Method and apparatus for allocating bandwidth at a network element
a network element and bandwidth technology, applied in the field of communication networks, can solve the problems of requiring the use of unable to share the excess bandwidth fairly, and each phb may therefore require a considerable amount of physical memory, so as to achieve the effect of fair treatmen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The following detailed description sets forth numerous specific details to provide a thorough understanding of the invention. However, those skilled in the art will appreciate that the invention may be practiced without these specific details. In other instances, well-known methods, procedures, components, protocols, algorithms, and circuits have not been described in detail so as not to obscure the invention.
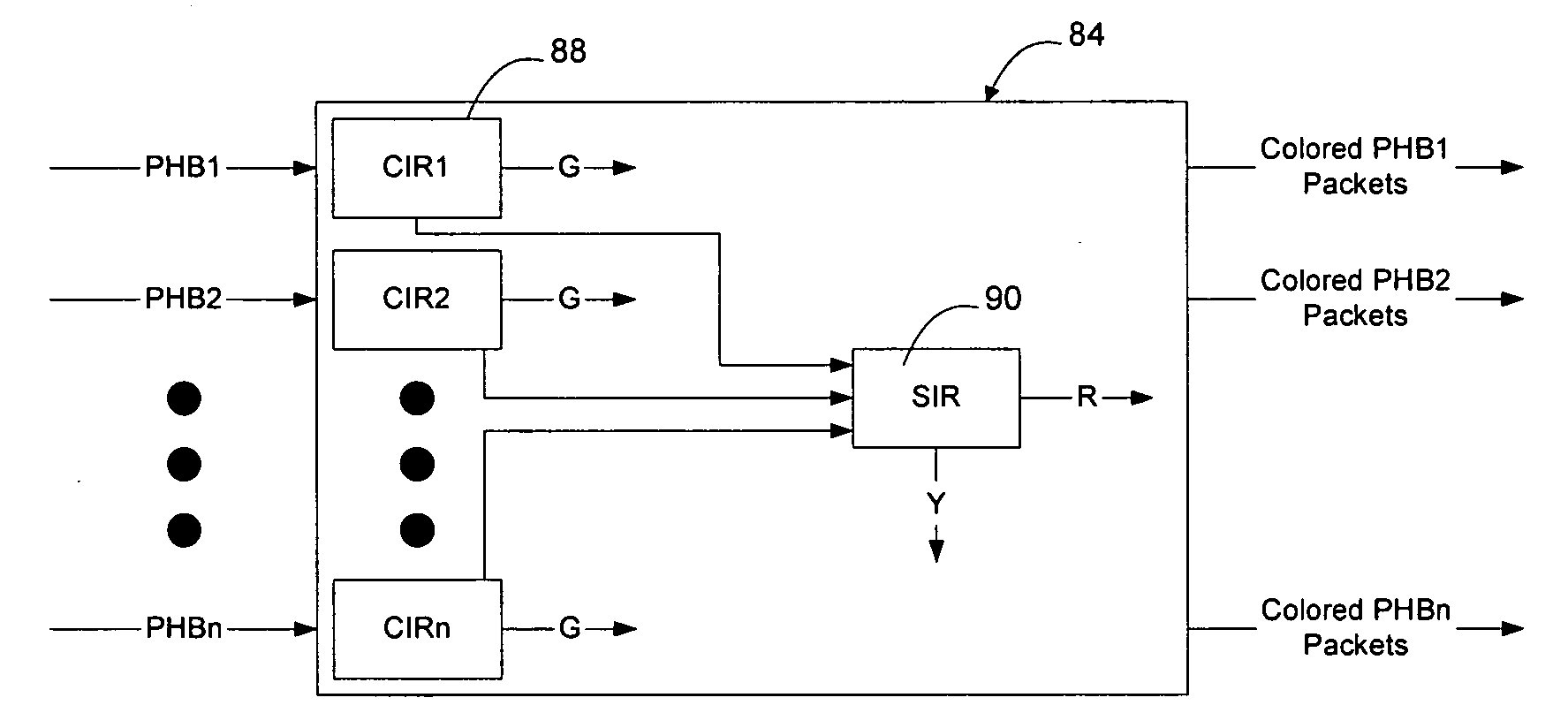
[0023] As described in greater detail below, the method and apparatus of the present invention enable packets in a multi-class flow to be metered per PHB and allow PHBs associated with a given link to share surplus bandwidth on the link fairly. According to one embodiment of the invention, packets not falling within a committed information rate for their respective PHB are metered together by a surplus information rate meter. By using a common meter to meter surplus packets destined to be transmitted on a given link, it is possible to allow packets from multiple PHBs to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com