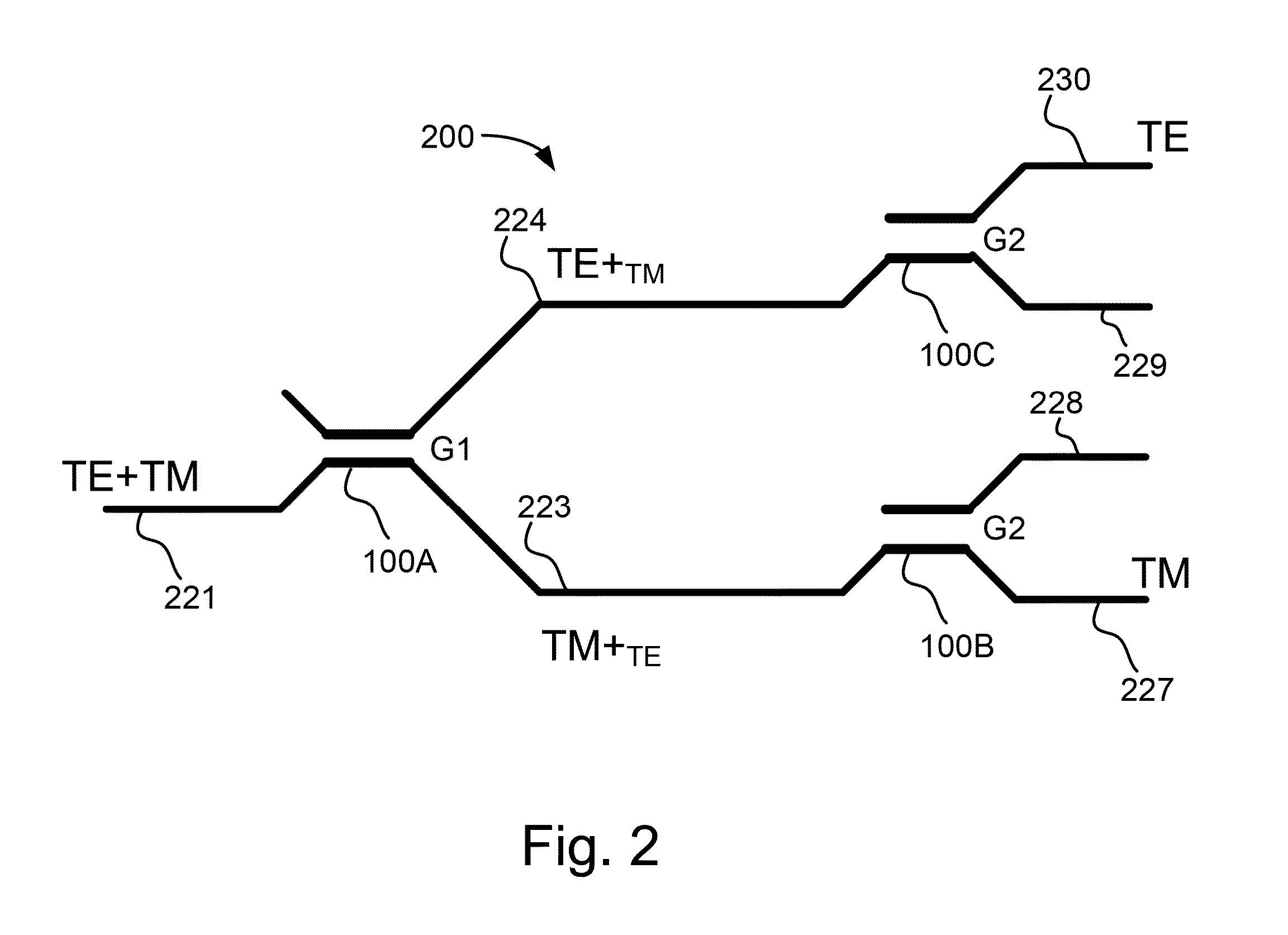
The invention discloses a photonic crystal waveguide polarizing beam splitter which introduces a line defect to form a structure of a coupled waveguide in a two-dimensional tellurium dielectric rod photonic crystal, and implements beam splitting for TE beam and TM beam by using different coupled lengths of waveguides of the TE beam and the TM beam. The characteristics of the implementation of the polarizing beam splitter by adopting a two-dimensional photonic crystal waveguide are as follows: firstly, compared with the prior various polarizing beam splitter devices, the polarizing beam splitter adopting the two-dimensional photonic crystal waveguide can implement a polarizing beam splitting with high degree of polarization and high extinction ratio; secondly, the device can be provided with a smaller size, and can be structurally compatible with the prior photonic crystal device to meet a requirement of integration ratio; thirdly, the polarizing beam splitter adopting the two-dimensional photonic crystal waveguide has a very flexible structure, and can implement the polarizing beam splitting of any wavelength in a range from 3.5 to 35mu m for wavelengths through adjusting a length of a coupling region or a lattice constant. The invention also discloses a designing idea and a particular structural design of the polarizing beam splitter, an optical performance, etc. of the polarizing beam splitter acquired from the designing idea.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Photonic Crystal Coupling Defect Waveguide and Photonic Crystal
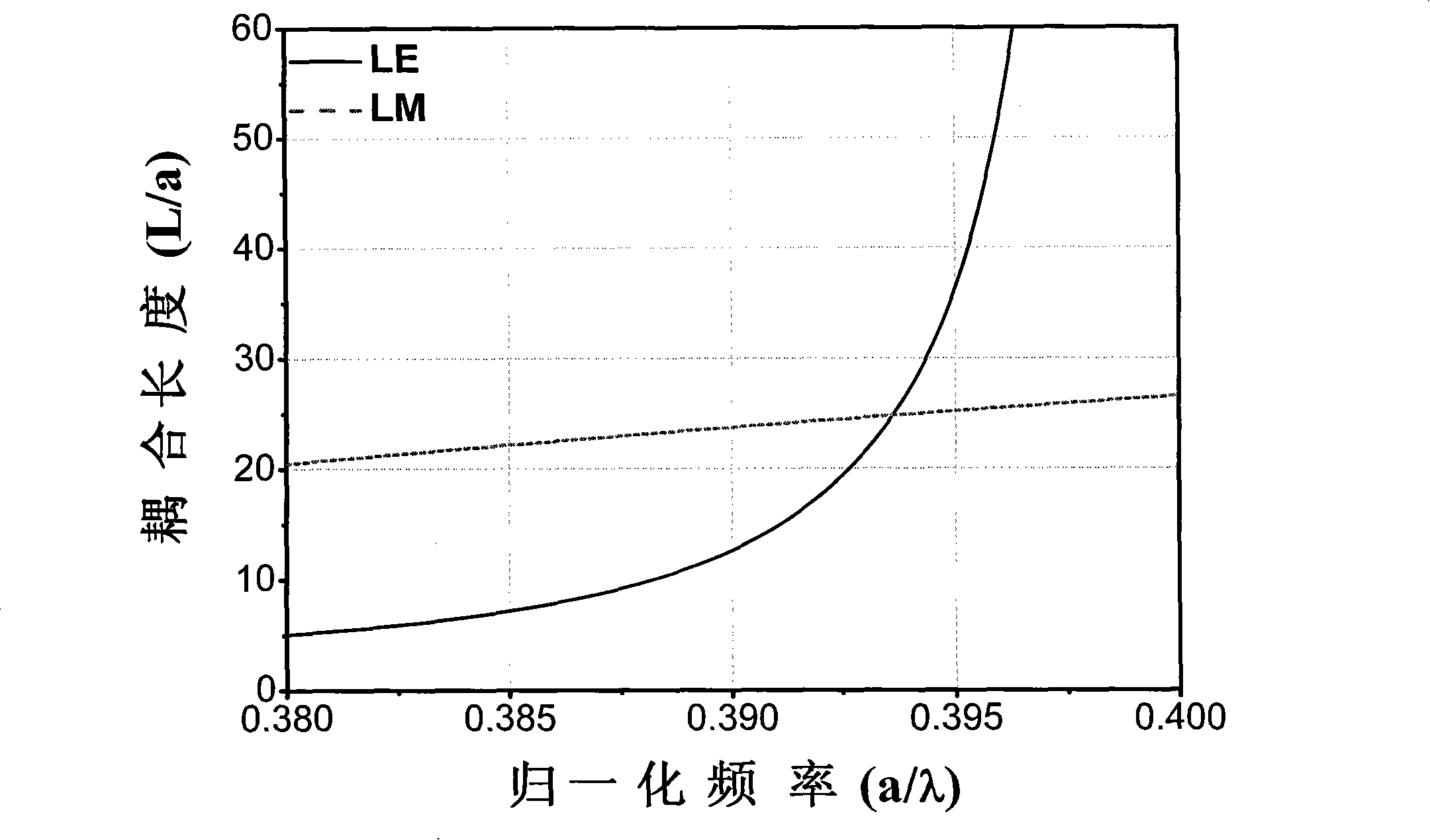
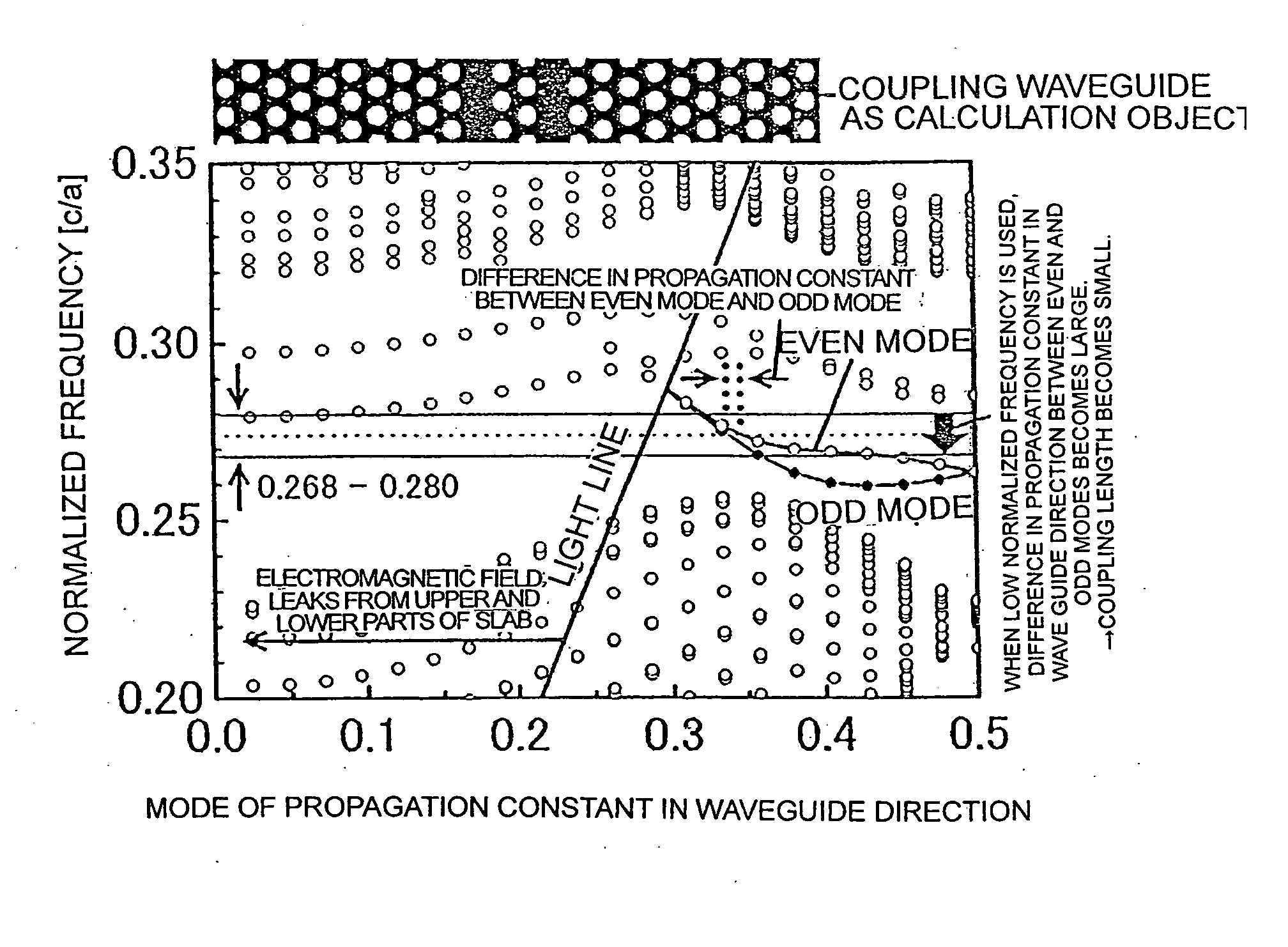
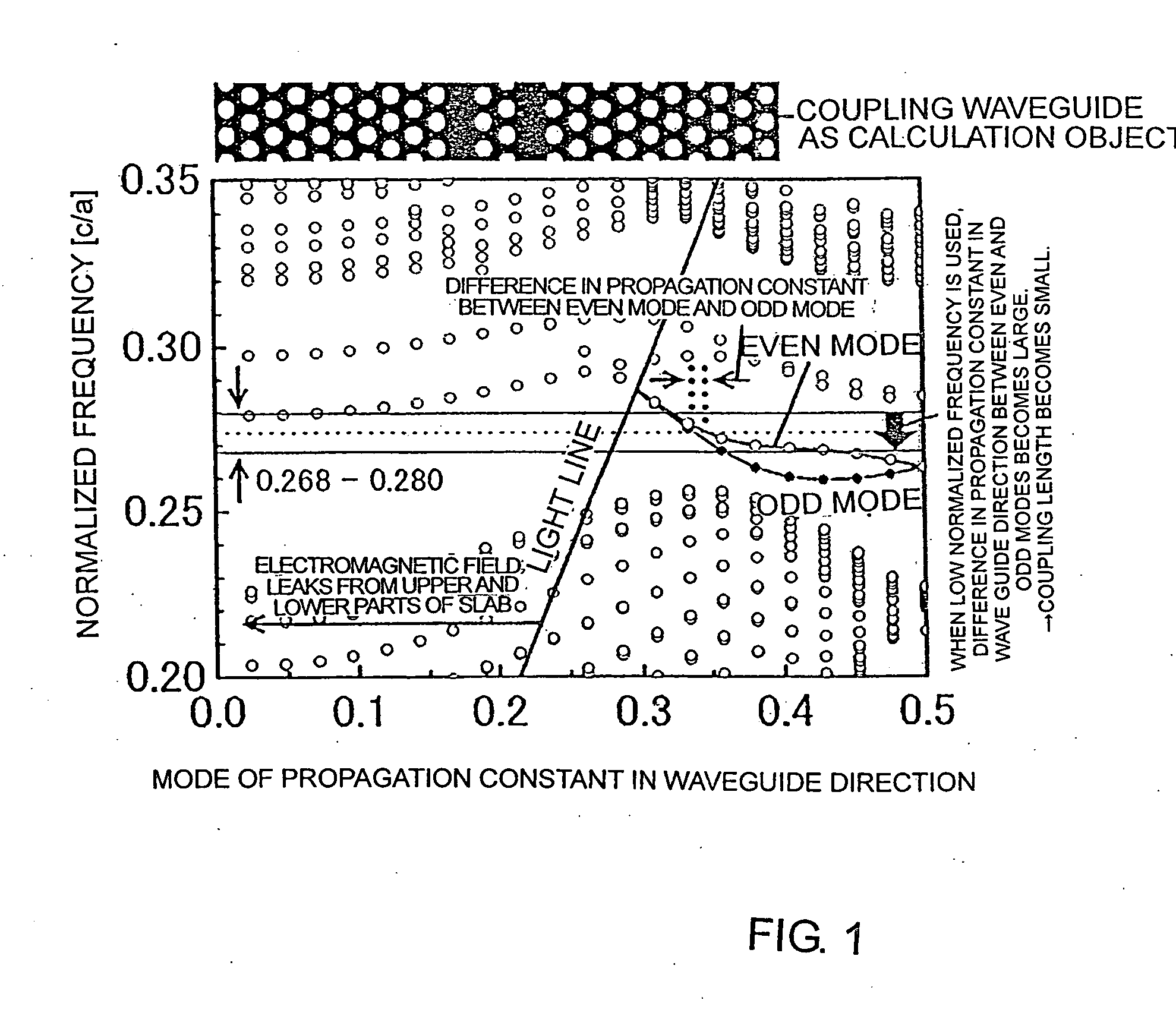
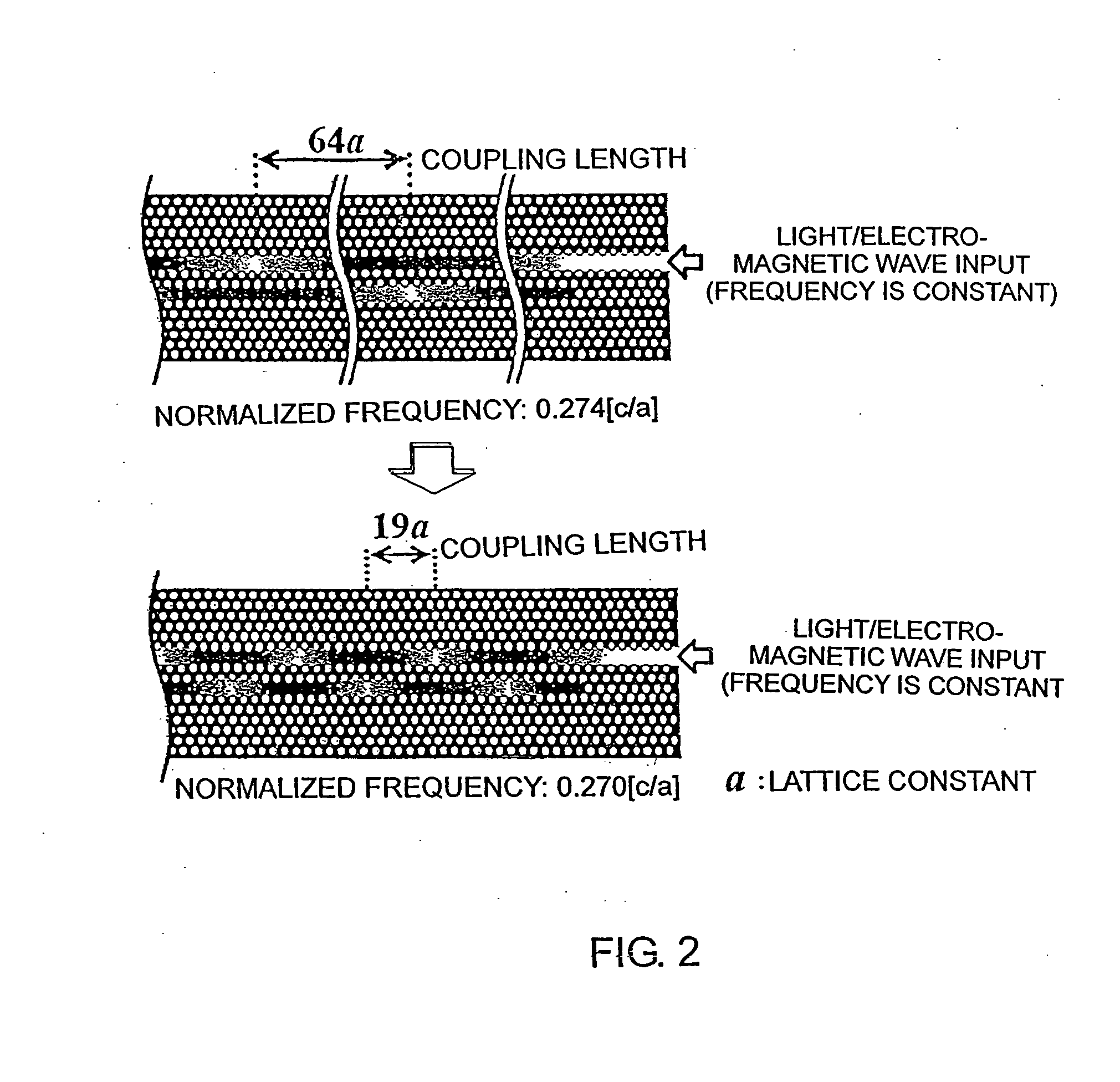
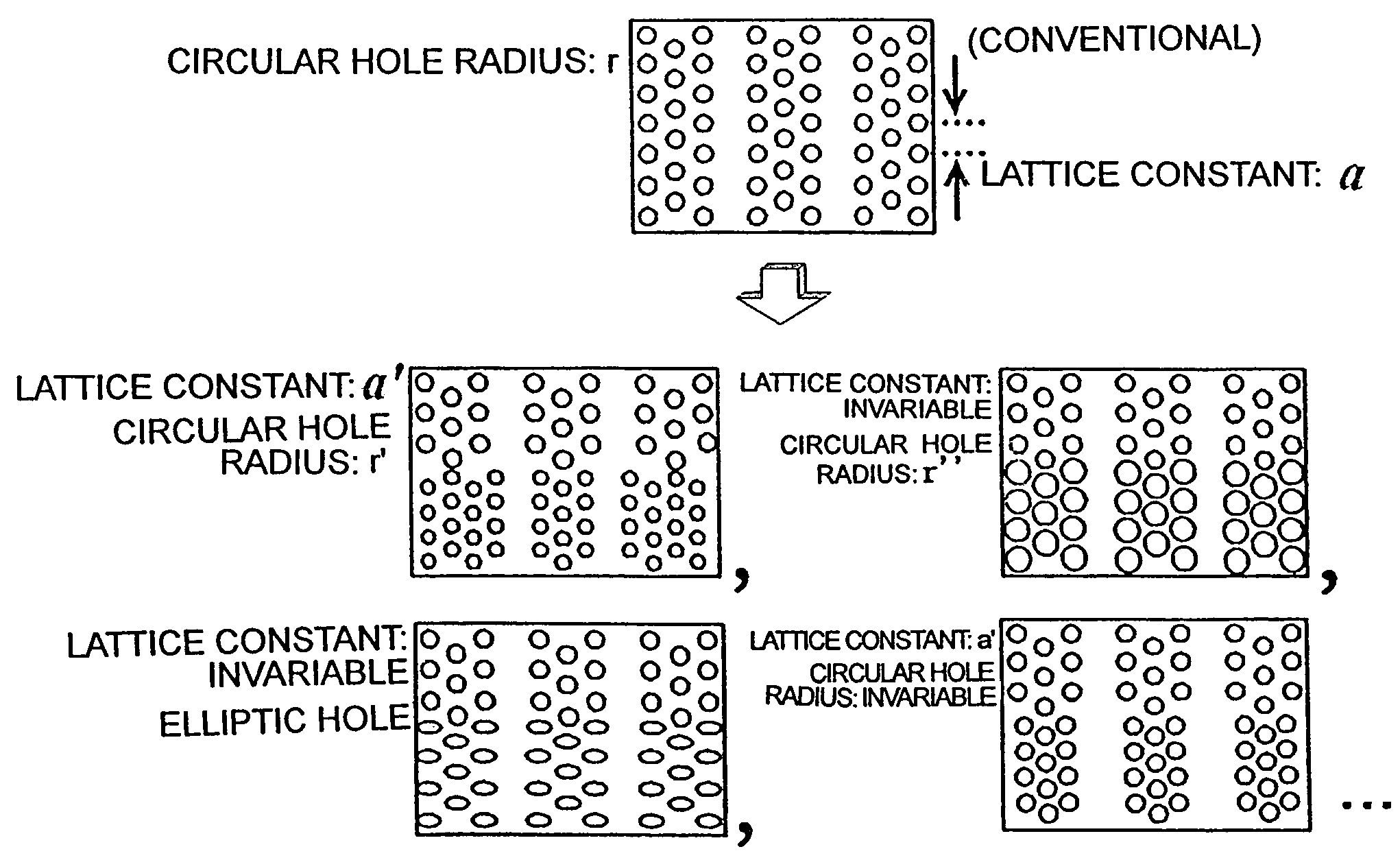
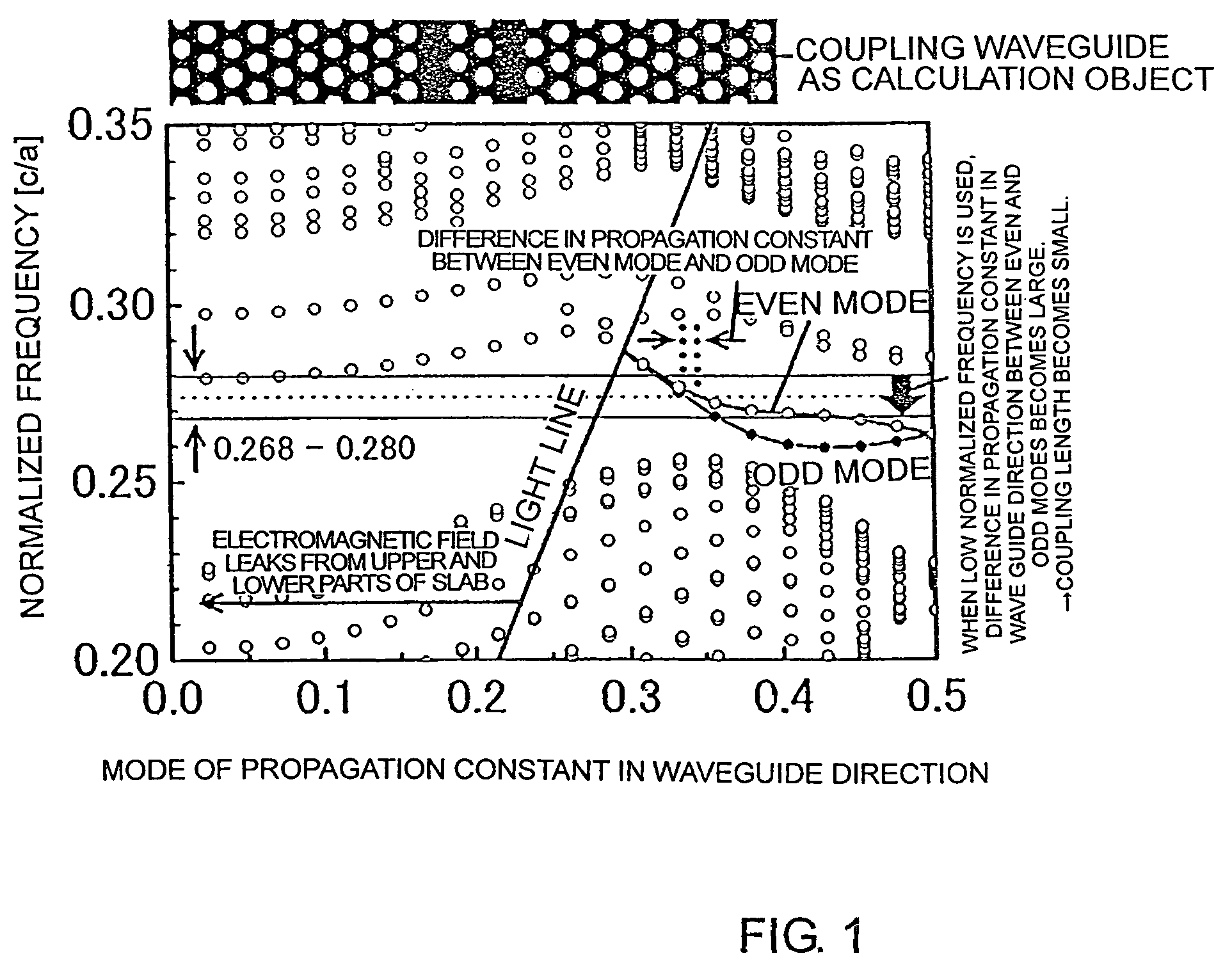
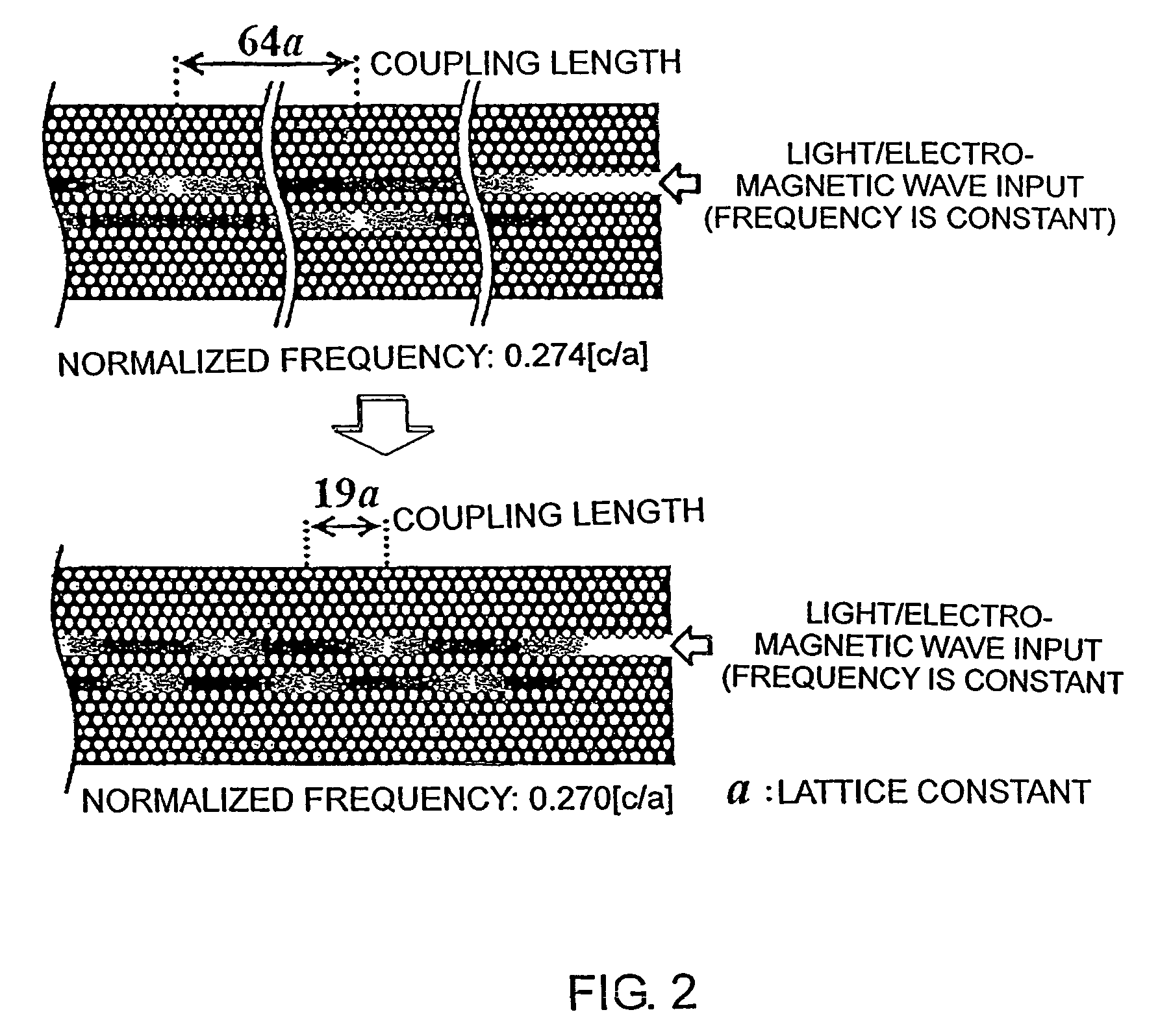
InactiveUS20070280592A1Coupling lengthCoupling length can be shortenedNanoopticsCoupling light guidesPhotonic crystalCoupling
A photonic crystal directional coupler composed of at least two linear defect waveguides introduced into a photonic crystal. The medium constant and the lattice constant of the photonic crystal at the photonic crystal directional coupling part, the sizes and shapes of the elements constituting the periodical structure of the photonic crystal are varied. Thereby the difference in propagation constant between the even and odd modes of the photonic crystal directional coupling part is increased, thus shortening the coupling length of the photonic crystal directional coupler.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
High-tolerance broadband-optical switch in planar lightwave circuits
InactiveUS20030118279A1Reduce lossHigh extinction ratioCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsOptical propagationOptical property
A broadband optical switch with high process tolerance designed and fabricated using Planar Lightwave Circuits (PLC) technology. A 2x2 configuration of the switch is based on a Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI) configuration that includes two 3 dB adiabatic couplers and two identical arms. Each adiabatic coupler is characterized by two straight branches having different widths, separated over a coupling length by a changing spacing therebetween and blending in a symmetric intersection area, which connect to two symmetric branches. The two adiabatic couplers are connected by the two arms with their symmetric branches facing each other along an optical propagation axis. Switch control is realized by changing an optical property of one or both of the MZI arms. Implementation in silica-on-silicon PLCs provides switches with an exceptional broadband range (1.2-1.7 mum), very high extinction ratios (>34 dB), low fabrication sensitivity and polarization independent operation.
