Big data-based flexible employment business knowledge inference engine construction method
A technology of knowledge reasoning and big data, applied in the field of knowledge reasoning engine construction for flexible employment based on big data, can solve problems such as the inability to objectively and scientifically verify the authenticity of business, and achieve the effect of improving authenticity and accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
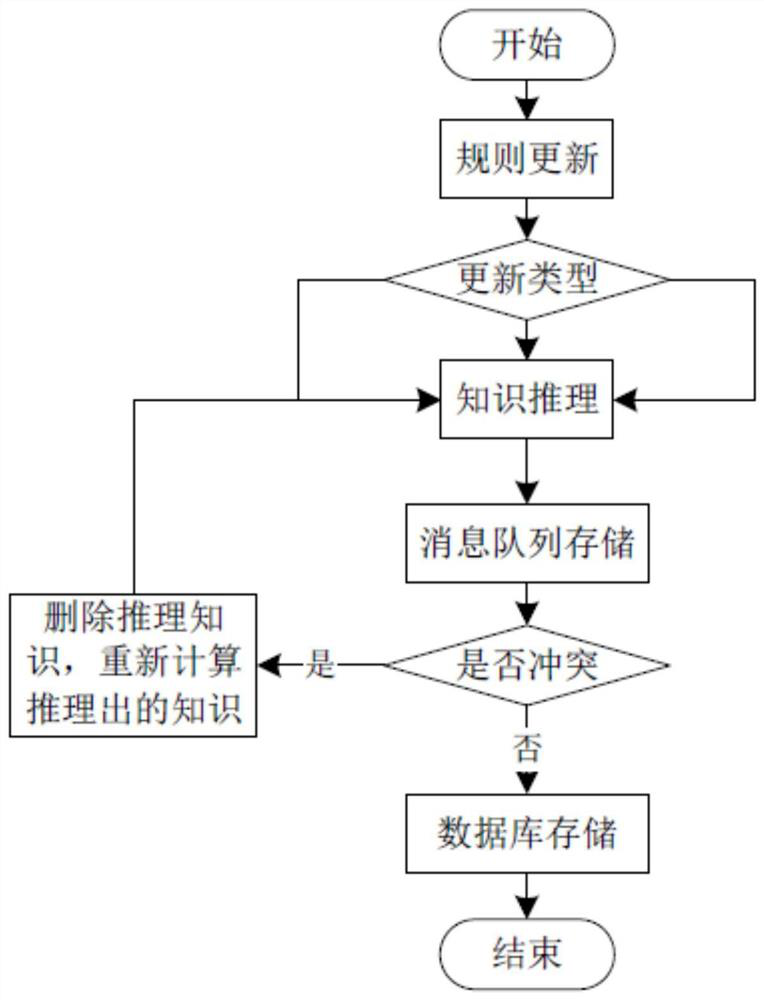
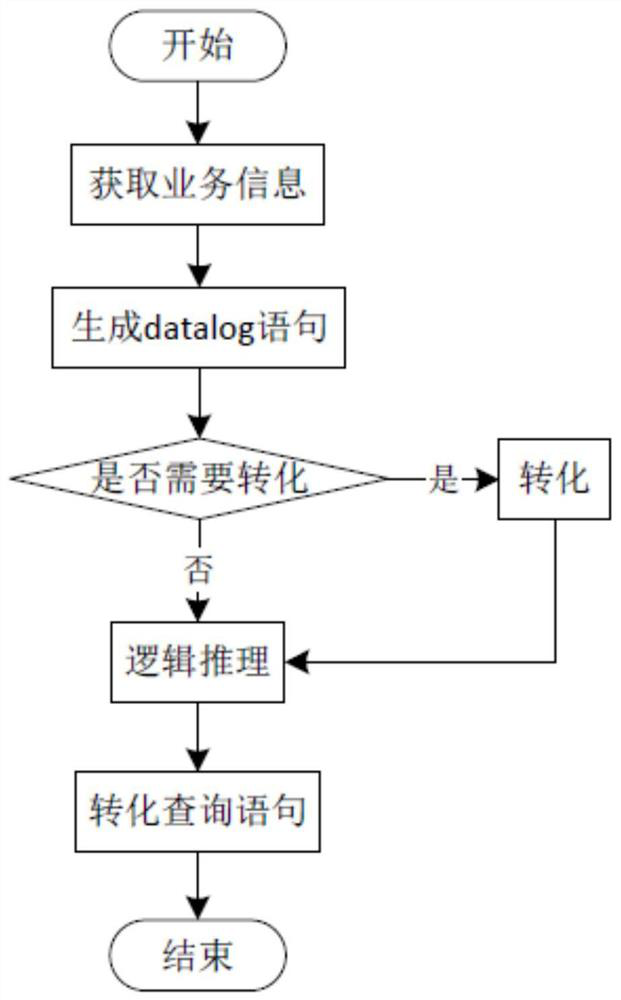
[0029] The construction method of flexible employment business knowledge reasoning engine based on big data, such as figure 1 and figure 2 shown, including the following steps:
[0030] Step 1. Receive employment data from multiple employment platforms. The employment data can be flexible employment data, such as the subject, willingness, contract, business, funds, and bills of the courier rider, and identify named entities in the employment data. Extract the association relationship in the employment data after named entity recognition, extract the attribute information of the named entity in the employment data, specifically, the employment data includes structured data, semi-structured data and unstructured data, and directly identify and name from the structured data Entities, through semantic recognition or dependency syntax analysis, identify named entities, extract association relationships, and extract attribute information from semi-structured and unstructured data....
Embodiment 2
[0070] The difference with Embodiment 1 is that in the step 1, after the named entity is identified, it is first judged whether the target type of the named entity is a name, and the target type of the named entity is judged through existing semantic analysis. When the target type is Name, count the named entities in the same employment data to get the count value, compare the count value with the threshold value, when the count value is equal to the threshold value, determine that the named entity is a place name or name through semantic analysis, when the count value is greater than the threshold value, First judge the location information of the named entity. The location information is judged by the structure of the sentence, such as subject, predicate, object, attributive and adverbial, etc., and then identify the semantics of the adjacent elements of the named entity and judge that the named entity is a place name based on the semantics of the adjacent elements. or name. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com