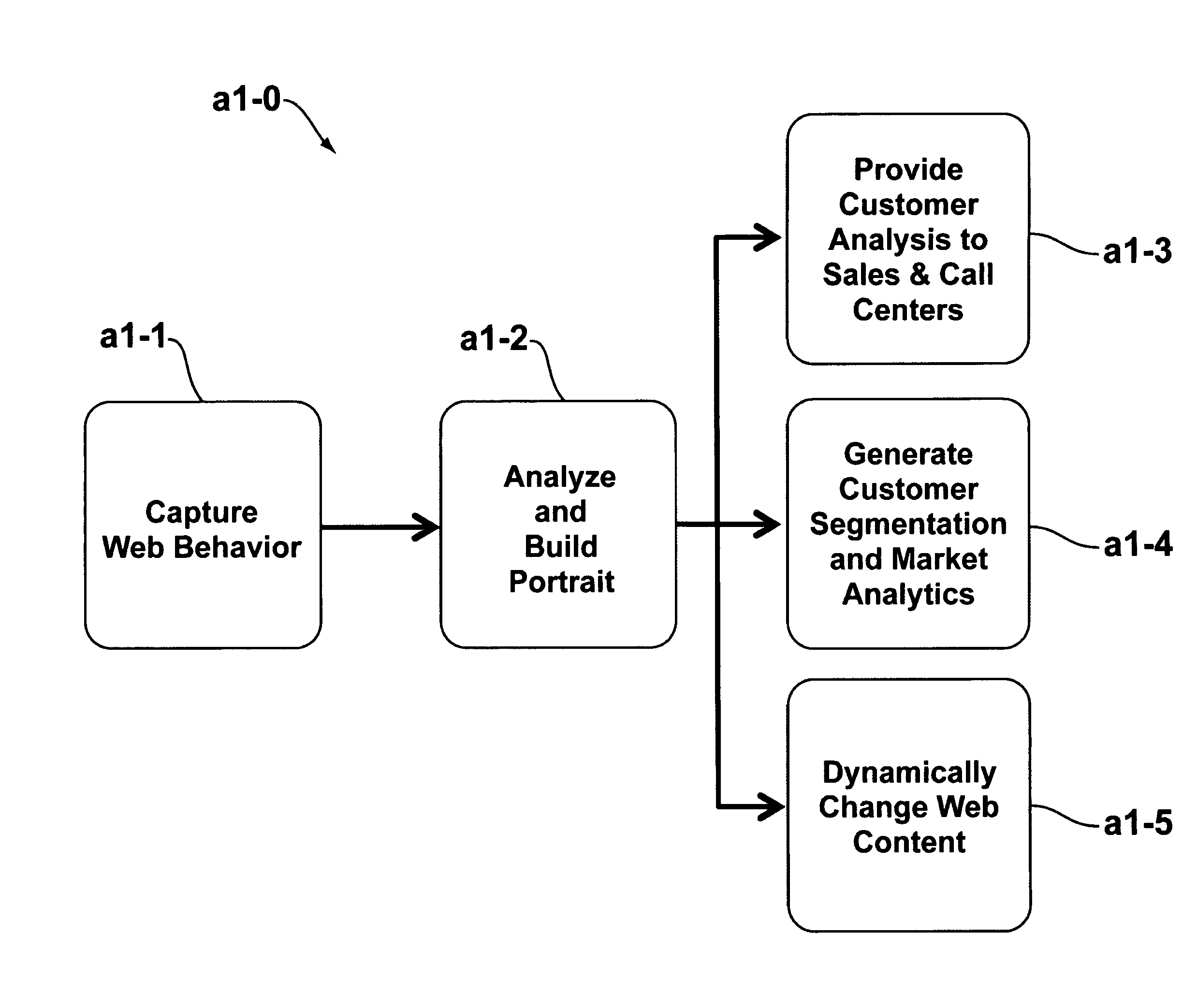
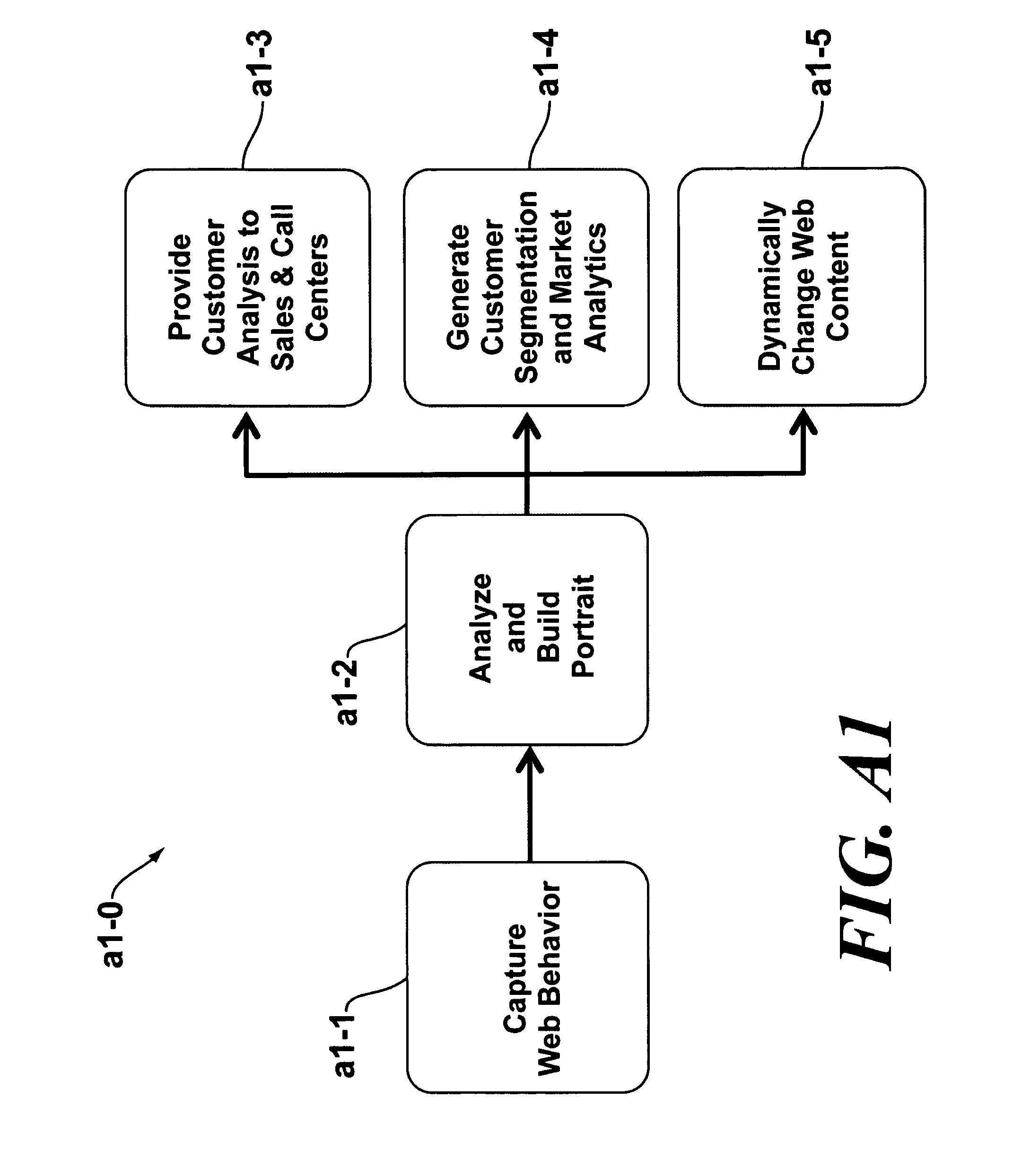
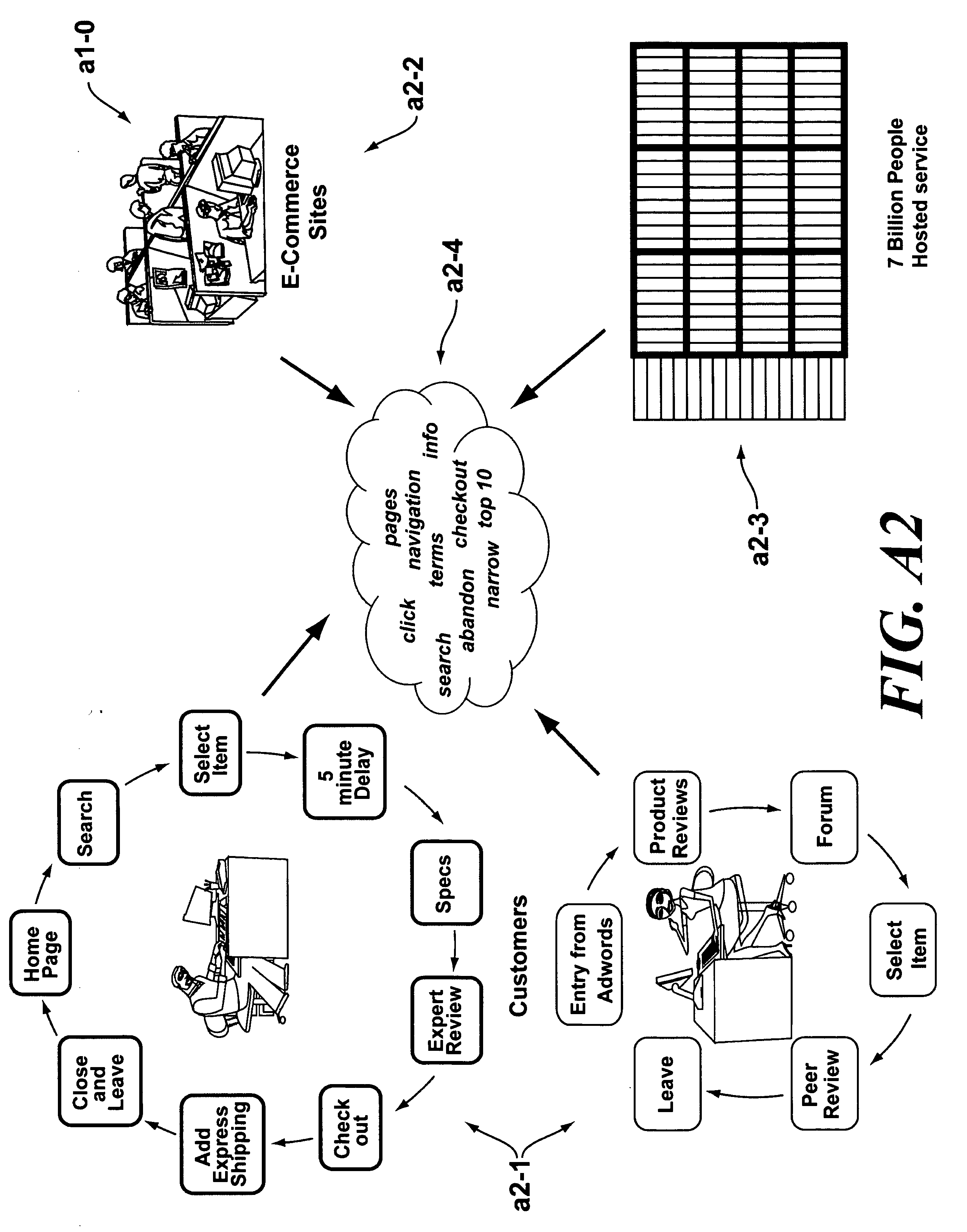
Use of behavioral portraits in web site analysis
a behavioral portrait and web site technology, applied in the field of customizing web page content, can solve the problems of low success rate of approach, a significant number of sales opportunities missed, and limited utility of methods based on data obtained from web site registration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example c1
[0090]The following example illustrates the application of some of the methodologies taught herein to an e-commerce transaction.
[0091]User A decides to purchase a DVD player from a multi-category website (that is, a website which sells electronics, books, clothing, and various other goods and services). The user's pass through the website involves the steps of:[0092](a) Searching for a specific DVD player model;[0093](b) Checking the detailed specifications of the model;[0094](c) Comparing the model with other top sellers;[0095](d) Adding the selected model to the shopping cart;[0096](e) Choosing expedited shipping; and[0097](f) Checkout.