Owner:LYNX PHOTONIC NETWORKS
High-tolerance broadband-optical switch in planar lightwave circuits
The invention relates to a broadband optical switch with a couple of asymmetric wave guide insulation couplers, the asymmetric wave guide has a curvature variable part, the broadband optical switch comprises two insulation couples with a two multiple two structure based on Mach-Zehnder interferometer and an insulation couple with an one multiple two structure, or a Y splitter with a two multiple one structure. Each insulation couple comprises two wave guide branches with different but constant width and two symmetric wave guide branches; wherein, the two wave guide branches are provided with variable radial bend, by changing the distance between the two wave guide branches, enabling to separate the two wave guide branches within the couple length, and mixed in asymmetric crossed area.. In two multiple two switches, two insulation couplers are faced to each other along the main propagation axis in the way of mirror image via the counterpart symmetric branch, and connected with the same two arms.The insulation coupler with variable curvature is used in the silicon dioxide MZI switch on the silicon substrate, which provides the switch with a special bandwidth range (1.2-1.7 Mum), high extinction ratio (more than 35dB), low manufacture sensitivity and operations having nothing to do with polarization. The broadband optical switch has the advantages of more compact size compared with known broadband switches, less extra loss, and faster switching time and lower power consumption.
Owner:LYNX PHOTONIC NETWORKS
Polarization independent broad wavelength band optical switches/modulators
Optical switches based on the balanced bridge interferometer design require precisely made (or half a coupling length) directional couplers to achieve minimum crosstalk for the two switch outputs. Precision 3 dB-directional couplers require the waveguide dimensions and fabrication parameters of the evanescent region to be tightly controlled making a low crosstalk switch difficult to manufacture and expensive. A new type of balanced bridge interferometer type switch is disclosed where the input and output directional couplers are asymmetrically biased to induce a certain difference in the propagation constants between the two waveguide in the directional couplers. By using the asymmetrically biased directional couplers with a certain tuning a bias voltage for the directional couplers. Low crosstalk switches can be achieved for a very wide range of directional coupler strengths, relaxing the precise half-coupling length directional couplers required in conventional design. This relaxation of the precise directional coupler waveguide regions allows a relaxation in the manufacturing tolerance of the devices and therefore make the switch much easier to make. Because low crosstalk switches can be a device with an extended operating range and broader directional coupler parameters, switches can be used for a much broader wavelength bandwidth. In one of the embodiments, this new design allows a device to switch both TE and TM mode optical signals simultaneously at low crosstalk levels to result in a polarization-independent optical switch.
