Medical garment for skin-to-skin care and methods of use
a skin-to-skin care and medical technology, applied in the field of medical garments, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory current draping technique, unequipped blanket or hospital gown, and insufficient and necessary privacy in a closed spa
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
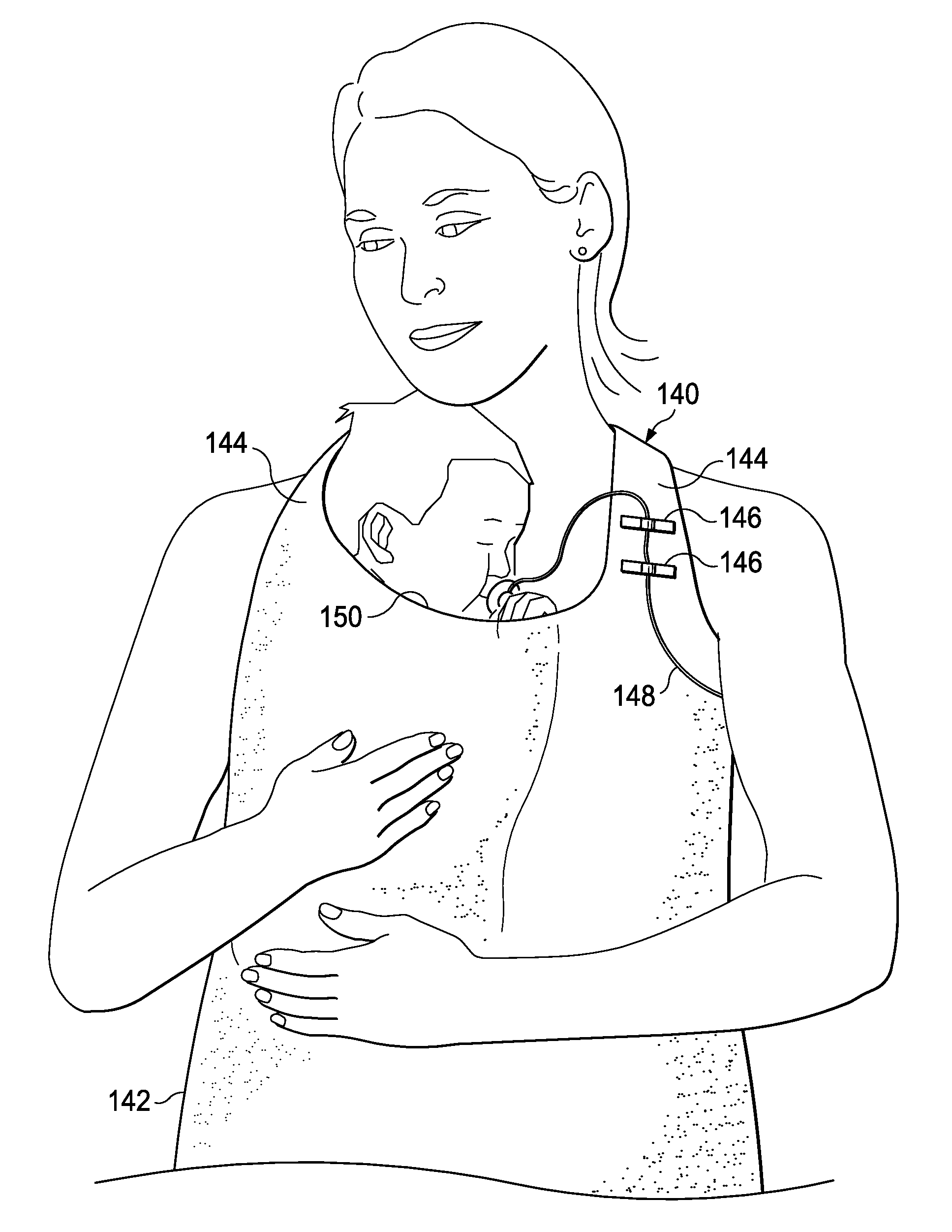
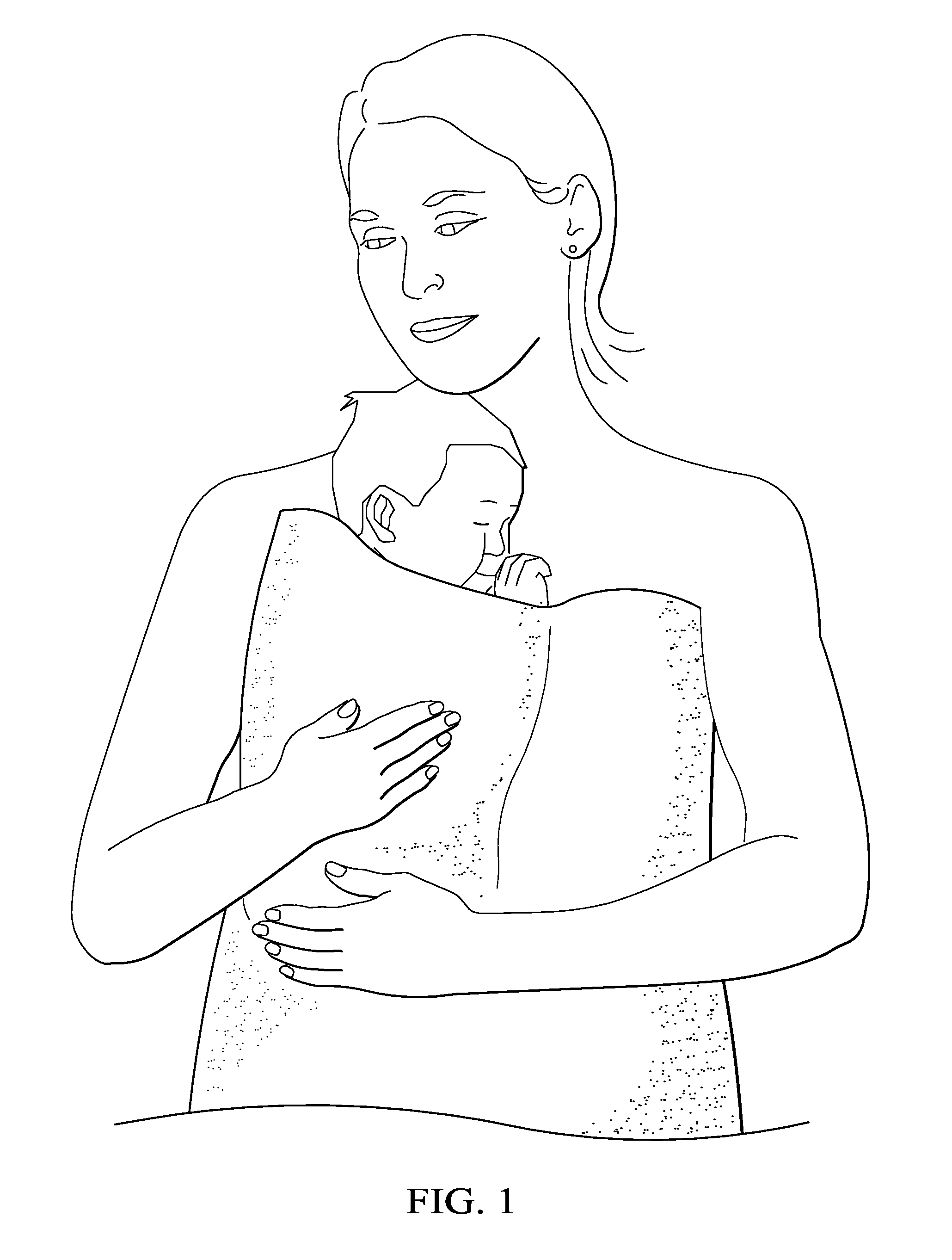
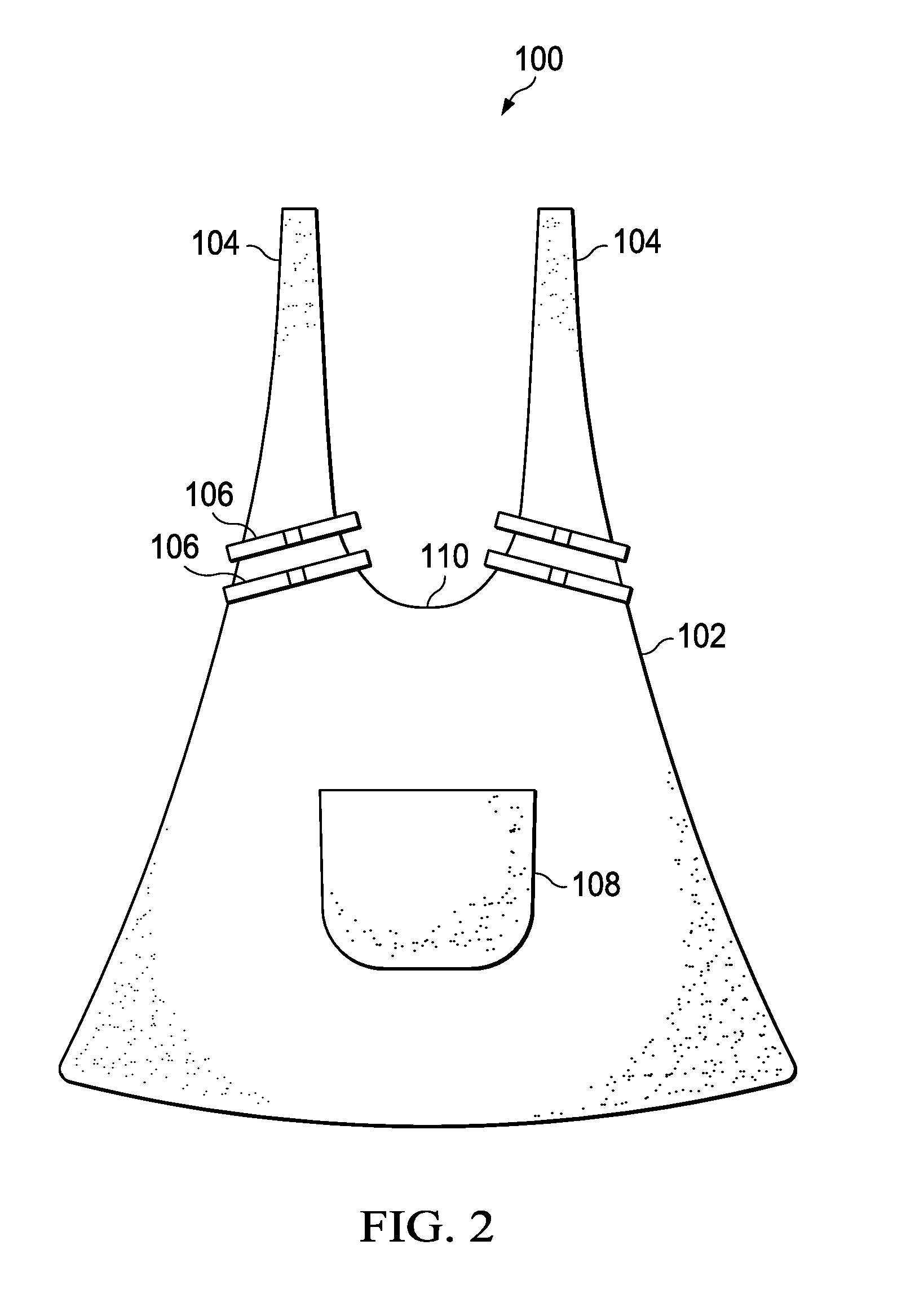
[0015]In one aspect, embodiments disclosed herein relate to a medical garment to provide improved skin-to-skin care for infants in the NICU. Referring now to FIG. 2, a front view of the medical garment 100 for providing skin-to-skin care for premature infants and infants with health issues is shown in accordance with embodiments of the present disclosure. Medical garment 100 includes an apron 102 that is configured to be worn by the parent and positioned on a front side of the parent such that the parent's front side (e.g., chest and abdomen) is adequately covered when worn. Additionally, apron 102 may extend around and cover the sides of the parent when worn. Apron 102 may be a soft material, such as cotton or other similar materials, to provide the most comfort for both the infant and the parent.
[0016]Medical garment 100 also includes straps 104 at a top portion of the apron 102. Straps 104 may be tied around the neck of the parent to secure the garment 100 when worn. In the alter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com