[0098]Each of these individual actions during the web session can be mapped to a set of rules or a knowledge base in the Portrait Engine. An example of such a mapping is shown in FIGS. C1-C2. In particular, FIG. C1 shows a standard e-commerce web page with a selection of electronics products, specifically DVD Players. FIG. C2 shows the same web page...
example c2
[0114]This example illustrates how user behavior may be tracked, weighted and utilized to develop a behavioral portrait for the user.
[0115]A user's behavior on a website is recorded and analyzed. That behavior may include such factors as:[0116](a) navigation selections (which navigation choices are made on the site);[0117](b) search text parsing and analysis (search used to navigate to a particular area on the site in conjunction with term analysis);[0118](c) icon selection (where the user clicks);[0119](d) marketing offer selection (the type of marketing offer a user selects);[0120](e) order of behavior (e.g., whether the user engages in seemingly random “browsing” or more focused selections);[0121](f) speed of navigation (timed clicks, e.g., speed of checkout or skipping less relevant pages); and[0122](g) omitted selections (what the user does not do or select).
[0123]After each action, the user's portrait is recalculated. This calculation is based upon a dynamic (real-time) weight...
example d-1
[0167]This example illustrates the modification of content (on the website of an on-line computer retailer) for two different types of users in accordance with a particular, non-limiting embodiment of the methodologies described herein.
[0168]With respect to FIG. D4 and FIG. D5, some of the behavioral traits of two different hypothetical users are summarized. With respect to FIG. D4, the first user (“Trish”) is a “thinker” type user. Trish is a type of user who is in control of her decisions d4-1, and will often say “I have a gut feel” d4-2. Trish typically makes her decisions based on a review of detailed specifications and trusted sources d4-3, and is motivated by how an offered product will help her to achieve her goals d4-4. She wants to see a positive result from her purchase d4-5, is heavily dependent on process and procedure d4-6, and is not likely to move to the next step in a purchase process before the current step is completed d4-7.
[0169]By contrast, the second hypothetica...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com