Owner:EOSPACE
Method For Characterizing An Optical Fiber Link
InactiveUS20070201786A1Reflectometers dealing with polarizationMaterial analysis by optical meansPolarizerPolarization mode dispersion
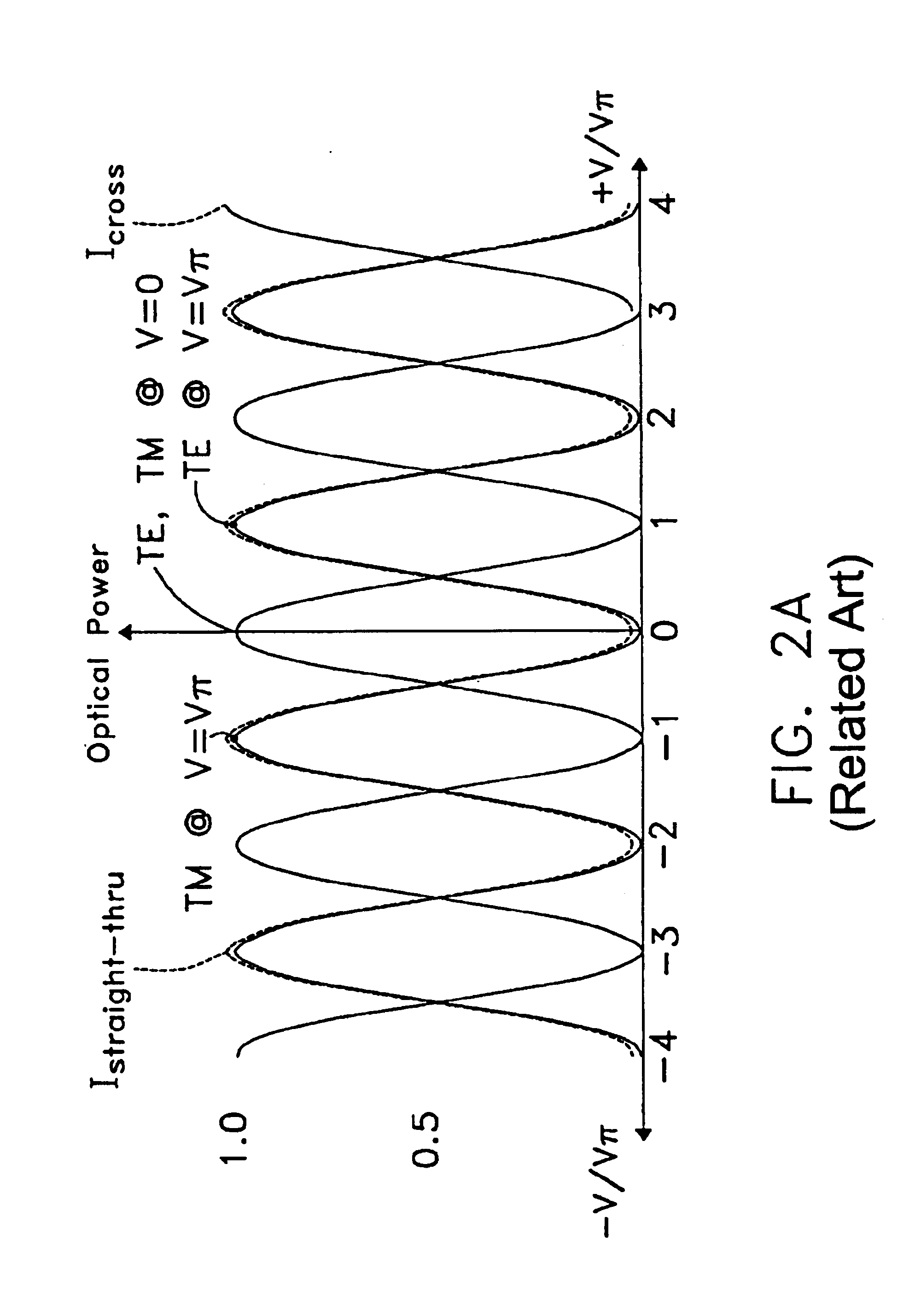
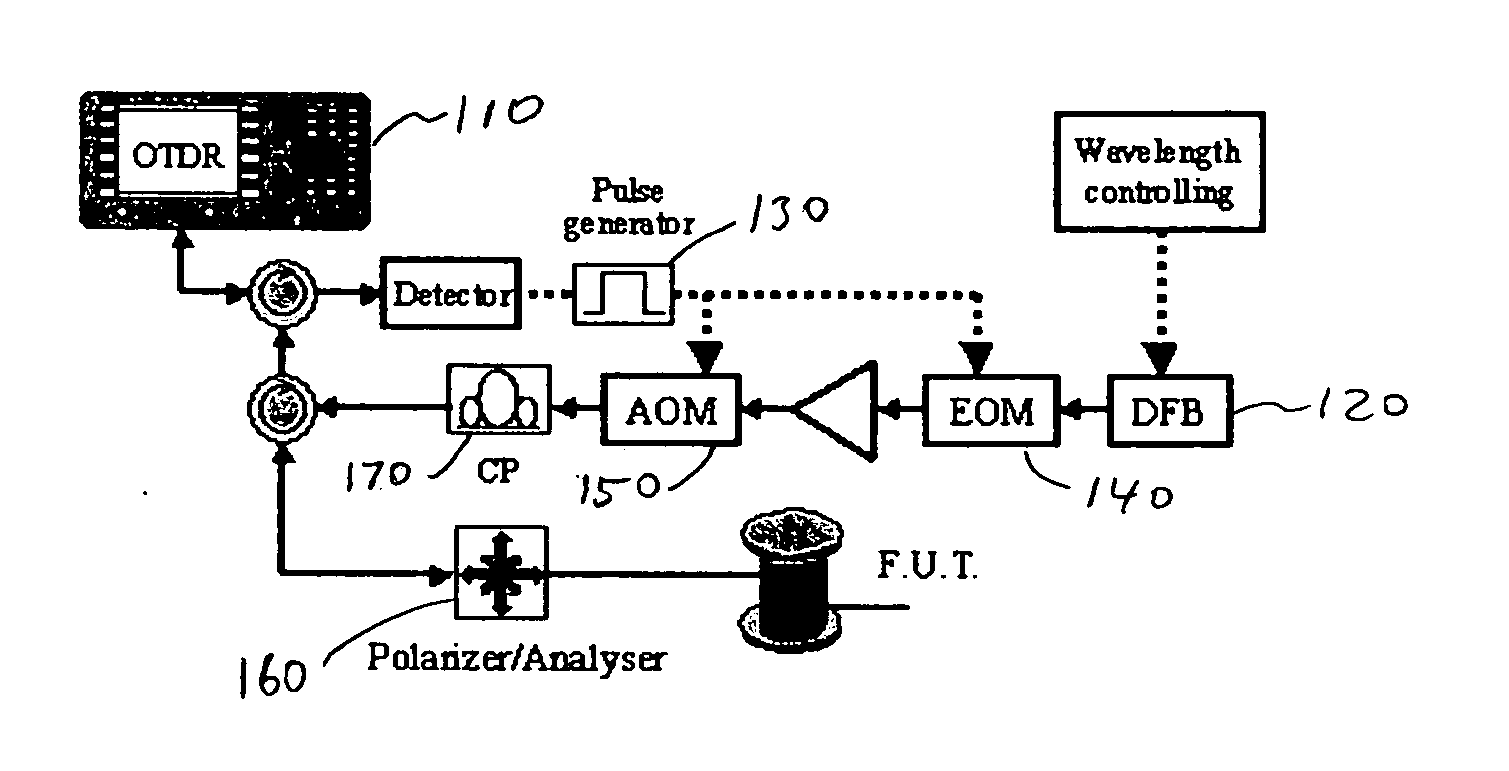
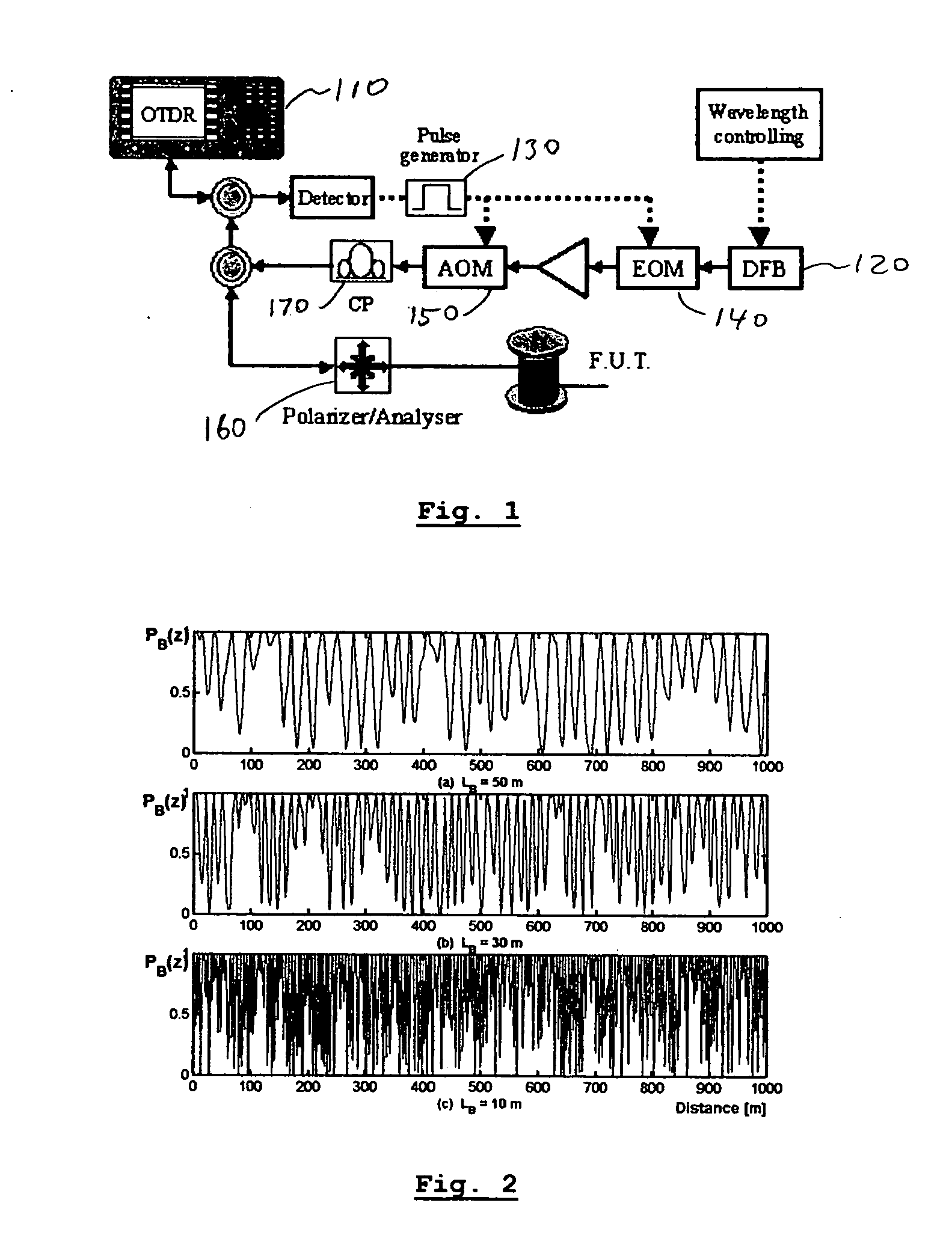
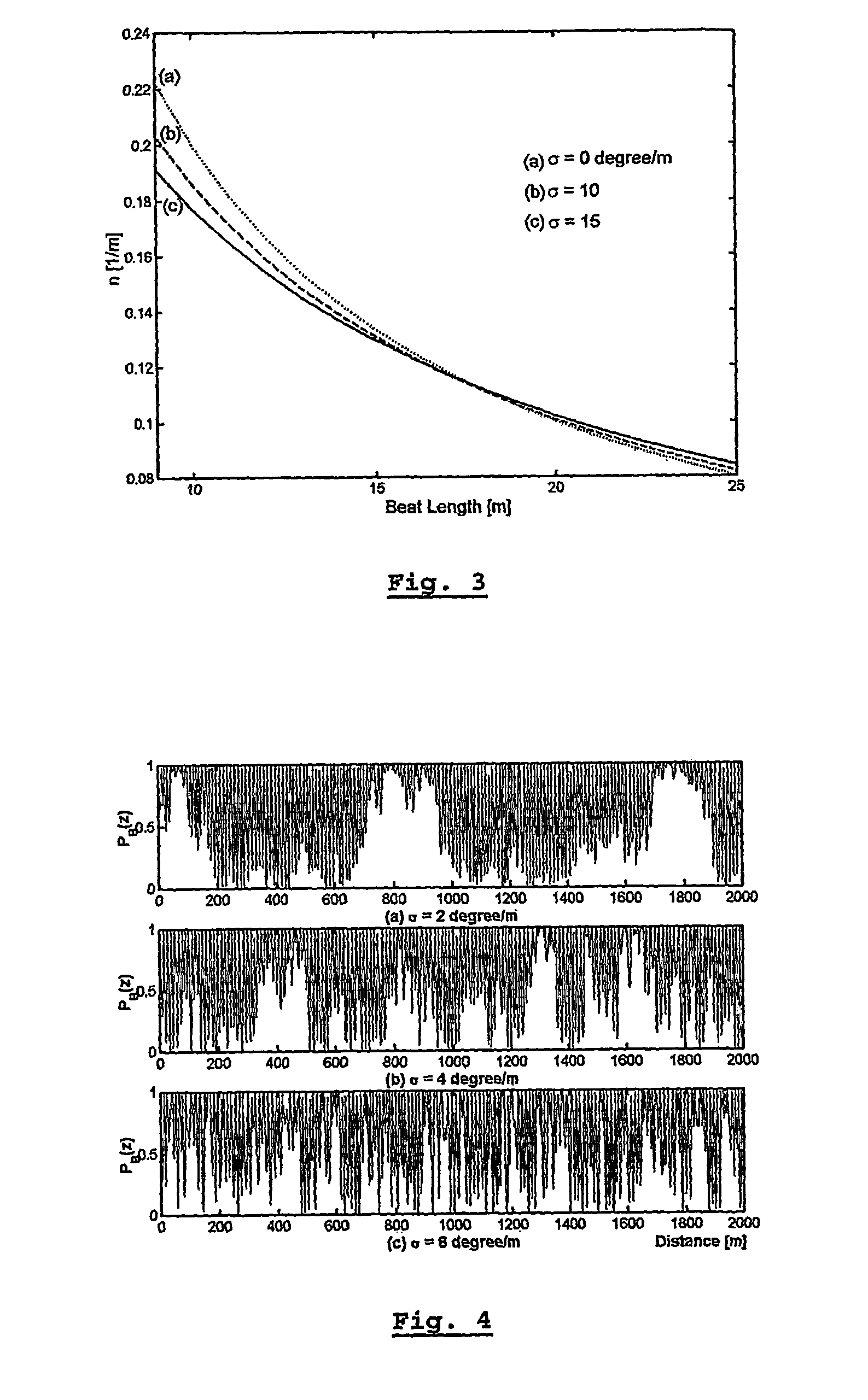
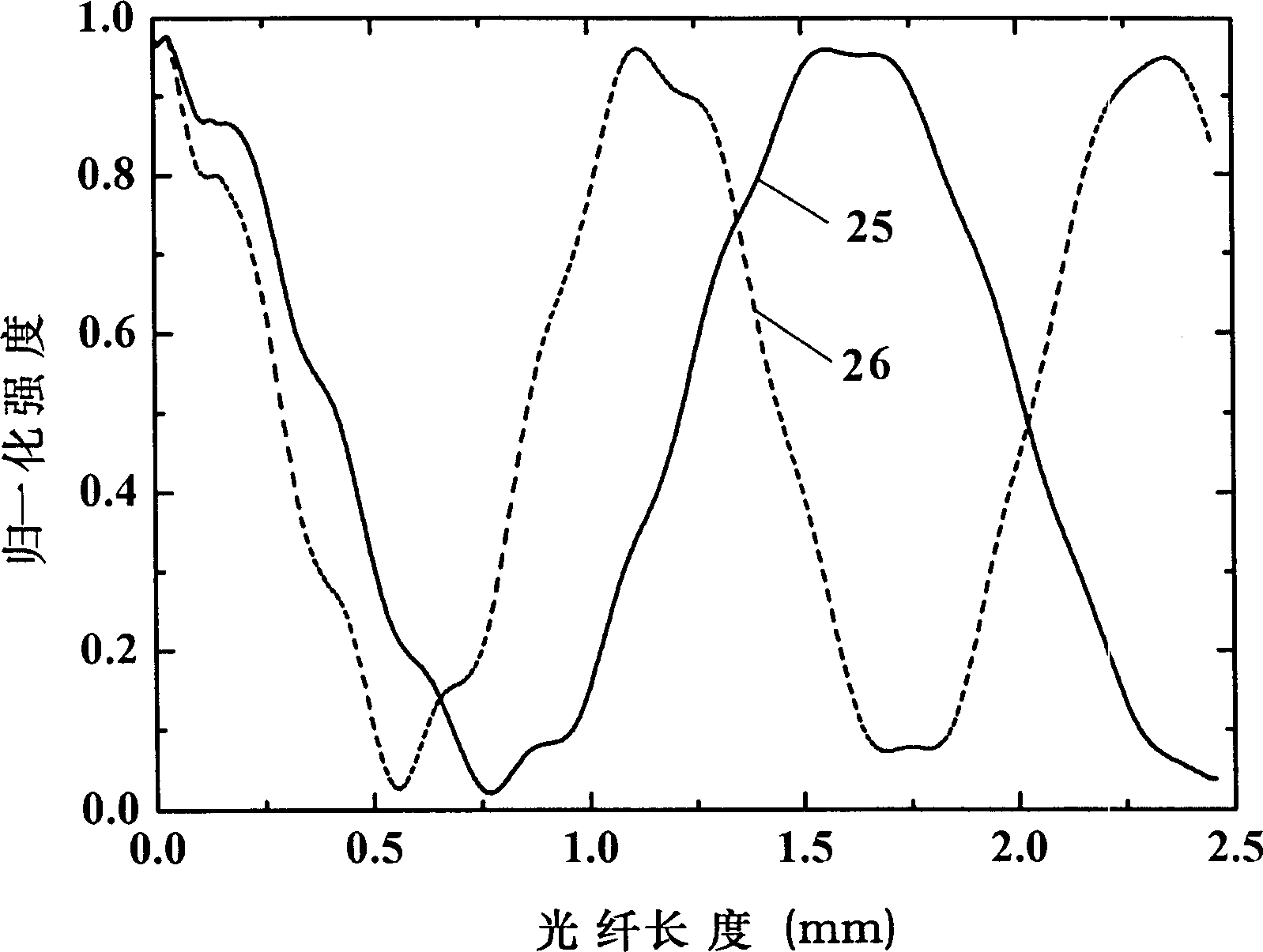
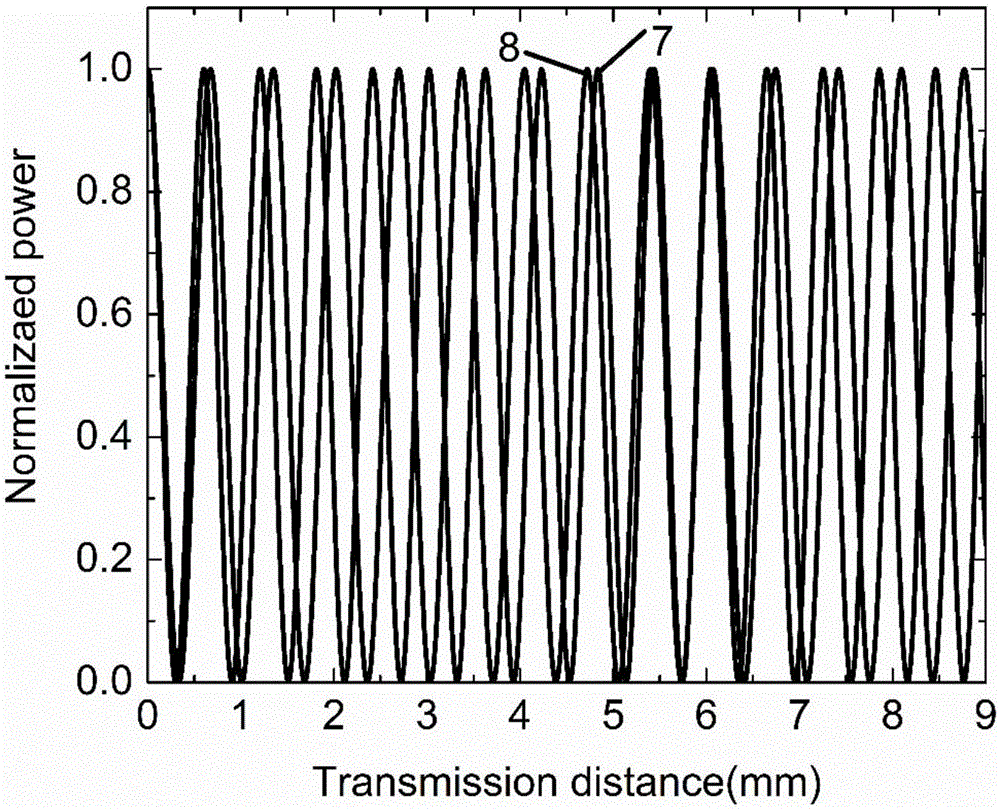
A method for characterizing an optical link by its beat length, coupling length and polarization mode dispersion is disclosed. A pulsed signal is sent along said optical fiber link and the backscattered signal (being a POTDR signal) is measured after passing through a polarizer. The length of said optical fiber, the average power difference between two successive minima of said backscattered signal and the number of maxima per unit length are derived. In an iterative way a beat length interval and an interval for the polarization mode coupling parameter are determined until the length of said intervals is below a predetermined value, yielding a value for the beat length and the coupling length, and the polarization mode dispersion is calculated.
