Waste heat recovery system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
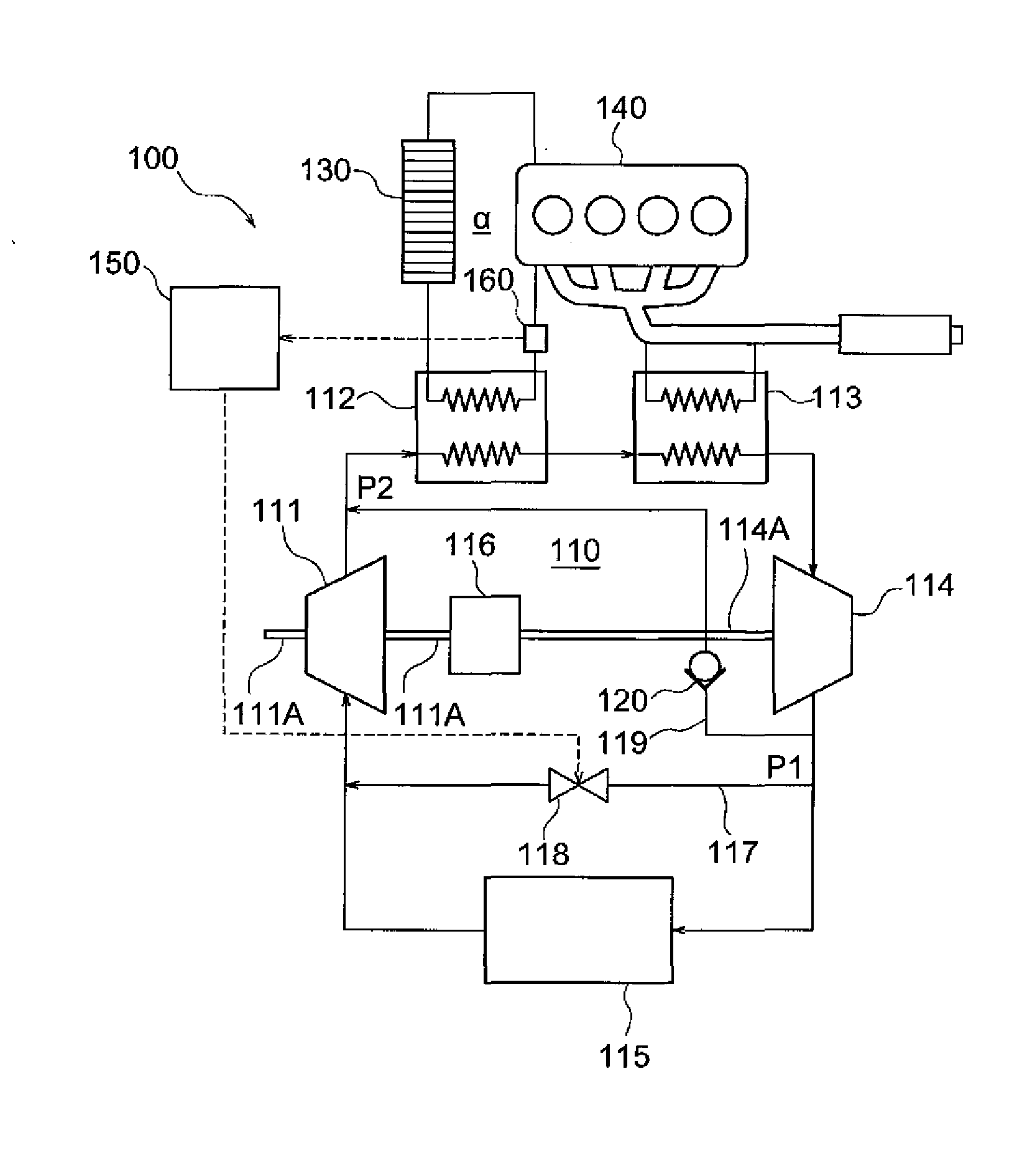
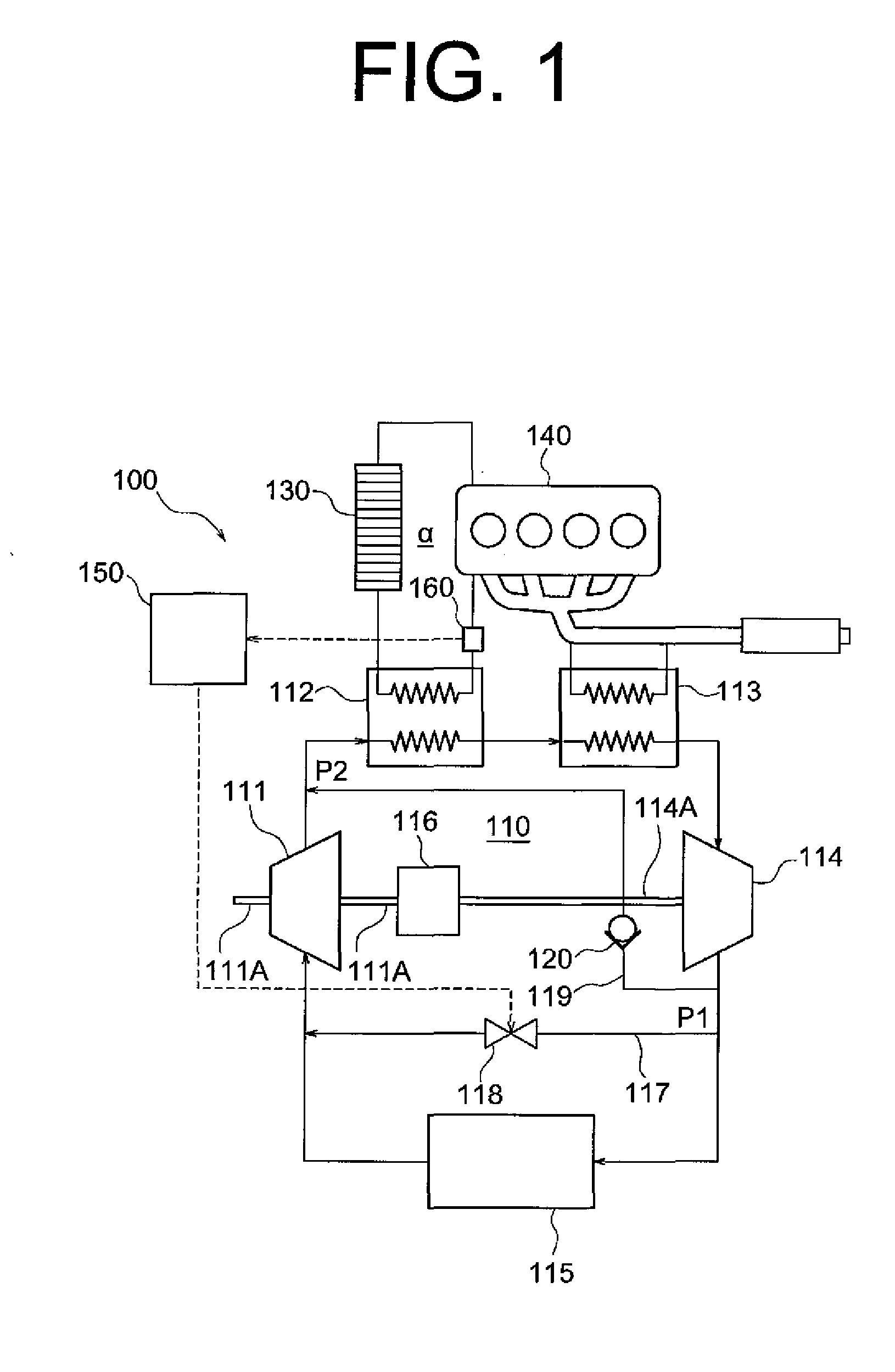
[0017]The following will describe the embodiments of the present invention with reference to the accompanying drawings. FIG. 1 shows a waste heat recovery system 100 according to the present invention. The waste heat recovery system 100 includes a Rankine cycle 110. The Rankine cycle 110 has a gear pump 111, a cooling water boiler 112, an exhaust gas boiler 113, an expander 114 and a condenser 115. The gear pump 111 is provided for pumping a working fluid. The cooling water boiler 112 is provided for exchanging heat between the working fluid and a cooling water exchanging heat with an engine 140, serving as the first heat exchanger of the present invention. The exhaust gas boiler 113 is provided for exchanging heat between the working fluid and an exhaust gas of the engine 140, serving as the second heat exchanger of the present invention. The expander 114 is provided for expanding the working fluid heated and vaporized by the cooling water boiler 112 and the exhaust gas boiler 113 ...
