Distal protection device and method
a protection device and shielding device technology, applied in the field of shielding devices, can solve the problems of restricted blood flow in the lumen of the shielding blood vessel, thrombosis can be particularly problematic, and certain problems are encountered
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
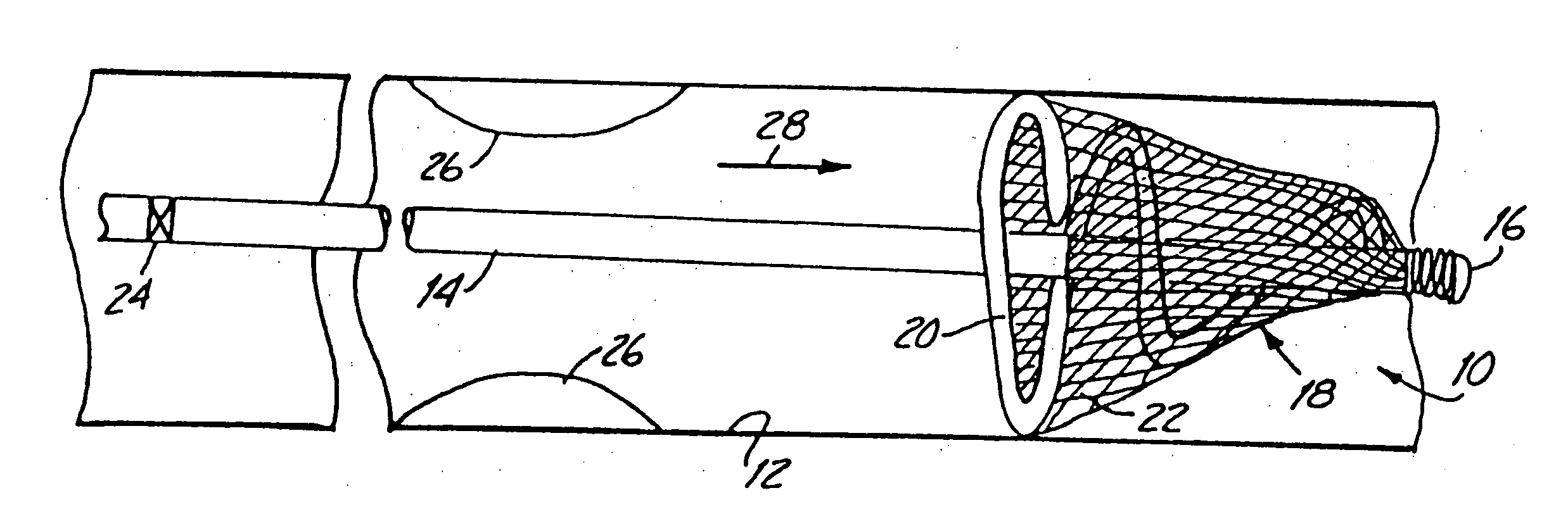
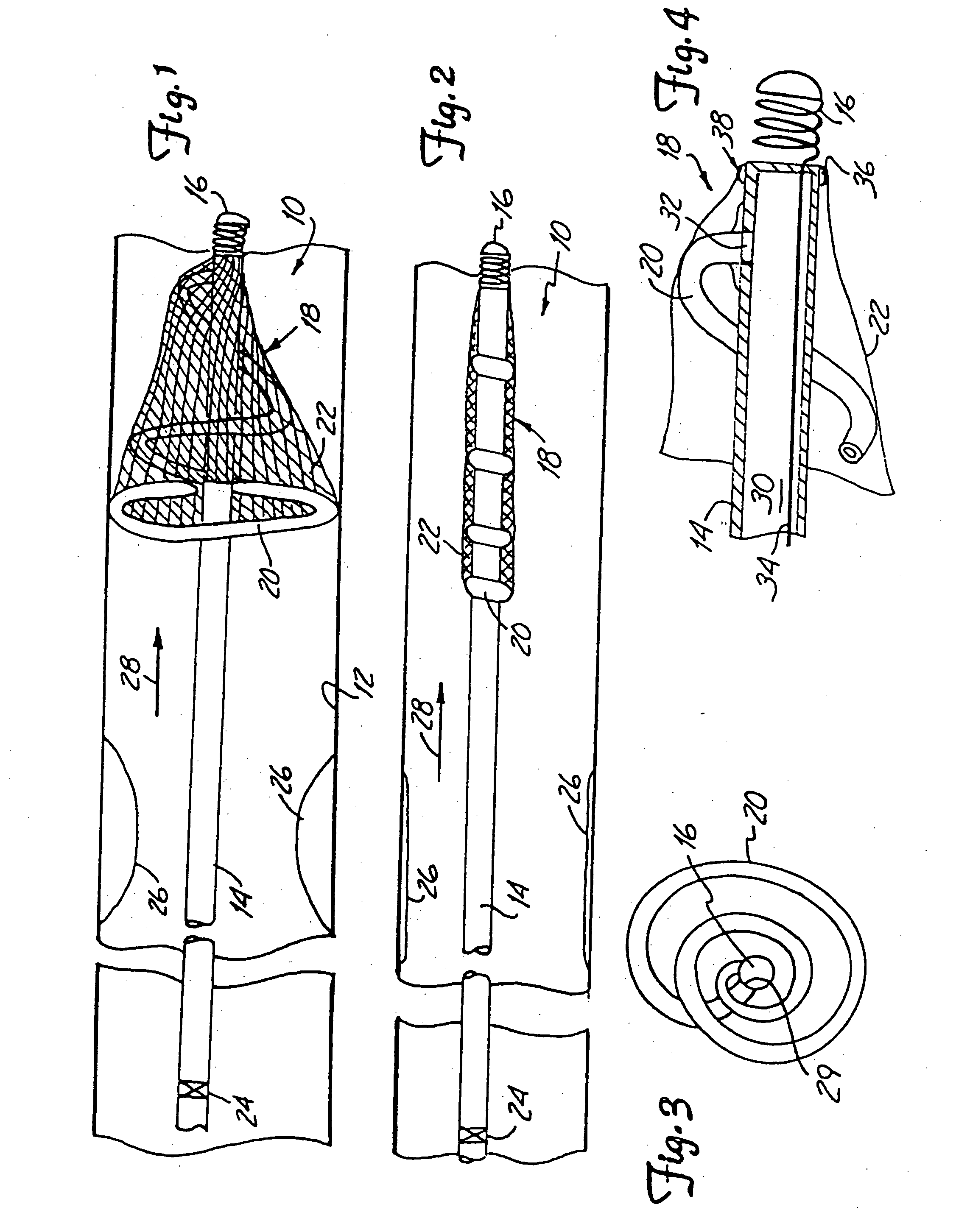
[0032]FIG. 1 illustrates protection device 10 in a deployed position within the lumen of a blood vessel 12. Protection device 10 preferably includes hollow guidewire 14 (or a hypotube having the same general dimensions as a guidewire) having a coil tip 16, and a capturing assembly 18. Capturing assembly 18, in the embodiment shown in FIG. 1, includes an inflatable and expandable member 20 and mesh 22.
[0033] An interior of expandable member 20 is preferably coupled for fluid communication with an inner lumen of guidewire 14 at a distal region of guidewire 14. When deployed, inflatable member 20 inflates and expands to the position shown in FIG. 1 such that capturing assembly 18 has an outer periphery which approximates the inner periphery of lumen 12.