Owner:FACULTE POLYTECHN DE MONS
Manufacturing equipment and method of optical fiber coupler
InactiveCN102096153APrecise alignmentAppropriate split ratioCoupling light guidesDriving currentPower flow
The invention provides manufacturing equipment and method of an optical fiber coupler. The manufacturing equipment specifically comprises a platform (1) and a control system (2), wherein the platform (1) comprises a platform base (9), a stretching assembly (3) arranged on the longitudinal middle part of the platform base (9), a positioning assembly (6) as well as a heating assembly (5), a vertical observation assembly (7) and a horizontal observation assembly (8) which are fixedly arranged on the upper part of the platform base (9); and the control system (2) comprises a motor controller (11) which is used for outputting drive current and respectively controlling a first electric translation stage (31a), a second electric translation stage (31b) and motors on the heating assembly (5), the vertical observation assembly (7) and the horizontal observation assembly (8) to move through drive leads. The invention is used for manufacturing an optical fiber coupler having small volume, large coupling length and small insertion loss.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Linear optical modulators and method of linear optical modulation
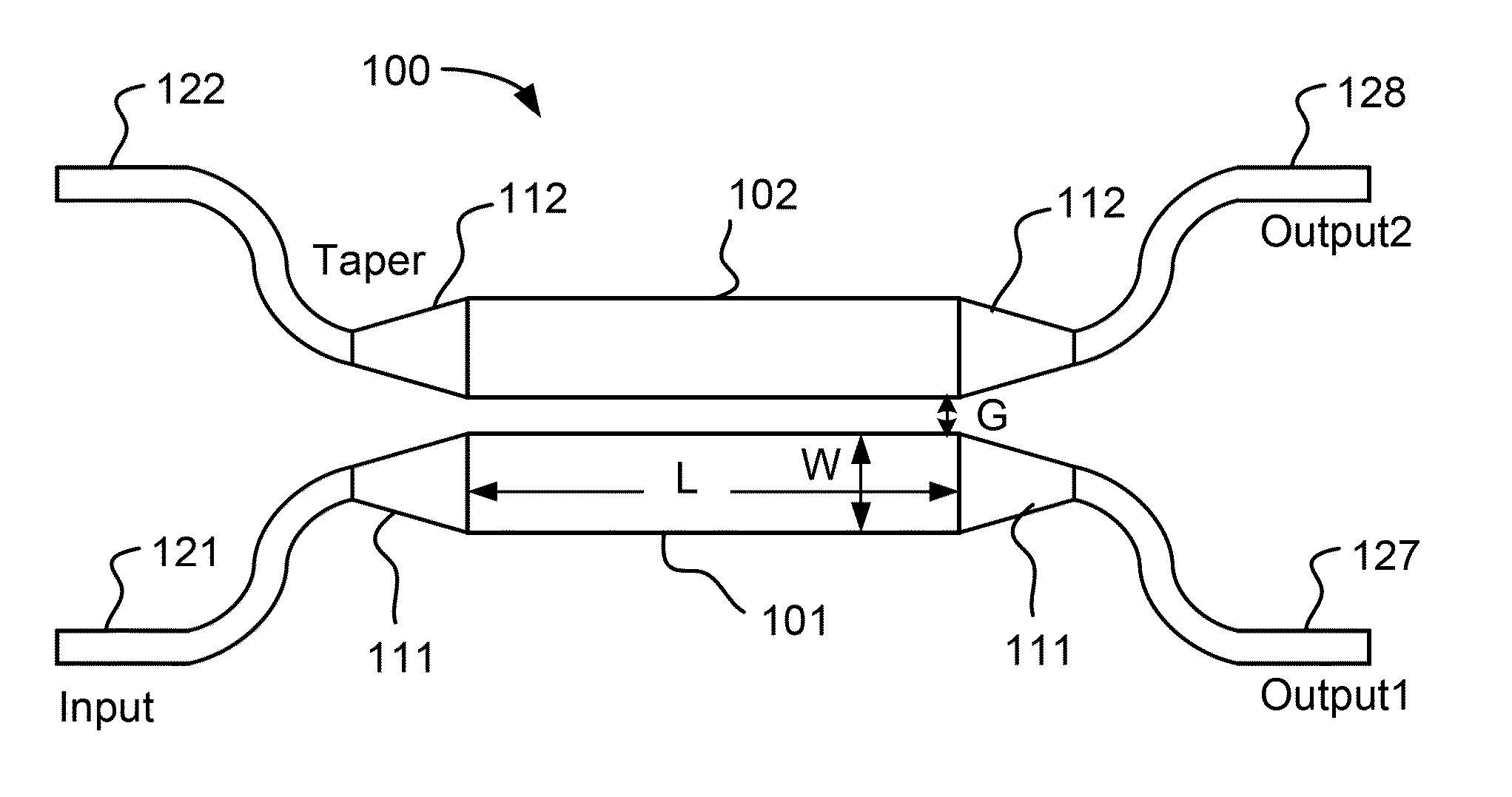
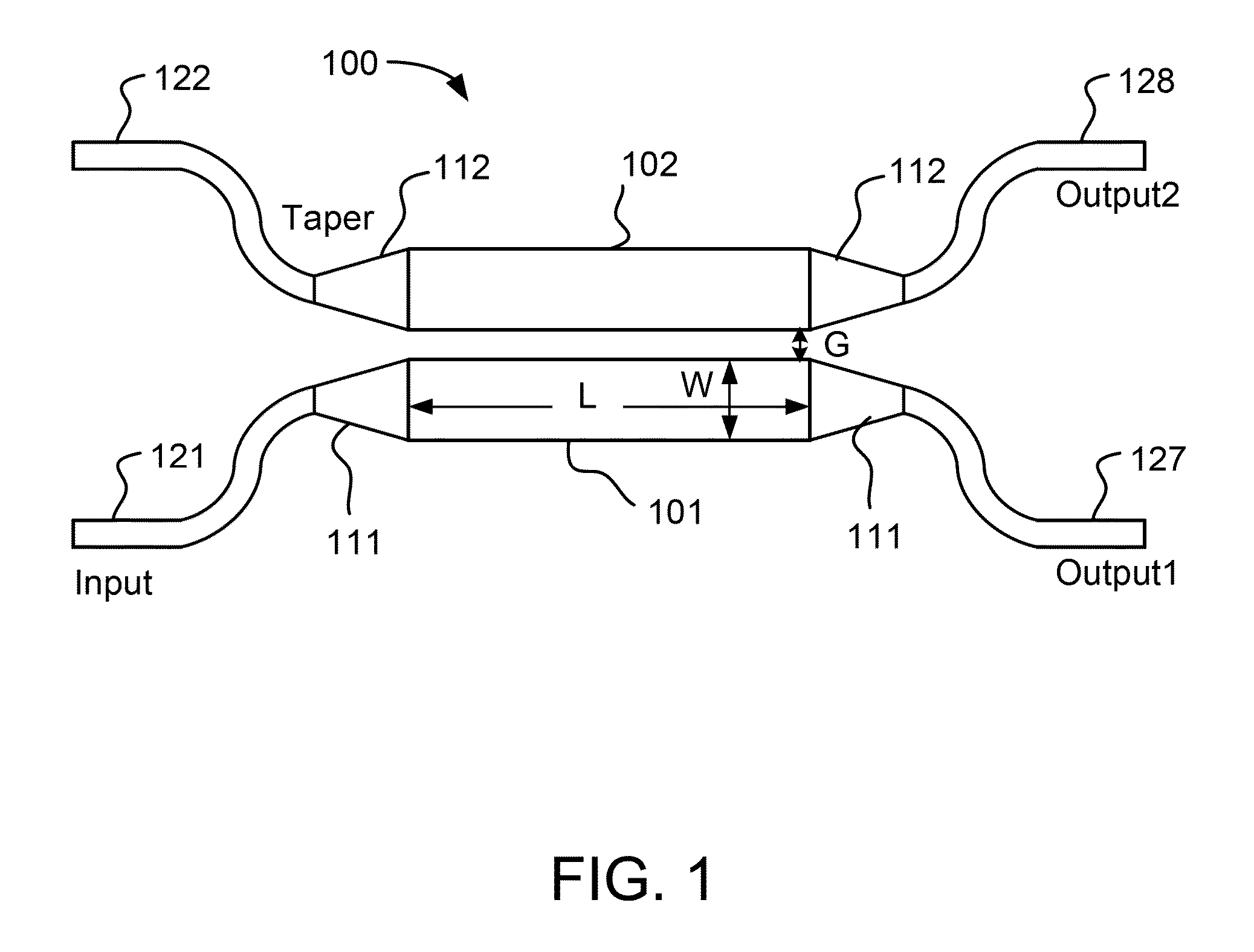
A device that comprises: a) a first optical waveguide; b) a second optical waveguide; c) an optical coupling region including the first and second optical waveguides, the optical coupling region characterized as having at least one coupling length and comprising a first bias section, a modulation section, and a second bias section arranged such that light propagates serially through the first bias section, the modulation section, and the second bias section; d) a first bias electrode for biasing the first bias section; e) a modulating electrode for applying a modulating voltage to the modulation section, the modulating electrode being positioned to control the refractive index of the first optical waveguide; and f) a second bias electrode for biasing the second bias section.
