BigFoot Mobility Device End Tip
a technology for mobility devices and canes, applied in walking aids, crutches, physical therapy, etc., can solve the problems of quad bases being a real trip hazard, quad bases contributing little to improving user comfort, safety or convenience, etc., and achieves the effects of widening the diameter, enhancing the compressibility, and altering the dimensions and functionality of components
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
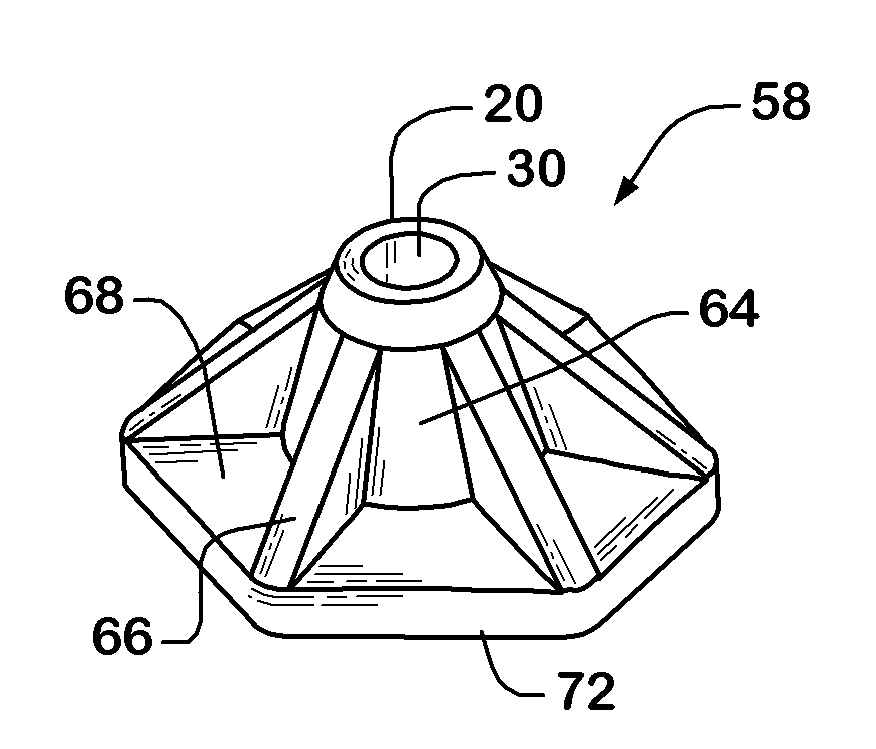
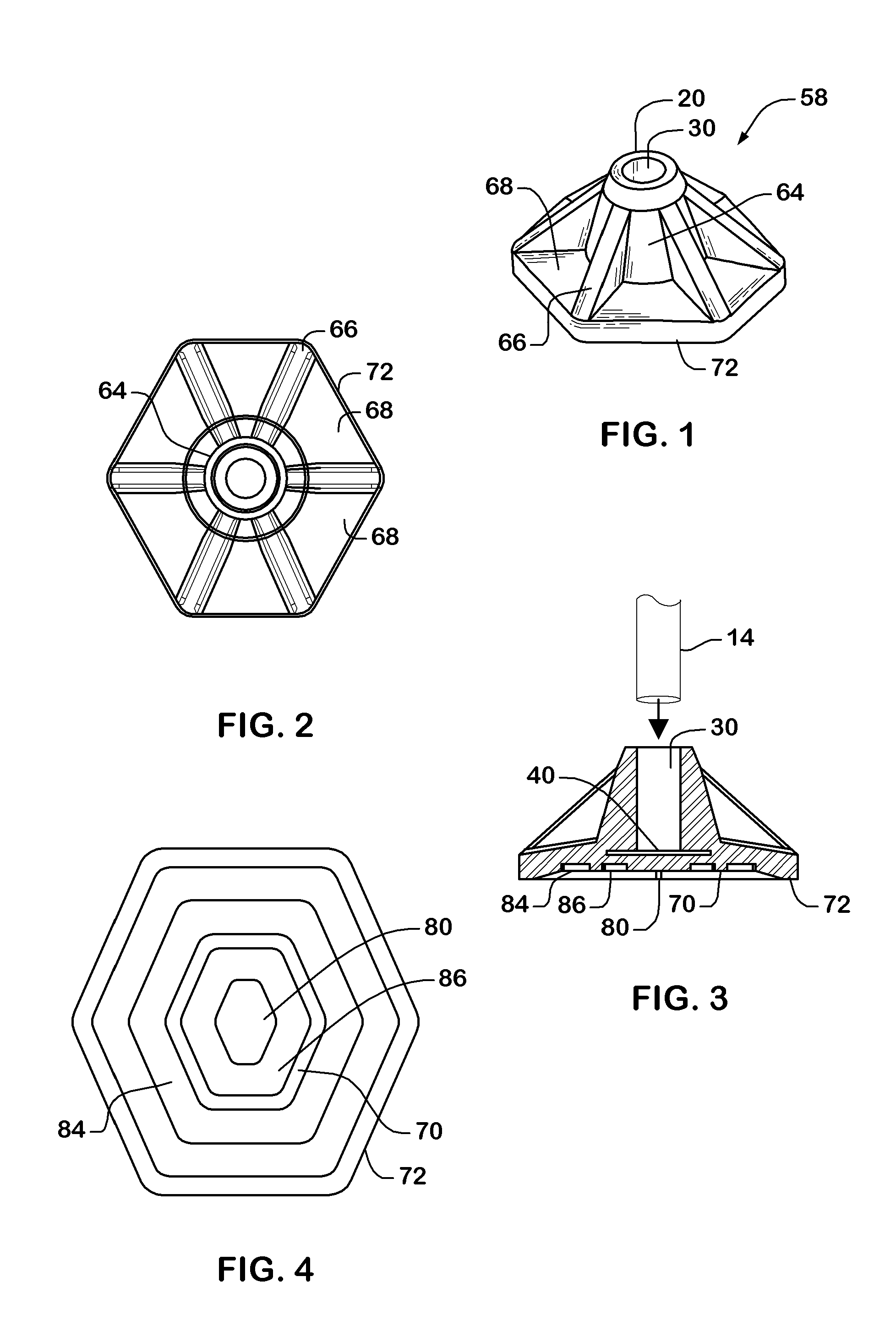
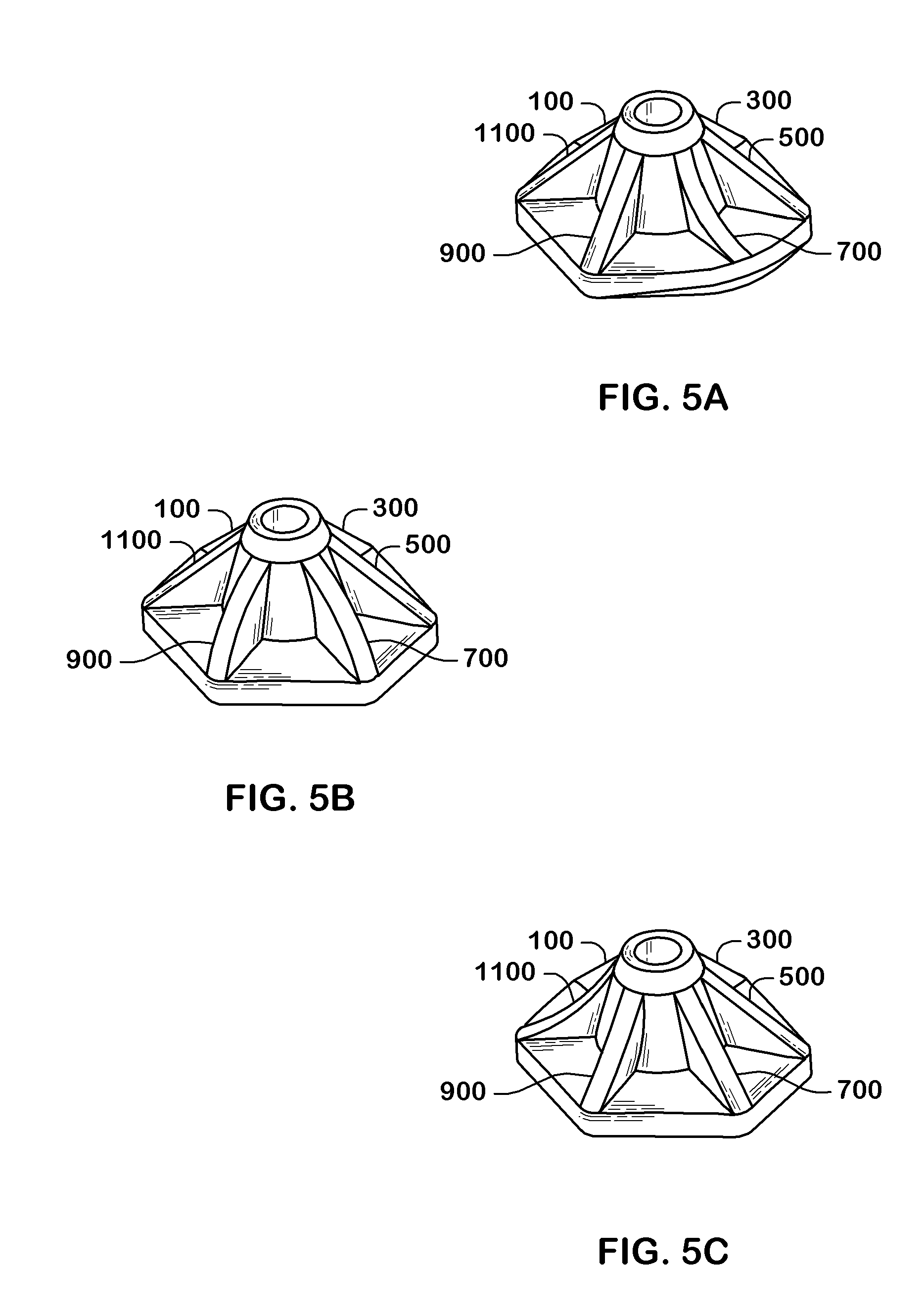
[0018]Previously, the prior art of the inventor of the present invention disclosed and claimed a mobility device comprising a hexagonal end tip as shown in U.S. Pat. No. 7,610,926 issued Nov. 3, 2009 entitled “Mobility Device”, the entirety of which is incorporated by reference. In particular, FIGS. 13-18 of U.S. Pat. No. 7,610,926 disclosed a pseudo-frustoconical shape with six facets or side walls 62. Each side wall 62 includes a depressed panel 64 surrounded by an outstanding rib-like frame 66, wherein the depressed panels are of a few millimeters in depth such that the side walls are almost vertical. The present invention is based on an unexpected discovery that a user of a mobility device experiences much increased stability, compressibility and measureable spring assistance to their ambulation when the end piece is re-modeled by dramatically increasing the depth of the depressed panels so as to make the resultant, circumferential ribs much more prominent. Additionally, a novel...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com