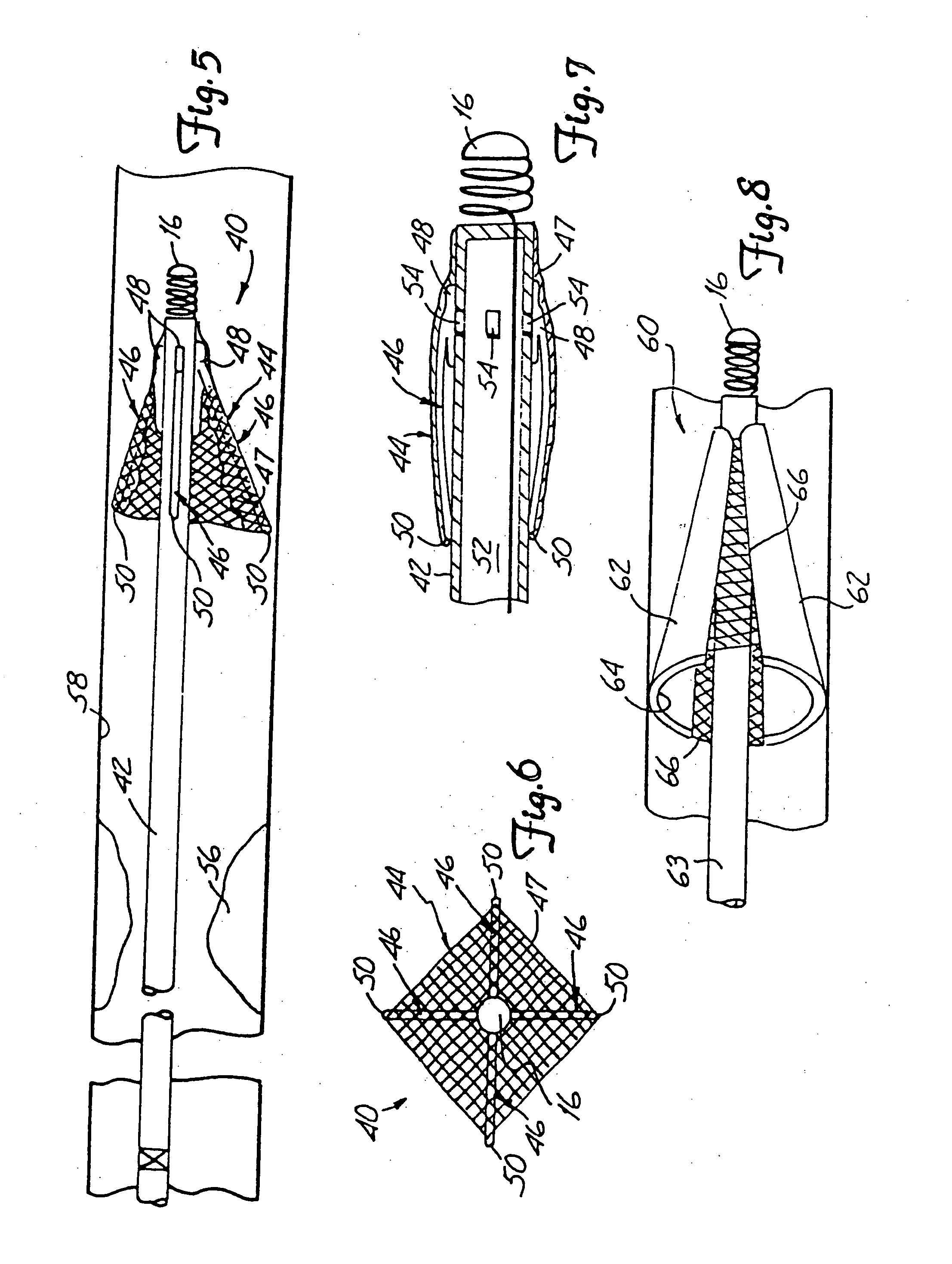
[0034] Mesh 22 is preferably formed of woven or braided fibers or wires, or a microporous membrane, or other suitable filtering or netting-type material. In one preferred embodiment, mesh 22 is a microporous membrane having holes there...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com