Owner:LUMERA CORP
Broadband silicon nitride polarization beam splitter
ActiveUS9366818B1High extinction ratioLow insertion lossCoupling light guidesCouplingPolarization beam splitter
A compact polarization beam splitter is formed by cascading two stages of directional couplers each containing two waveguides laid in parallel with a coupling gap. Each waveguide is made by silicon nitride material having a minimum length configured to be comparable with a coupling length for a TE polarization mode being set as twice of a coupling length for a TM polarization mode. A first-stage direction coupler is optimized by making the coupling gap smaller / greater than a nominal value to maximize TE / TM extinction ratio at least for a shorter / longer wavelength window of a designated wavelength band and each of two second-stage directional couplers is optimized by making the coupling gap greater / smaller than the nominal value to maximize TE / TM extinction ratio at least for a complementary longer / shorter wavelength window of the same designated wavelength band.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Double core photon crystal optical fibre
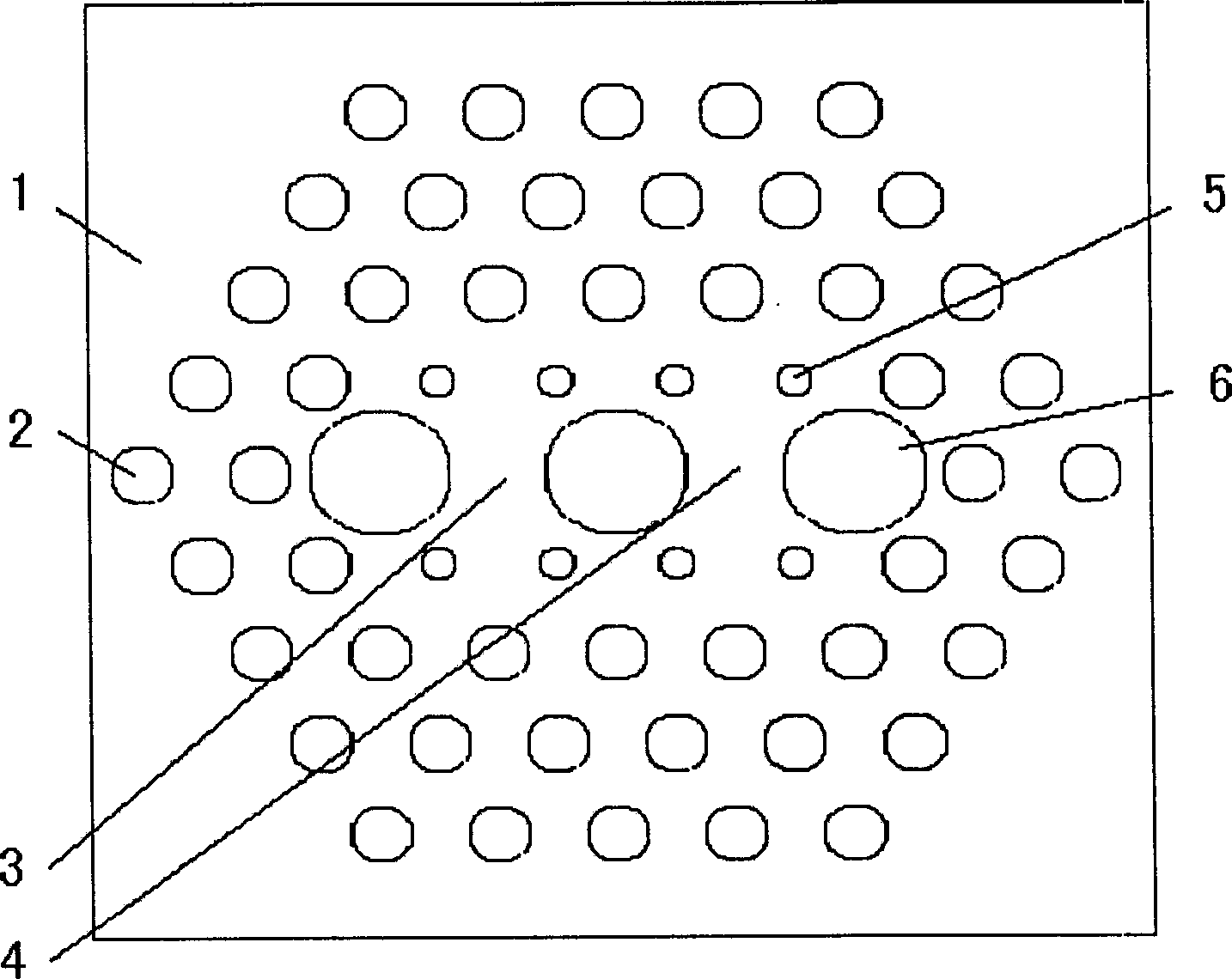
InactiveCN1425930ARealize the polarization splitting functionShorten the lengthFibre transmissionOptical light guidesFiberShortest distance
The present invention belongs to the field of fiber communication and optical signal processing, and is especially the design of double core photon crystal optical fiber as one photon device with polarizing split function. The double core photon crystal optical fiber includes one coating layer of low refractive index area formed by pore structure in regular lattice nodes and two high refractive index core areas formed by pore deletion in regular lattice nodes. The present invention features different pore size near the two core areas in two orthogonal polarization directions, unsymmetrical pore deletion, the deflection of the pore center near the core areas to the lattice nodes, or filling of polar material in the pores near the core area. Each of the core areas can produce high double refraction, so that two polarized light beams have great length difference and can be polarizing split in short distance.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Photonic crystal coupling defect waveguide
A photonic crystal directional coupler composed of at least two linear defect waveguides introduced into a photonic crystal. The medium constant and the lattice constant of the photonic crystal at the photonic crystal directional coupling part, the sizes and shapes of the elements constituting the periodical structure of the photonic crystal are varied. Thereby the difference in propagation constant between the even and odd modes of the photonic crystal directional coupling part is increased, thus shortening the coupling length of the photonic crystal directional coupler.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Photonic bandgap fiber
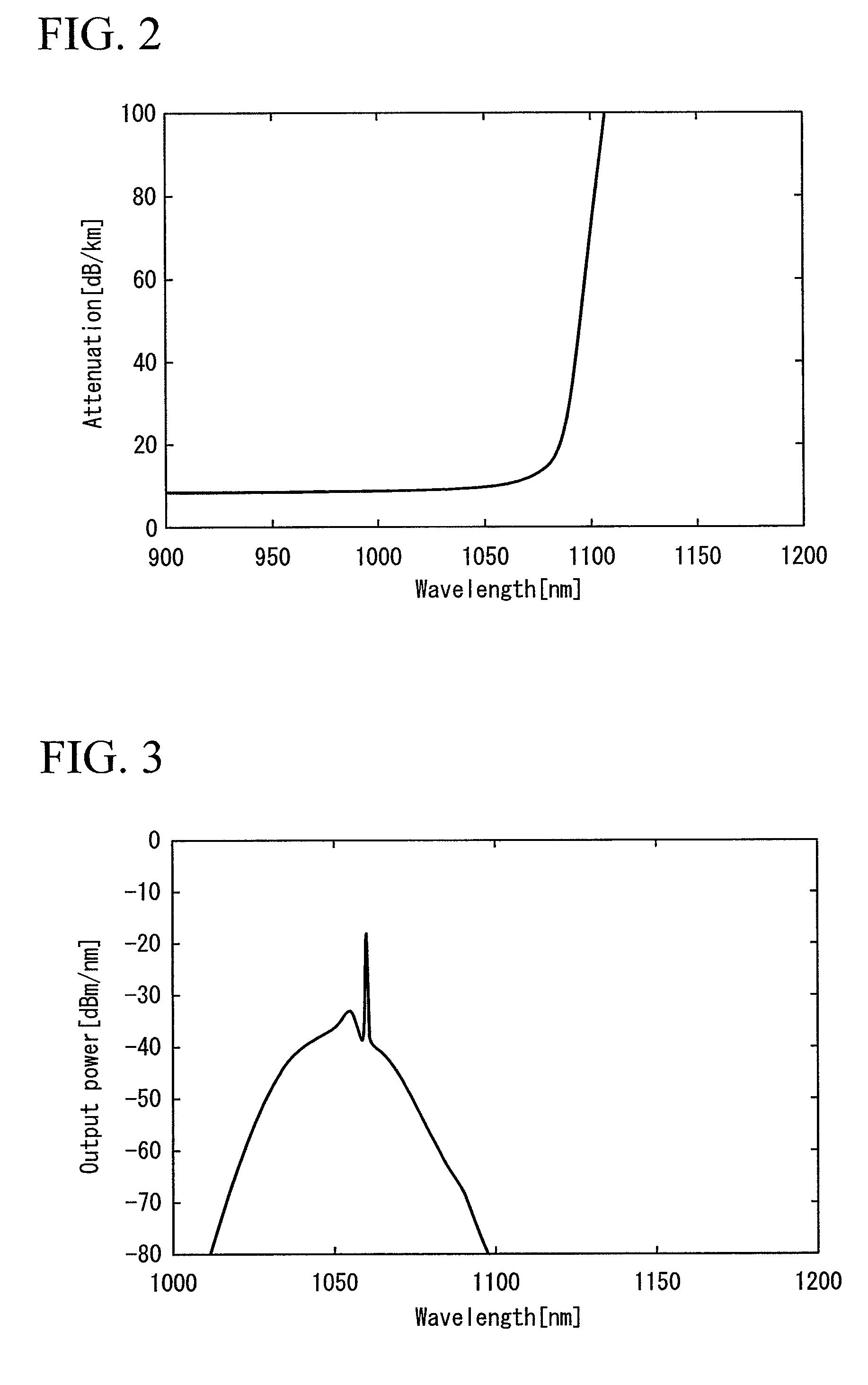
ActiveUS8035891B2Suppressing propagation of lightAccelerate emissionsLaser detailsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingPhotonic bandgapRefractive index
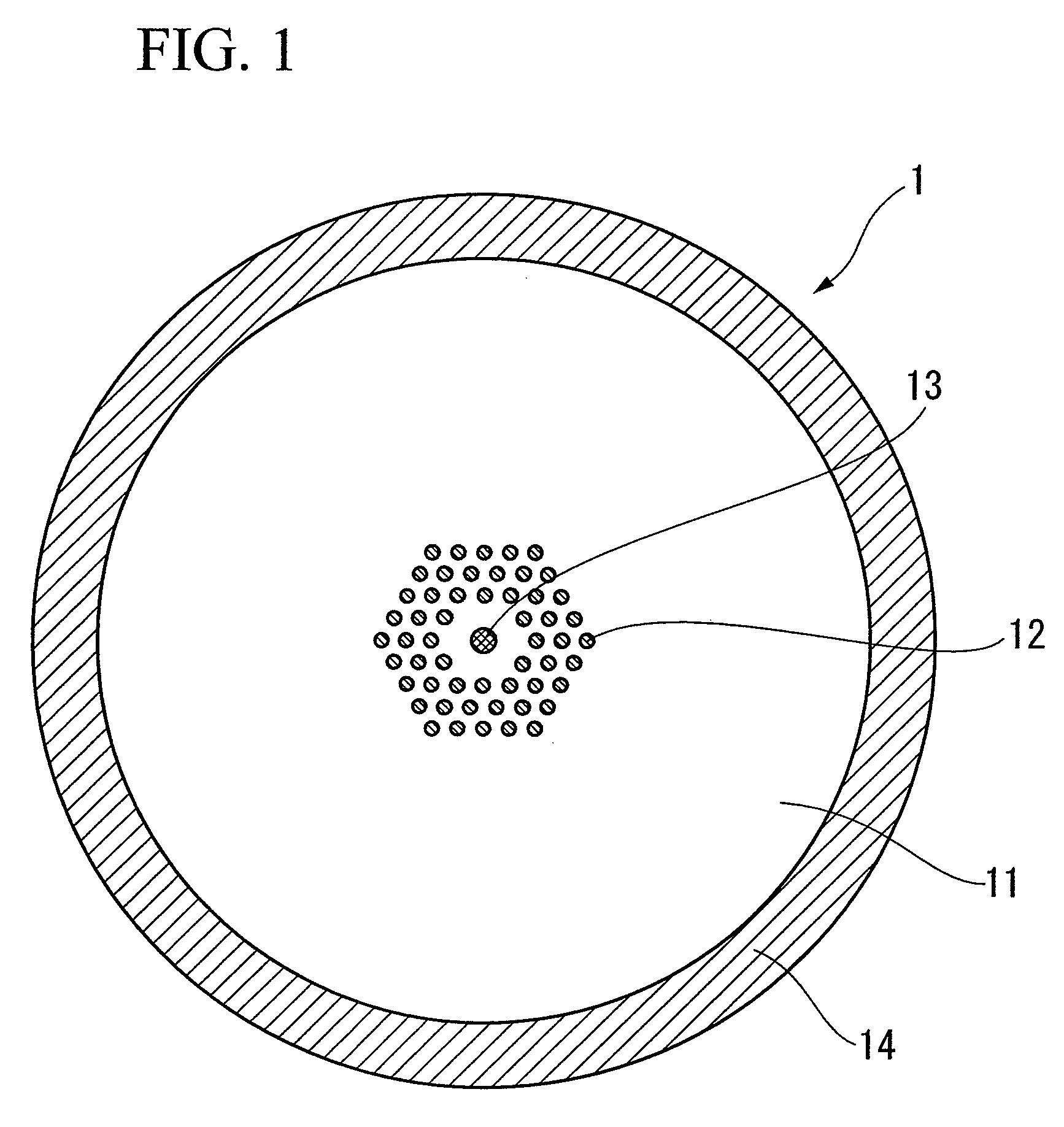
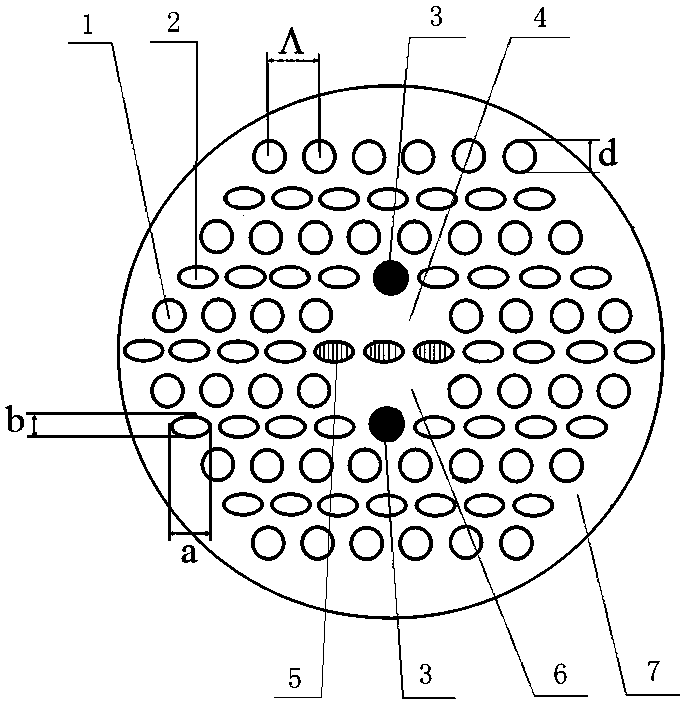
A photonic bandgap fiber includes a core and a cladding that surrounds the core. In this photonic bandgap fiber, high refractive index portions which have a refractive index higher than that of a medium of the cladding are provided in the cladding so as to form a triangular lattice structure with a lattice constant Λ, and the refractive index of the core is higher than the refractive index of the medium of the cladding and lower than the refractive index of the high refractive index portion. The coupling length between the core and the high refractive index portion that is closest to the core is longer than the coupling length between adjacent high refractive index portions, or a periodic structure formed by the high refractive index portions is not provided around the entirely of the area along the circumference of the core.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Optical waveguide structure of photoelectric detector for vertical coupling
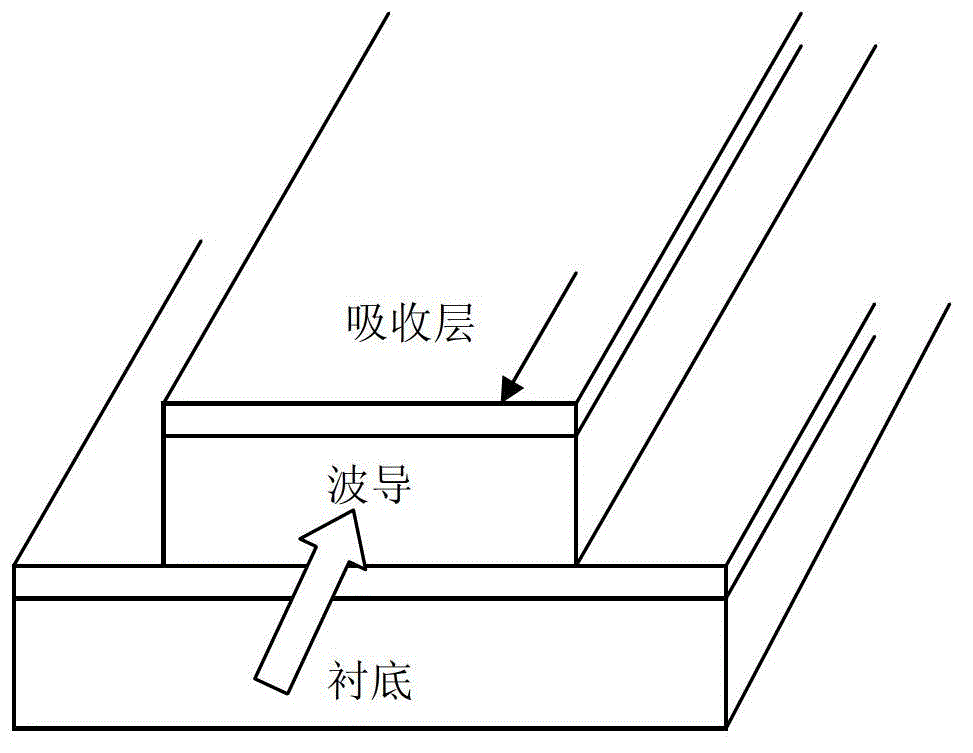
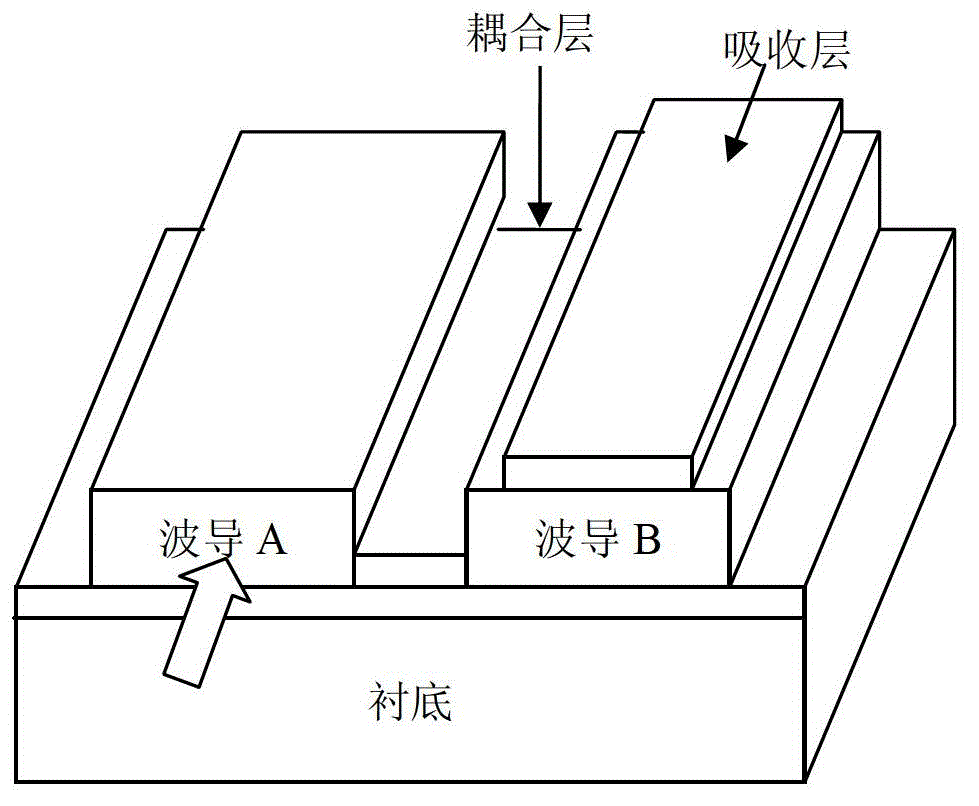
InactiveCN102723383AEvenly distributedIncrease powerOptical light guidesSemiconductor devicesPhotovoltaic detectorsCoupling
The invention relates to an optical waveguide structure of a photoelectric detector for vertical coupling. The structure comprises an intrinsic layer, an absorption layer, an upper waveguide layer, a clearance layer, a lower waveguide layer, a cover layer and a substrate which are sequentially stacked from top to bottom, wherein the clearance layer is used as a low-refractive index coupling layer between the upper waveguide layer and the lower waveguide layer; and a vertical coupler (equivalent to a vertically-coupled photoelectric diode) composed of the upper waveguide layer and the lower waveguide layer is used for realizing that the light enters from the lower waveguide layer and is gradually coupled to the upper waveguide layer and transmitted in the upper waveguide layer and the lower waveguide layer while being absorbed by the absorption layer. The structure provided by the invention has the beneficial effect of overcoming the defects that the coupling length and the absorption length are changed when the air clearance in the horizontally-coupled photoelectric diode structure changes and the photoetching corrosion processing technology is difficult.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Liquid-filled double-core photonic crystal fiber
PendingCN108594360AShort coupling lengthShort physical lengthMulticore optical fibreOptical waveguide light guidePolarization beam splitterEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of optical fibers and discloses a liquid-filled double-core photonic crystal fiber. The liquid-filled double-core photonic crystal fiber comprises two fiber cores and a wrapping layer arranged on the outer periphery of the two fiber cores and is characterized in that a plurality air holes are arranged in the wrapping layer along the length direction ofthe wrapping layer at intervals, the projection of the air holes on the cross section of the wrapping layer are distributed in rows, the odd-number row of the air holes comprises a plurality of firstair holes with circular cross sections, and the even-number row of the air holes comprises a plurality of second air holes with elliptical cross sections; the first fiber core which is formed by the wrapping layer part between the two first air holes closest to the center of the wrapping layer is formed in the row of first air holes closest to the central axis of the cross section of the wrappinglayer, and the second fiber core which is formed by the wrapping layer part between the two first air holes closest to the center of the wrapping layer is formed in the other row of first air holes closest to the central axis of the cross section of the wrapping layer. The liquid-filled double-core photonic crystal fiber is short in coupling length, high in extinction ratio and quite suitable forbeing used to manufacture a polarization beam splitter and a coupler unrelated to polarization.
