Probabilistic learning method for XML annotation of documents
a learning method and document technology, applied in the field of probabilistic learning method for xml annotation of documents, can solve the problems of limited robustness of the tree structure, followed by tree parsing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
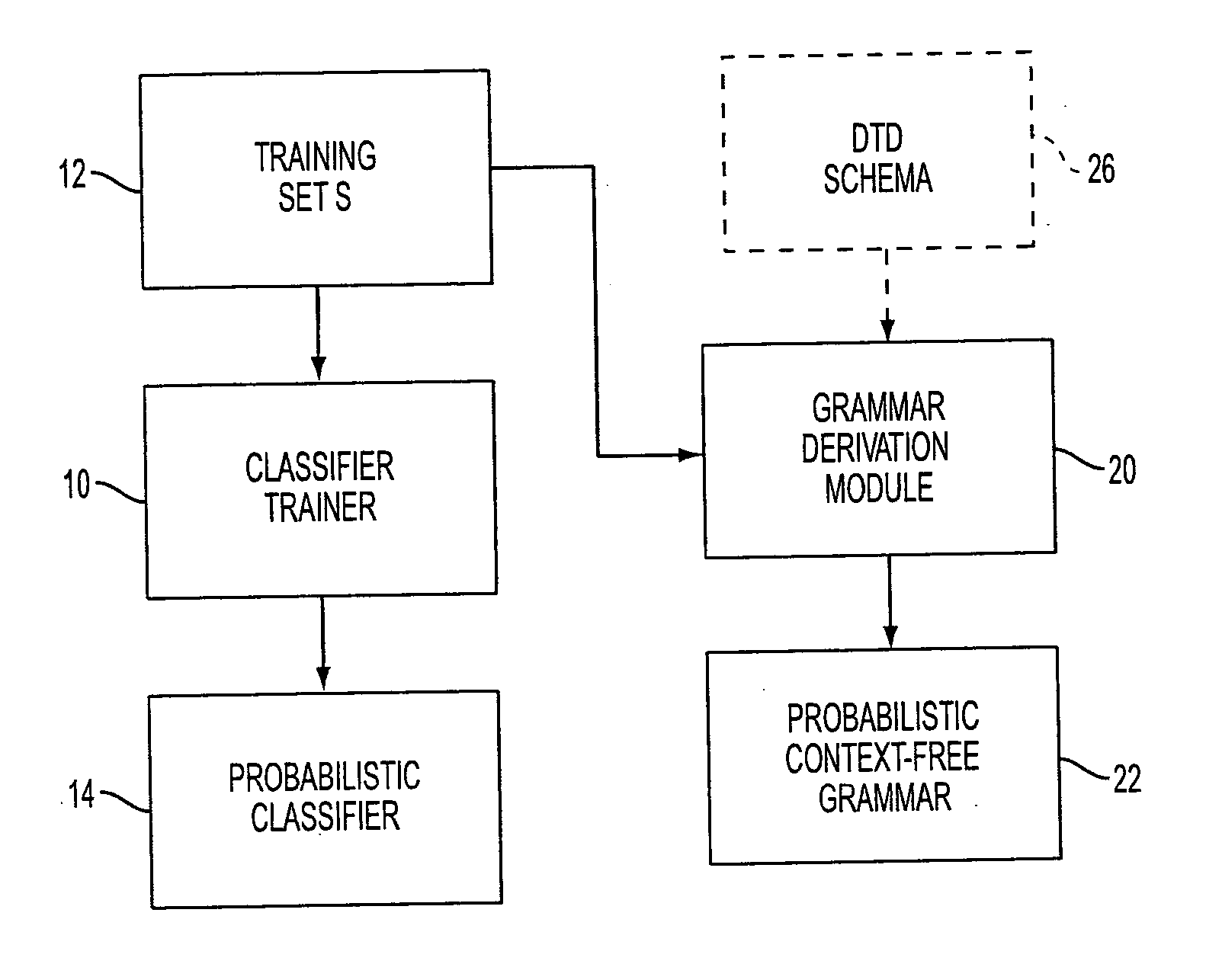
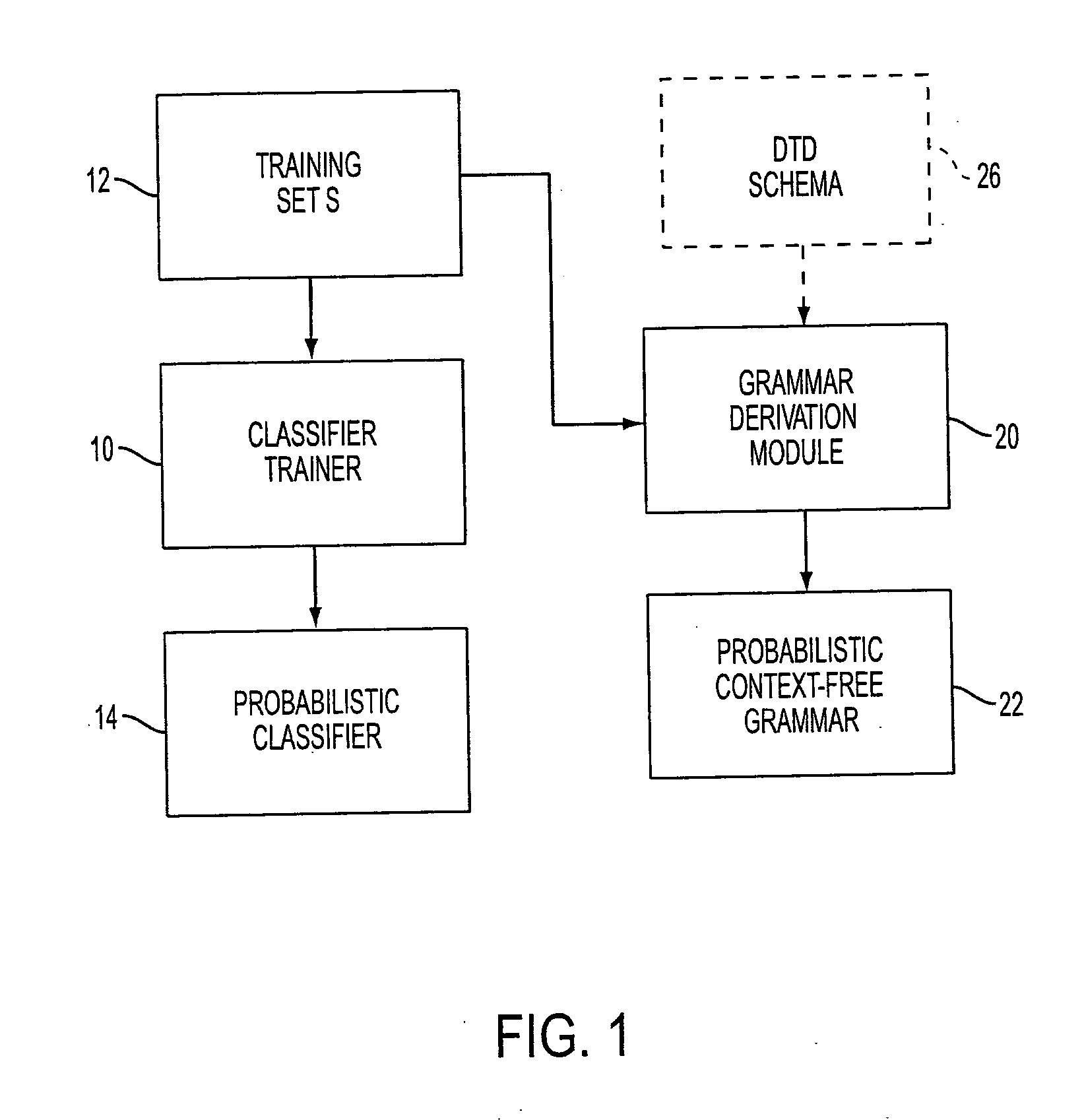
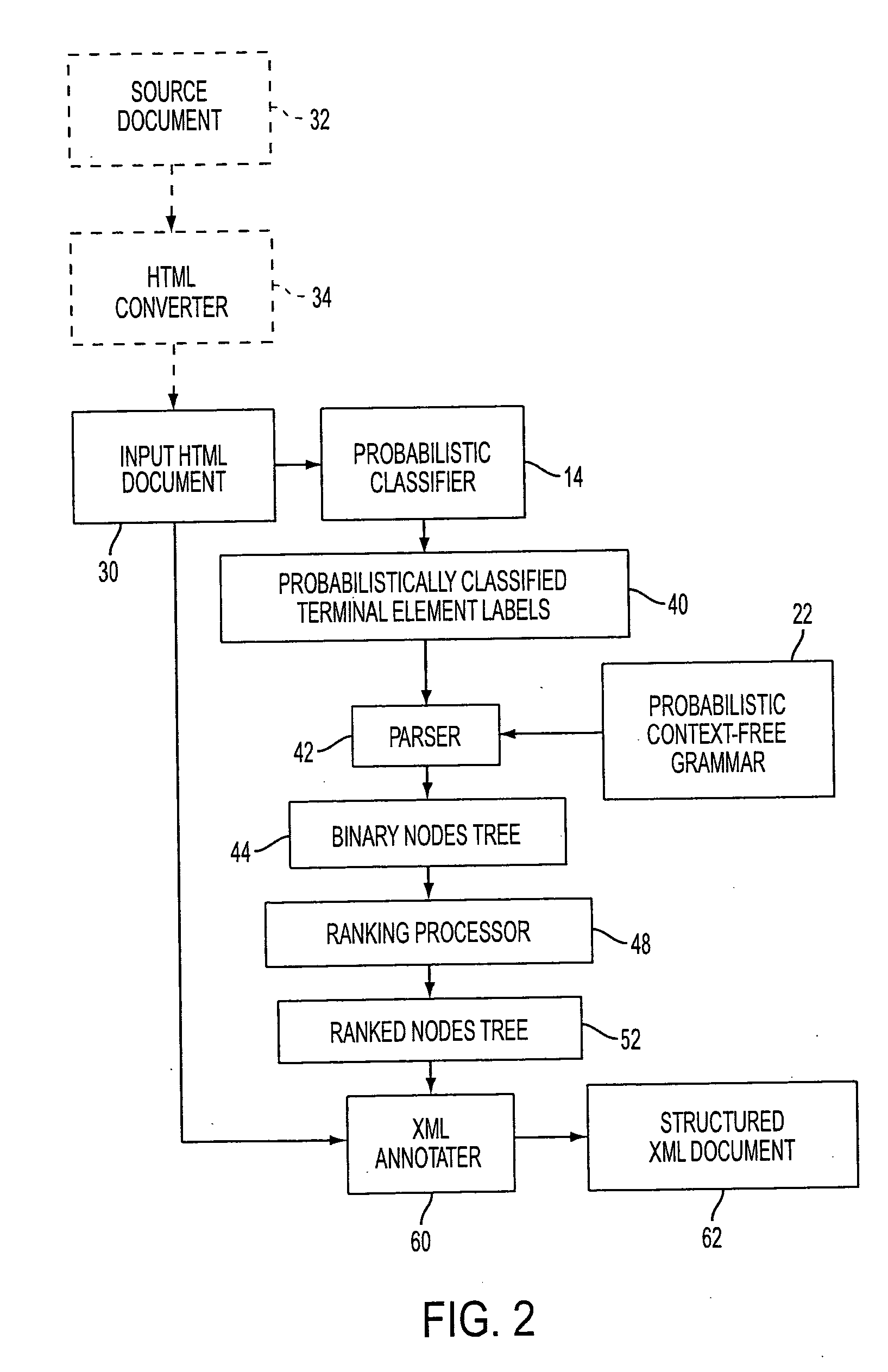
[0012] With reference to FIG. 1, a classifier trainer 10 receives a training set 12 of documents. Each document of the training set 12 is suitably represented as a triplet (x,y,d) where x={xi} is a sequence of fragments xi of the training document, y={yi } is a sequence of terminal elements yi labeling the fragments xi, and d represents internal nodes of a structural tree. The document fragments xi are leaves of the training documents, such as paragraphs, footnotes, endnotes, and so forth. In the illustrated examples, the training documents are HTML documents; however, other standardized formats can be used as the input document format.
[0013] The document organizing described herein is based upon a close analogy between the document structure (y,d) and grammatical structuring used in natural language parsing. In natural language parsing, a sentence or other natural language expression x can be parsed as (y, d), where italics are used to represent parameters of the analogous situati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com