second embodiment
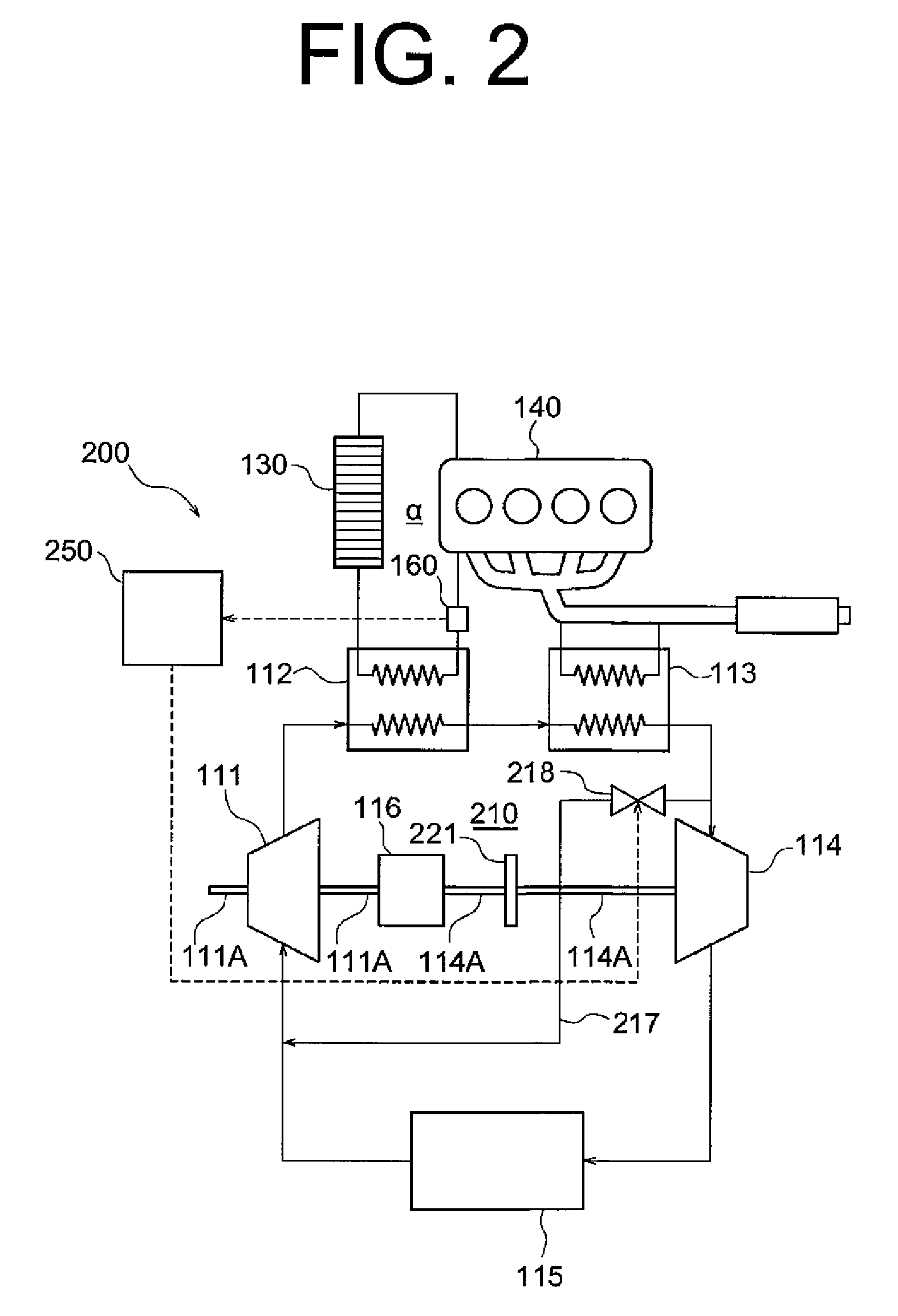
[0031]The following will describe the operation of the waste heat recovery system 200 of the The description will be made for two cases, i.e. one case where the temperature of the cooling water of the engine 140 is the first predetermined value Th1 or higher and the other case where the temperature of the cooling water of the engine 140 is lower than the first predetermined value Th1.
[0032]When the temperature of the cooling water of the engine 140 obtained by the temperature sensor 160 is the first predetermined value Th1 or higher, the control unit 250 causes the electromagnetic valve 218 to close thereby to close the first bypass passage 217.
[0033]With the first bypass passage 217 closed, the working fluid delivered from the gear pump 111 circulates through the cooling water boiler 112, the exhaust gas boiler 113, the expander 114 and the condenser 115 in this order in the Rankine cycle 210. The output shaft 114A of the expander 114 is driven to rotate by the expansion of the wo...
third embodiment
[0043]The following will describe the operation of the waste heat recovery system 300 of the The description will be made for two cases, i.e. one case where the temperature of the cooling water of the engine 140 is a second predetermined value Th2 that is slightly higher, e.g. by two degrees, than the aforementioned first predetermined value Th1 or higher and the other case where the temperature of the cooling water of the engine 140 is lower than the first predetermined value Th1.
[0044]When the temperature of the cooling water of the engine 140 is the second predetermined value Th2 or higher, the control unit 350 moves the first three-way valve 318 to such a position that allows the working fluid flowed out of the expander 114 into the condenser 115. That is, the first bypass passage 317 is closed thereby to cut off the circulation of the working fluid through the first bypass passage 317. In addition, the control unit 350 moves the second three-way valve 323 to such a position th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com