Owner:BAOJI UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
Front end input waveguide structure of direction coupling optical waveguide detector
InactiveCN104238010ASolve the problem of overheating and burningAvoid disadvantagesCoupling light guidesCouplingWaveguide
The invention belongs to the field of photoelectric technology and discloses a front end input waveguide structure of a directional coupling optical waveguide detector. The front end input waveguide structure of the directional coupling optical waveguide detector comprises a substrate layer, a covering layer, a lower waveguide layer, a gap layer, an upper waveguide layer and an absorption layer which are sequentially stacked from bottom to top. The front end face of the substrate layer, the front end face of the covering layer, the front end face of the lower waveguide layer, the front end face of the gap layer and the front end face of the upper waveguide layer are flush with one another, the absorption layer is located on the upper surface of the rear of the upper waveguide layer, the gap layer is a coupling layer, and the distance from the front end face of the absorption layer to the front end face of the upper waveguide layer is twice of the coupling length. The front end input waveguide structure overcomes the defects of a waveguide detector and a horizontal direction coupling waveguide detector, light current can be effectively increased, and the problem that the front end of a waveguide is overheated and burnt because of the pattern evolution problem is solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
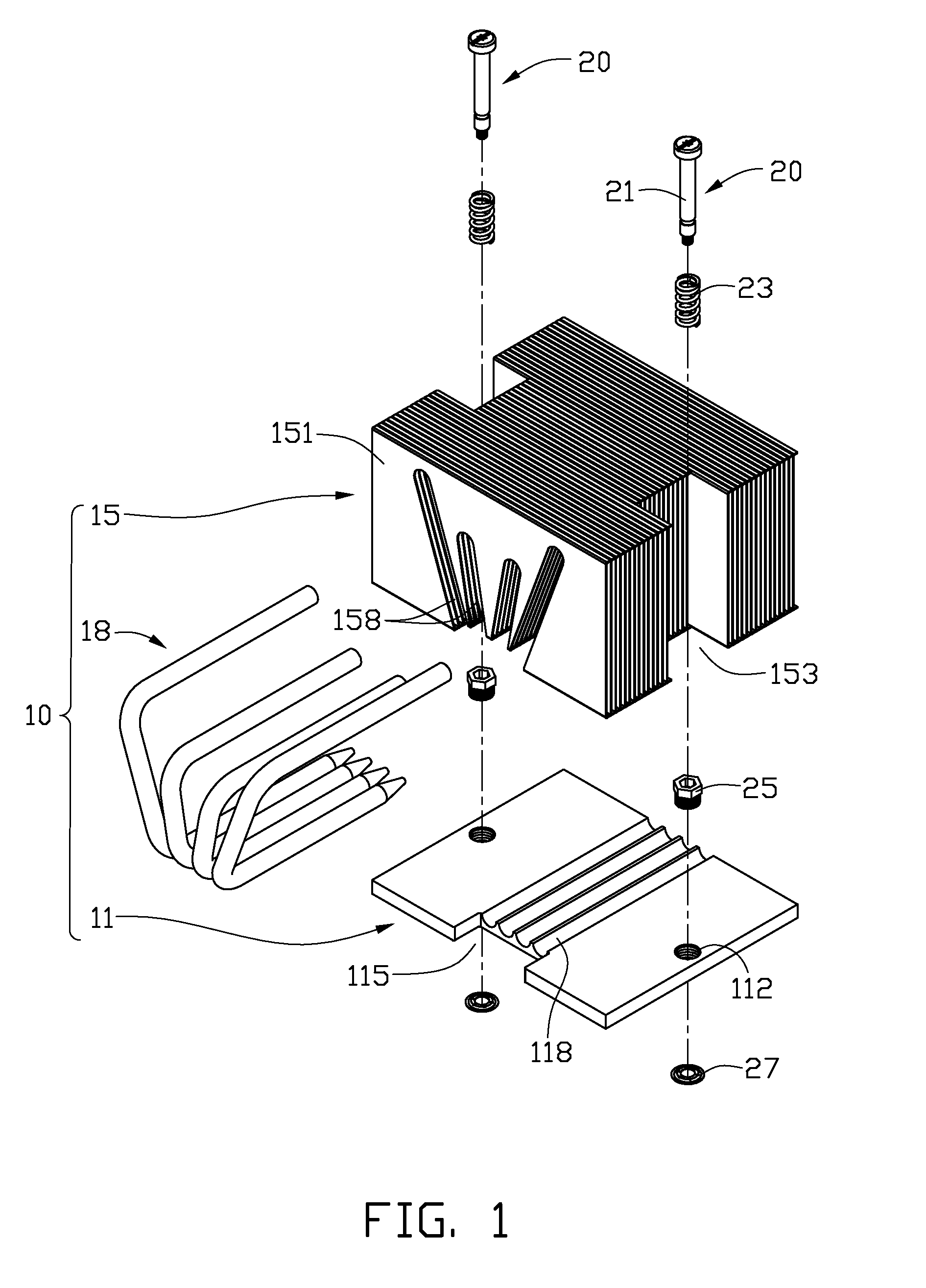
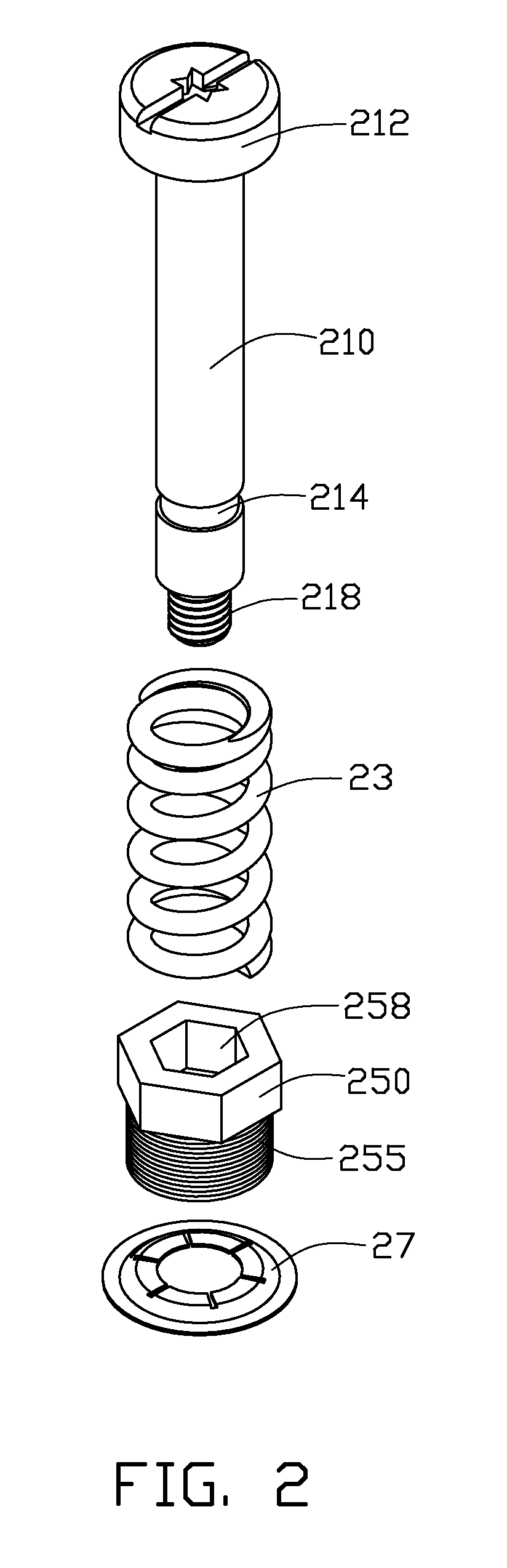
Heat dissipation device
InactiveUS20100000715A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringFastener
A heat dissipation device includes a base, a sleeve coupling with the base, and a fastener engaging with the base and the sleeve. The base defines a hole extending therethrough. The sleeve includes a first portion coupling with the hole of the base and a second portion extending from an end of the first portion. The second portion is located at a first side of the base. The fastener includes a body portion extending through the sleeve and the base, a head portion and a foot portion formed at two ends of the body portion, respectively. The head portion is located at the first side of the base. A spring member is compressed between the head portion and the second portion. A compressed length of the spring member is adjustable by adjusting a coupling length of the first portion with the hole of the base.
Owner:FU ZHUN PRECISION IND SHENZHEN +1
OLEDs COMPRISING LIGHT EXTRACTION SUBSTRUCTURES AND DISPLAY DEVICES INCORPORATING THE SAME
ActiveUS20140091292A1Generate efficientlyImprove light extractionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsDisplay device
An organic light emitting diode comprising a light extraction substructure and a diode superstructure is provided. The light extraction substructure comprises a light expulsion matrix distributed over discrete light extraction waveguide elements and a waveguide surface of the glass substrate. The light expulsion matrix is distributed at varying thicknesses to enhance the planarity of a diode superstructure-engaging side of the light extraction substructure and to provide light expulsion sites at the waveguide element termination points of the discrete light extraction waveguide elements. In operation, light originating in the organic light emitting semiconductor material of the diode superstructure is coupled to the discrete waveguide elements of the light extraction substructure as respective coupled modes characterized by an approximate coupling length defined as the propagation distance required for an optical mode to be coupled from the superstructure waveguide to one of the discrete waveguide elements of the light extraction substructure.
Owner:CORNING INC
Photonic bandgap fiber
ActiveUS20090207485A1Suppressing propagation of lightAccelerate emissionsLaser detailsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingPhotonic bandgapRefractive index
A photonic bandgap fiber includes a core and a cladding that surrounds the core. In this photonic bandgap fiber, high refractive index portions which have a refractive index higher than that of a medium of the cladding are provided in the cladding so as to form a triangular lattice structure with a lattice constant Λ, and the refractive index of the core is higher than the refractive index of the medium of the cladding and lower than the refractive index of the high refractive index portion. The coupling length between the core and the high refractive index portion that is closest to the core is longer than the coupling length between adjacent high refractive index portions, or a periodic structure formed by the high refractive index portions is not provided around the entirely of the area along the circumference of the core.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Polarization beam splitter
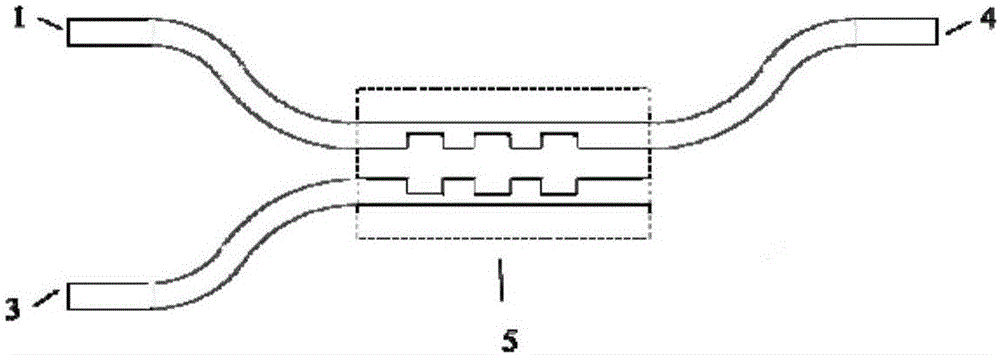
ActiveCN106094107APolarization beam splitting implementationReduce lossOptical light guidesGratingCoupling
The invention discloses a polarization beam splitter. The polarization beam splitter comprises a first input port 1 or a second input port 2, a coupling area 5, a first output port 3, and a second output port 4. The first input port 1 or the second input port 2 is connected with the input port of the coupling area 5, and the first output port 3 and the second output port 4 are connected with the output port of the coupling area 5. The coupling area 5 is formed by two adjacent optical waveguides, which are disposed in evanescent field ranges of waveguide modes of opposite sides. In the coupling area 5, grating structures of preset quantity are connected with the two waveguides, and are extended toward the outer sides of the two waveguides by preset lengths, and then a coupling length of a transverse electric wave TE is a half of a coupling length of a transverse magnetic wave TM. The polarization beam splitter provided by the invention is advantageous in that by adopting a function of gratings regulating and controlling a waveguide mode equivalent refractive index, an equivalent refractive index between the odd symmetric mode and the even symmetric mode of the TE is twice that of the TM, and the coupling length of the TE is a half of that of the TM, and therefore polarization beam splitting is realized.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Two periodically bending non-linear optical waveguide coupled all-optical switch
InactiveCN101216655ALower the thresholdAdd nonlinearityNon-linear opticsUltimate tensile strengthWaveguide
The invention provides a full optical switch which is made by coupling two cycle-bending nonlinear light wave guides. The full optical switch comprises two light wave guides arranged in parallel, which are bent by a synchronous cycle along the propagation direction of light and whose lengths are equal to one another and are odd multiples of the coupling length. The full optical switch bends the cycles of the two parallel light wave guides along the propagation direction of the light. Since the bending of the cycles of the wave guides is equivalent to the increase of nonlinearity of a coupler, a switch threshold value can be greatly reduced. The critical power of the switch of the bent light wave guide coupler mainly depends on the bending strength and the bending cycles of the wave guides. And the improved full optical switch has the advantages of remarkably improved contrast and higher sensitivity of the switch threshold value; in addition, the improved full optical switch overcomes the shortcomings of a full optical switch based on a traditional light wave guide coupler, such as progressive operation and incompletion.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polarizing coupler based on double-core photonic crystal fibers mixed with metal wire
InactiveCN103217743AImplement polarization filteringWorking bandwidthCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesTransmittanceCoupling length
The invention relates to a polarizing coupler based on double-core photonic crystal fibers mixed with a metal wire. The polarizing coupler based on the double-core photonic crystal fibers mixed with the metal wire is characterized by comprising background materials, cladding, a first fiber core, a second fiber core and the metal wire. The background materials are silica glass materials. Air holes arranged in a regular hexagon structural cycle mode are formed in the background materials to form the cladding. The first fiber core and the second fiber core are symmetrically located on two air hole defects in the center of the cladding. Metal materials are filled in one or two air holes to form the metal wire, wherein the one or two air holes are arbitrarily selected in the cladding. According to the polarizing coupler based on the double-core photonic crystal fibers mixed with the metal wire, the transmissivity of two cross-polarized components and coupling lengths of the two cross-polarized components are different, control over the transmissivity of output light and a polarization state can be achieved, and the functions of polarization separation and polarization filtering are achieved. The polarizing coupler based on the double-core photonic crystal fibers mixed with the metal wire has the advantages of being wide in operating bandwidth, stable in performance and capable of achieving the functions of polarization separation and polarization filtering.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Photon crystal optical fibre polarization-maintaining beam splitter
InactiveCN101122652ANot easy to influenceExcellent polarization maintaining performanceCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideBeam splitterPhotonic crystal
The invention discloses a photonic crystal fiber polarization beam splitter provided with a two-dimensional periodical structure of photonic crystal fiber. The periodical structure is constituted by a background medium and periodically distributed dielectric rods arranged in the medium; the cross section is a parallelepiped; a periodically arranged defect area without single dielectric rod in the background medium is a waveguide core. The advantages of the photonic crystal fiber polarization beam splitter are: easy to achieve stable isophotal power or a certain percentage of splitting ratio, small structural size, not vulnerable to the impact of environmental conditions, small light loss, good polarization of polarized coupling and easy to design. The invention can select different coupling length through structural adjustment to achieve splitting ratio regulation and splitting function.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
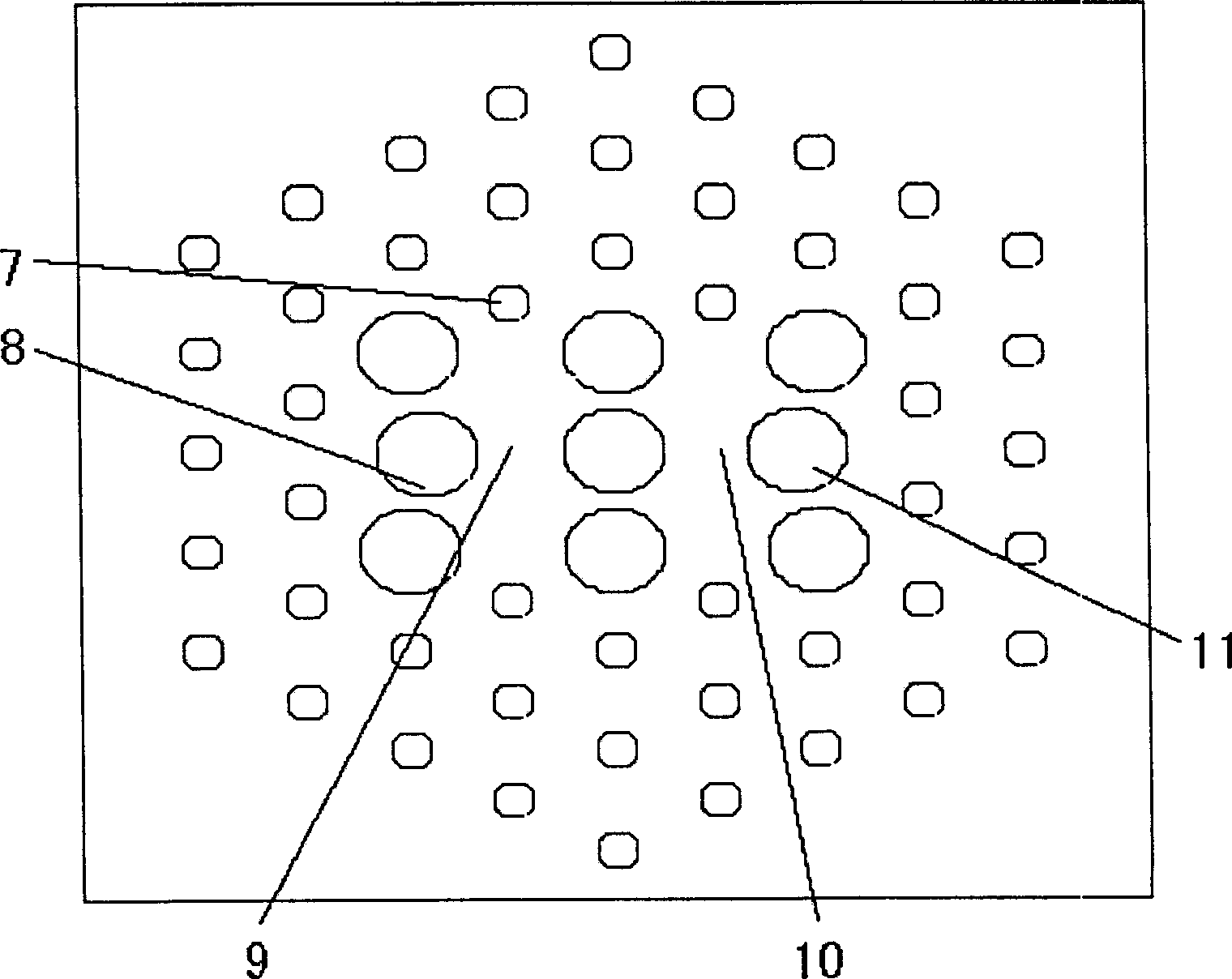
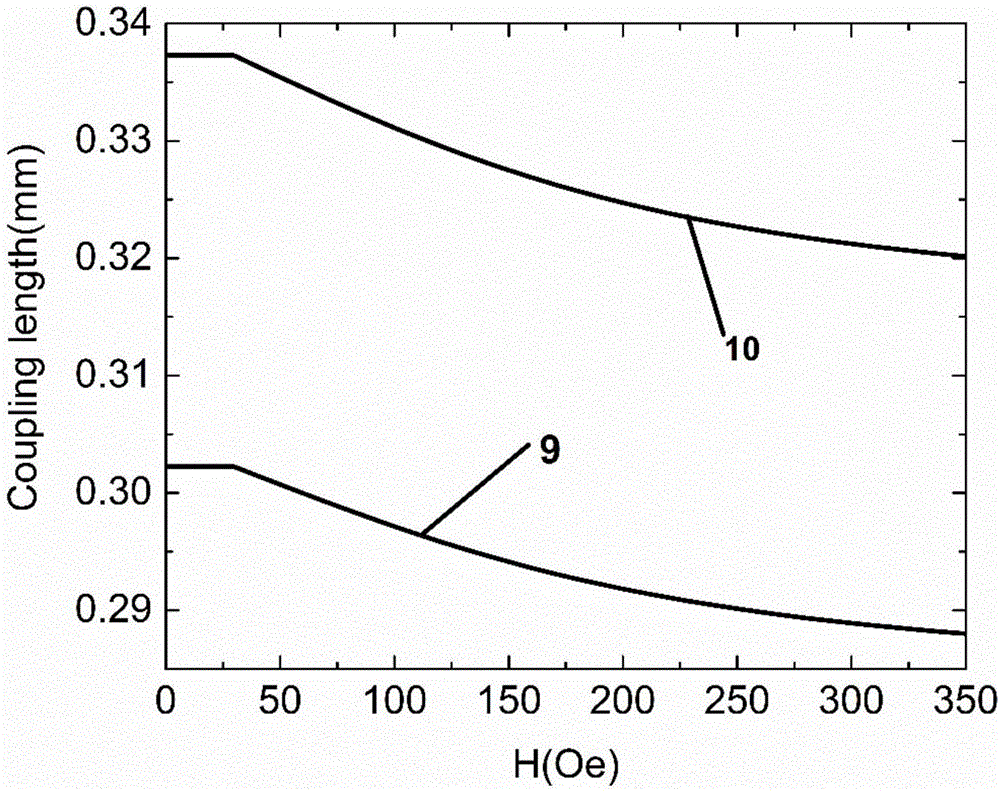
Tunable polarization beam splitter of magnetic fluid filled double-core photonic crystal fiber
InactiveCN106125197ASimple structureFlexible designOptical light guidesRefractive indexQuartz substrate
The invention discloses a tunable polarization beam splitter of a magnetic fluid filled double-core photonic crystal fiber, and belongs to the fields of special fibers, fiber communication and signal processing. The polarization beam splitter is based on a double-core photonic crystal fiber structure. The double-core photonic crystal fiber comprises a pure quartz substrate (1), two identical cores (2) and air holes arranged periodically, and the air holes (3) on the upper and lower sides of the cores, the air holes (3) on the left and right sides of the cores and the air holes (5) away from the cores are different in radius. The air holes (6), close to the cores, of the double-core photonic crystal fiber are filled with magnetic fluid. The polarization beam splitter adopts single-channel output. The refractive index of the magnetic fluid is changed along with the intensity of an external magnetic field, and when the outside does not have a magnetic field, the polarized light in a single direction is output by the output end of the double-core photonic crystal fiber, while the other polarized light is not output. When a certain magnetic field is applied from the outside, the coupling length of the two beams of polarized light is changed with the change of the refractive index of the magnetic fluid, so that the energy of the polarized light at the output end is reduced, but the energy of the other polarized light is increased. In certain magnetic field intensity, the polarization mode at the output end of the double-core photonic crystal fiber is converted, so that the polarization mode is tunable.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
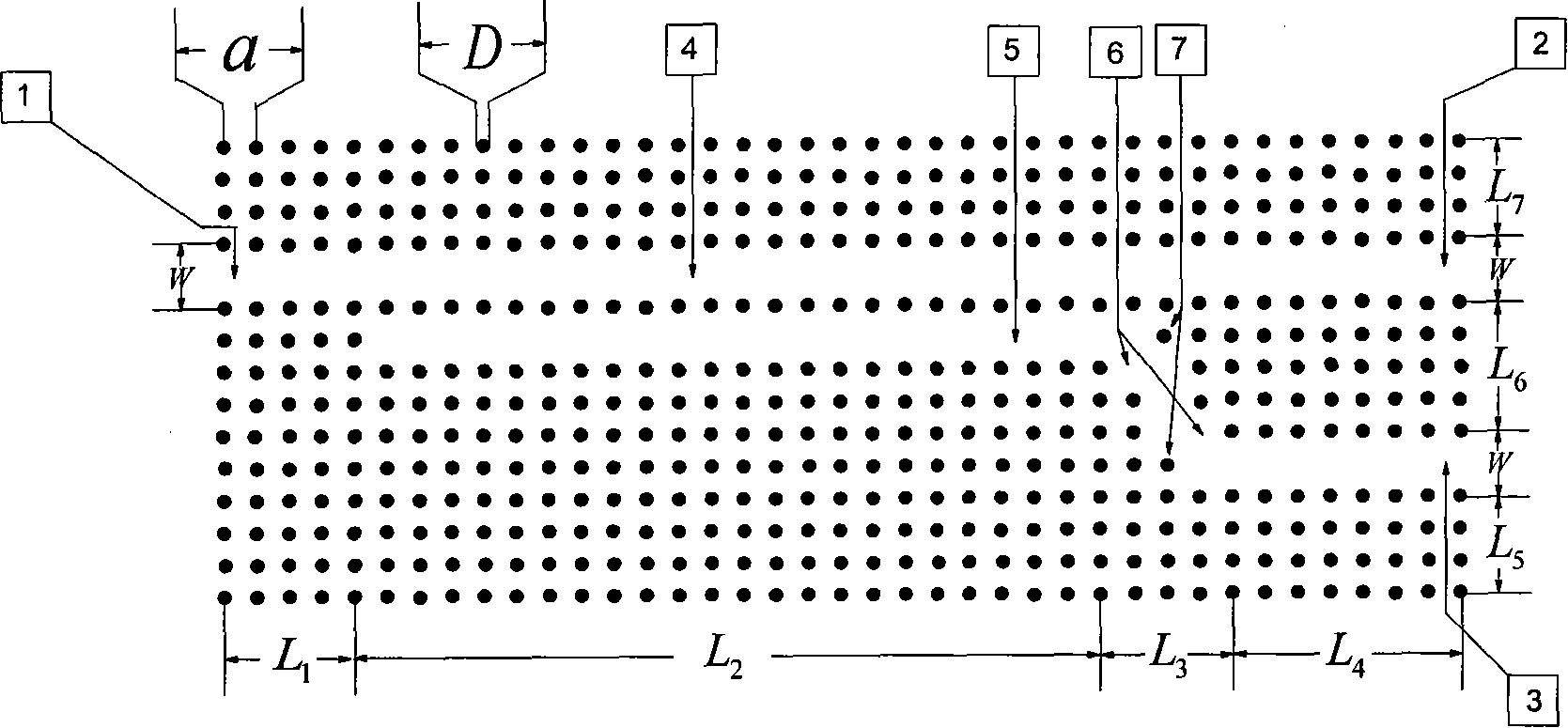
Tire bead reinforcement comprising discontinuous reinforcing elements
InactiveUS20050087281A1Control stressWithout separate inflatable insertsSpecial tyresTire beadEngineering
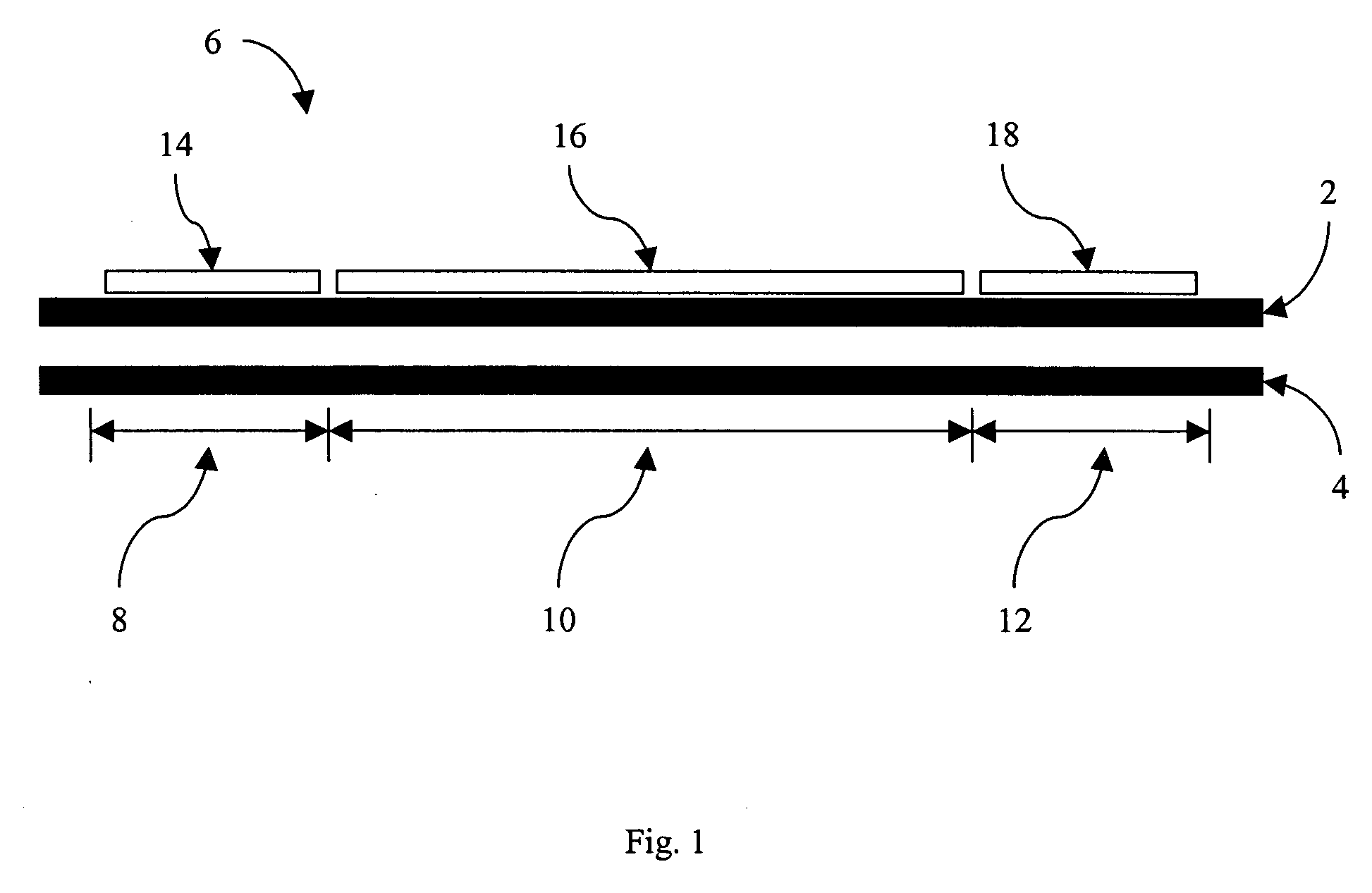
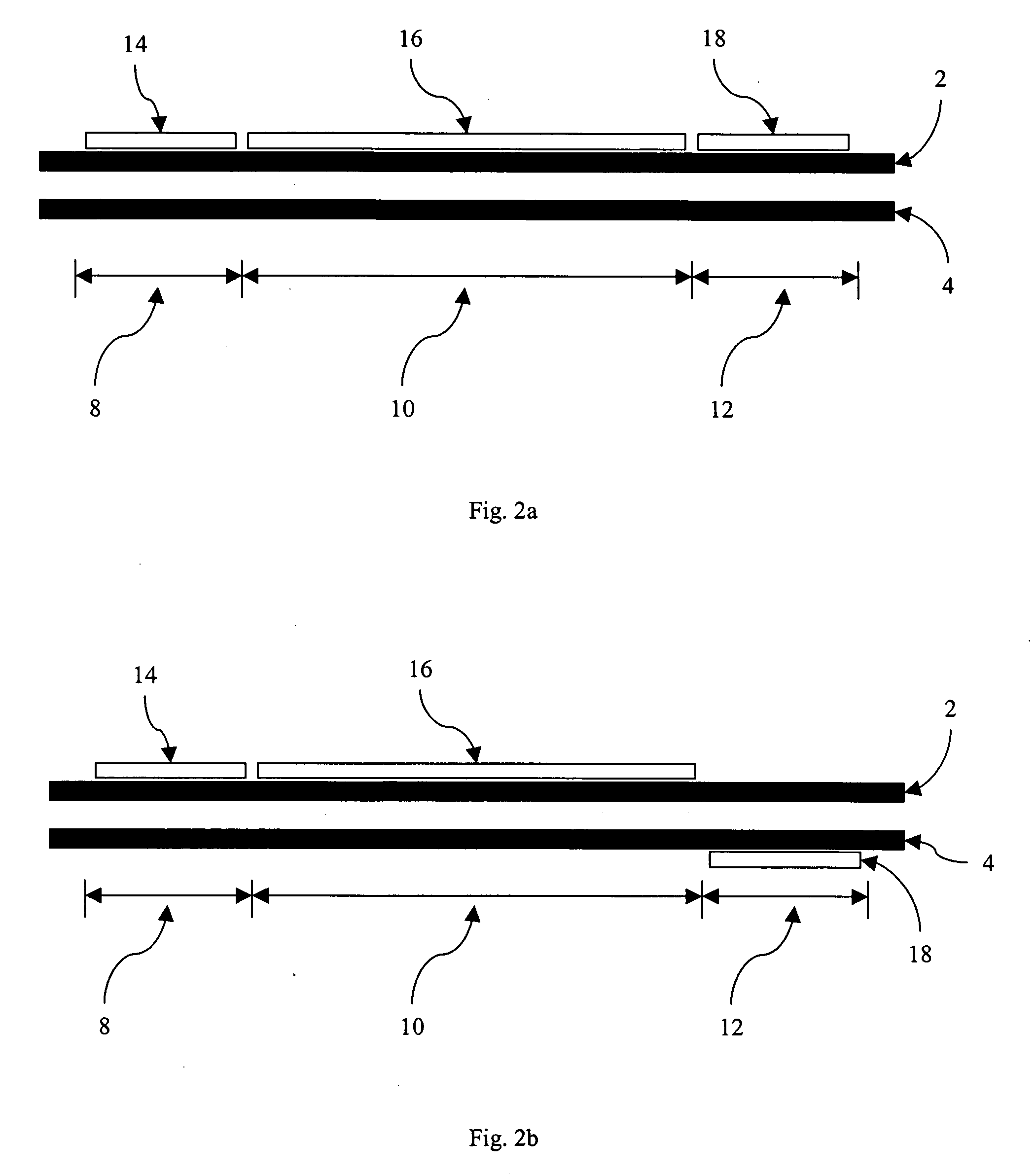
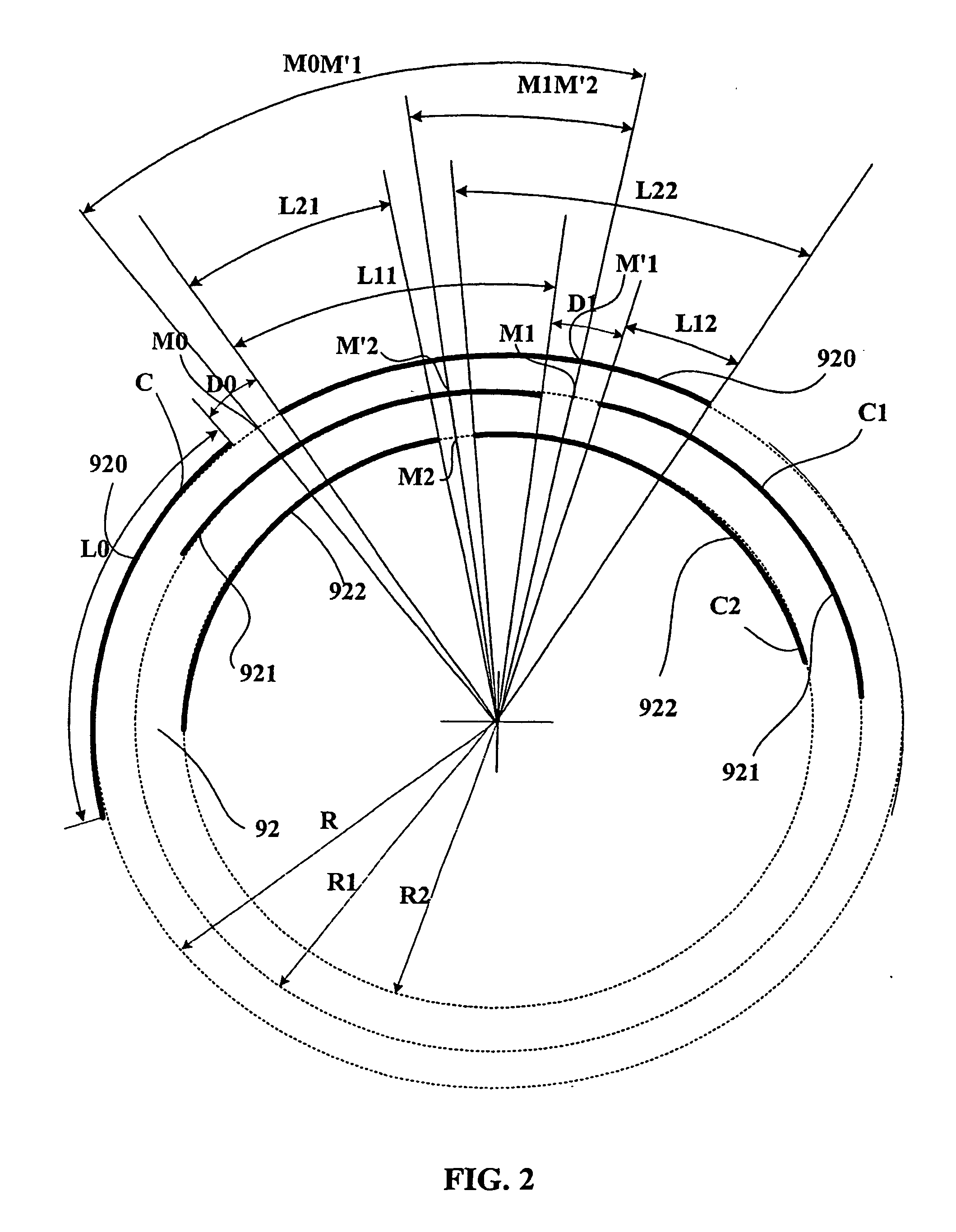
A tire for vehicles carrying heavy loads, comprising in at least one bead an additional reinforcement composed of a plurality of discontinuous reinforcing elements, these discontinuous reinforcing elements being orientated essentially circumferentially to form a plurality of circles C, C1, C2 concentric on the rotation axis of the tire mounted on its rim, each circle being defined by a mean radius (R, R1, R2) measured relative to the said rotation axis, and wherein [0001]each discontinuous reinforcing element of length L0 located on a circle C of radius R is mechanically coupled over coupling lengths L11 and L12 with two discontinuous reinforcing elements located on a circle C1 of radius R1, this circle being immediately adjacent to the circle C, the coupling length L11 being between 55 and 75% of L0 and the coupling length L12 being between 10 and 30% of L0; [0002]each discontinuous reinforcing element on the same circle C of radius R is mechanically coupled over coupling lengths L21 and L22 with two discontinuous reinforcing elements located on a circle C2 of radius R2 immediately adjacent to the circle C1, the coupling length L21 being between 20 and 40% of L0 and the coupling length L22 being between 45 and 65% of L0.
Owner:MICHELIN RECH & TECH SA
Linear optical modulators and method of linear optical modulation
InactiveUS7161726B2Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideRefractive indexOptical coupling
A device that comprises: a) a first optical waveguide; b) a second optical waveguide; c) an optical coupling region including the first and second optical waveguides, the optical coupling region characterized as having at least one coupling length and comprising a first bias section, a modulation section, and a second bias section arranged such that light propagates serially through the first bias section, the modulation section, and the second bias section; d) a first bias electrode for biasing the first bias section; e) a modulating electrode for applying a modulating voltage to the modulation section, the modulating electrode being positioned to control the refractive index of the first optical waveguide; and f) a second bias electrode for biasing the second bias section.
Owner:LUMERA CORP
Slow light controlled photon crystal coupled switch
InactiveCN101078851AReduce volumeHighly integratedCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideDielectricSignal light
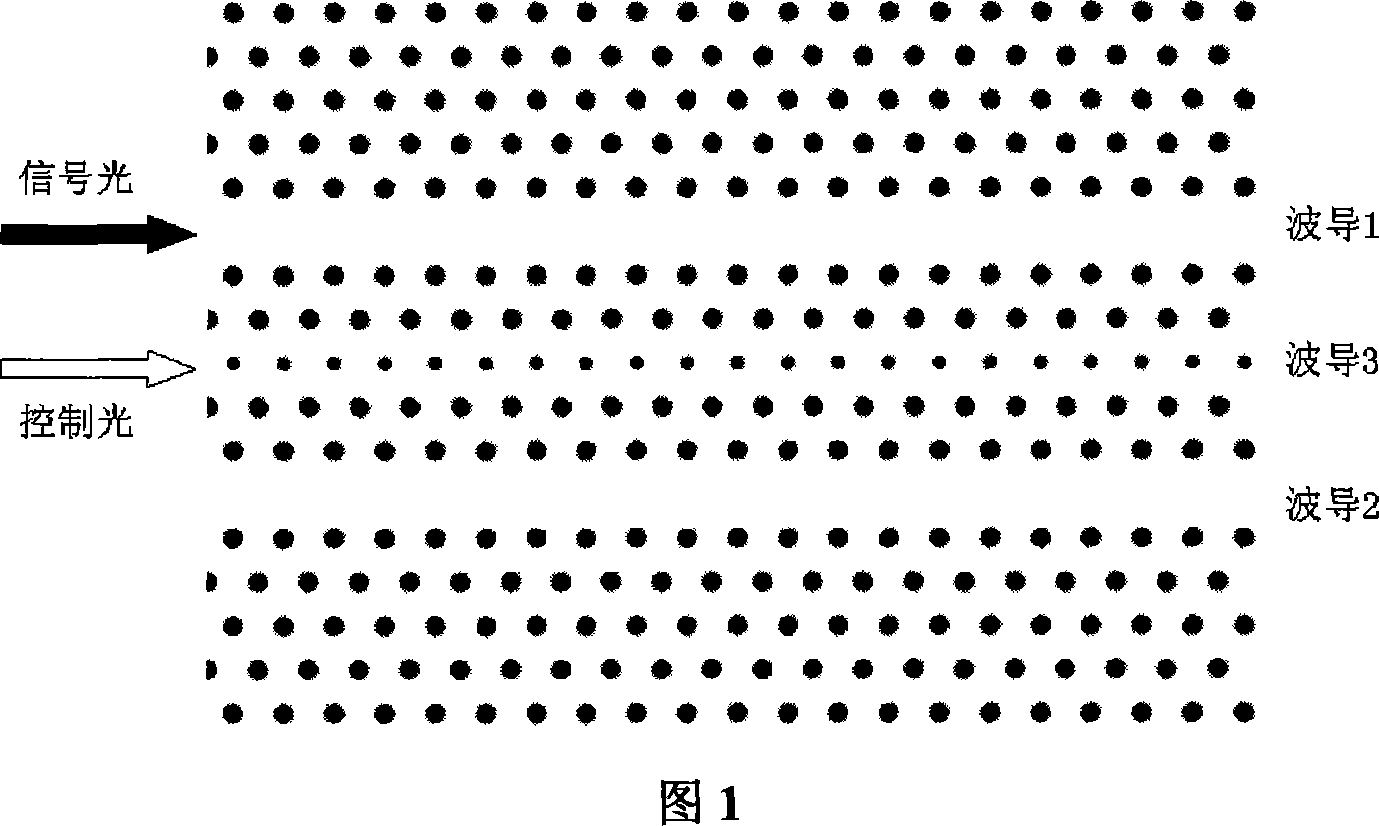
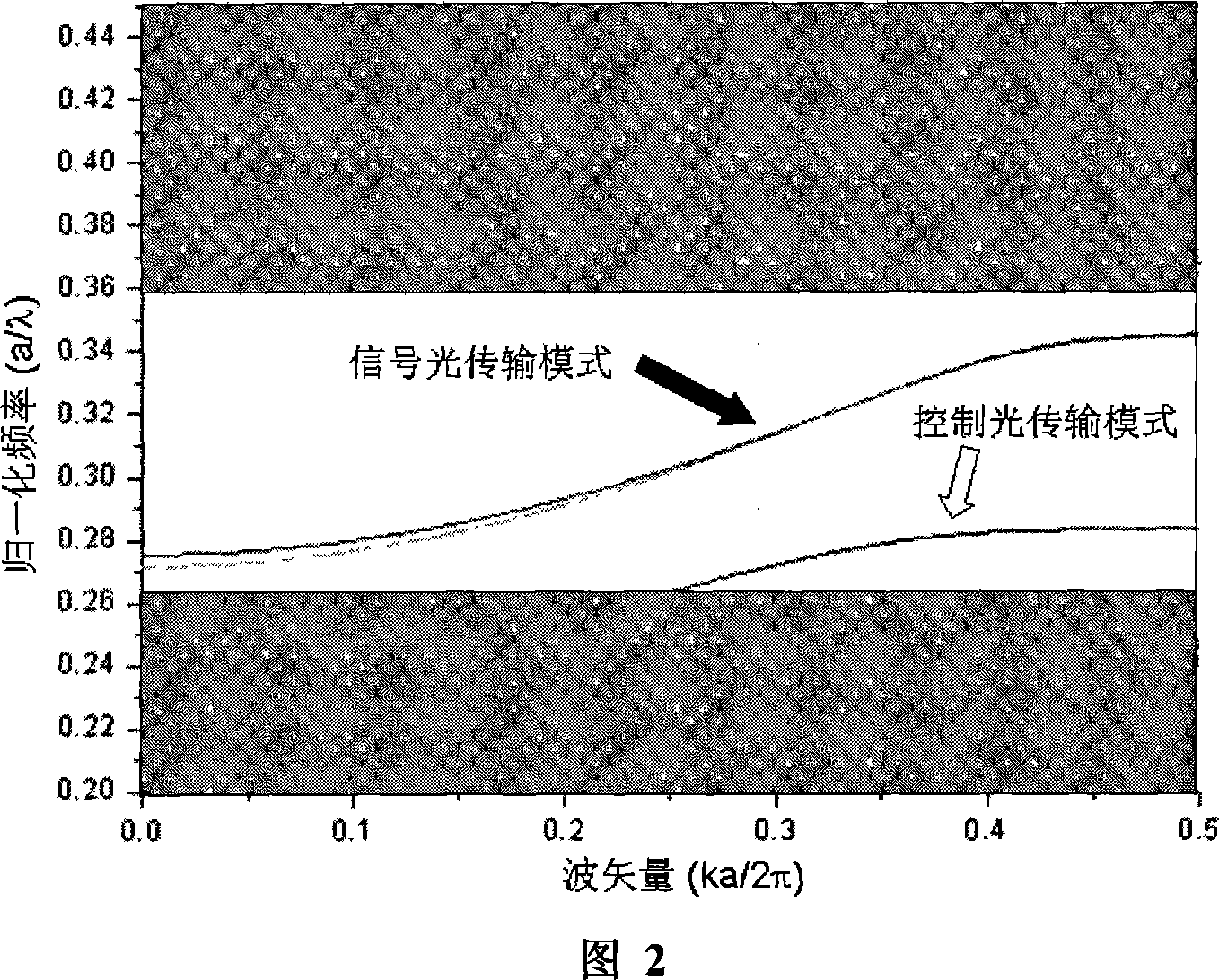
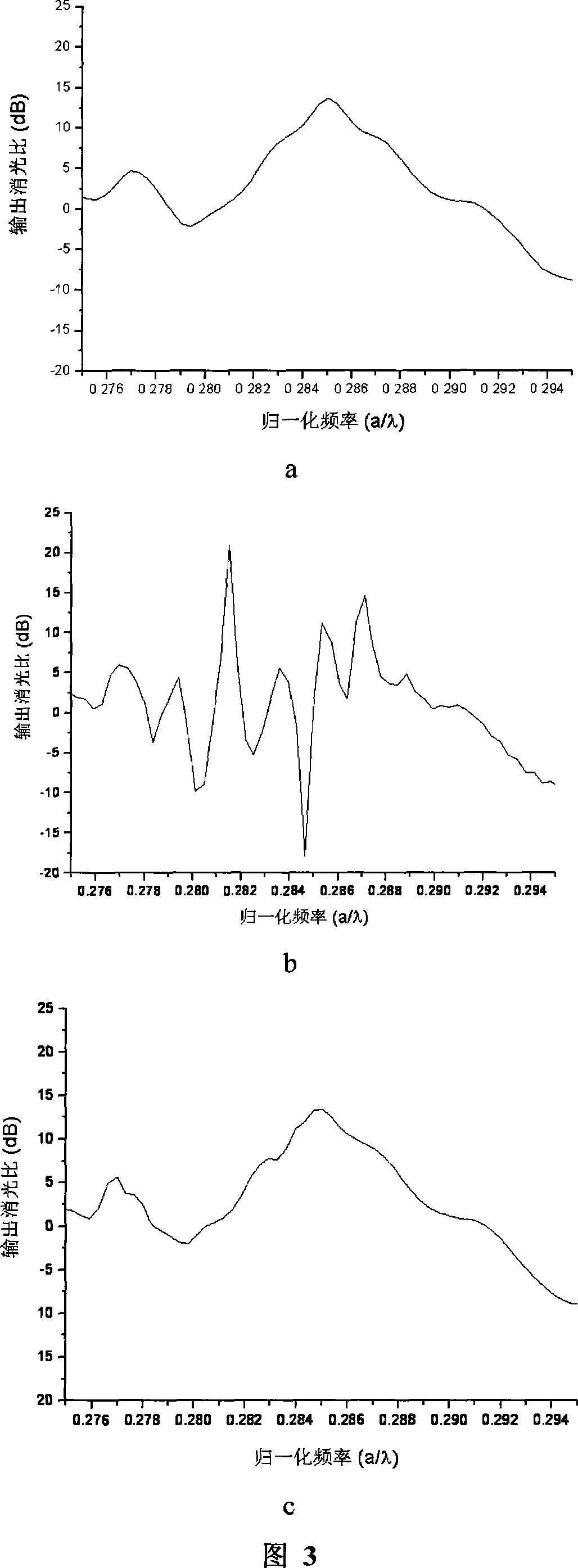
The invention discloses a photon transistor coupling switch controlled by slow light, which is characterized by the following: adding dielectric bar with different dielectric constants as the background material into the background material; arranging the dielectric bar at square lattice or hexagonal lattice; removing two rows of dielectric rod to realize defective waveguide of signal transmitting wire with two non-linear Kerr effect; separating two defective waveguides of signal transmitting wire by odd rows of dielectric bar; changing the radius of one row of dielectric bar in the center of the odd rows of dielectric bar to control the defective waveguide; selecting optical signal with minimum group speed to pass the defective waveguide as slow light control light; inputting the slow light control light through controlling the defective waveguide; changing the strike of signal light of certain defective waveguide of signal transmitting wire into another defective waveguide of signal transmitting wire to output; using shorter coupling length to change the coupling switch condition dynamically; improving the integrated degree of integrated light path and reducing the operational power.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com