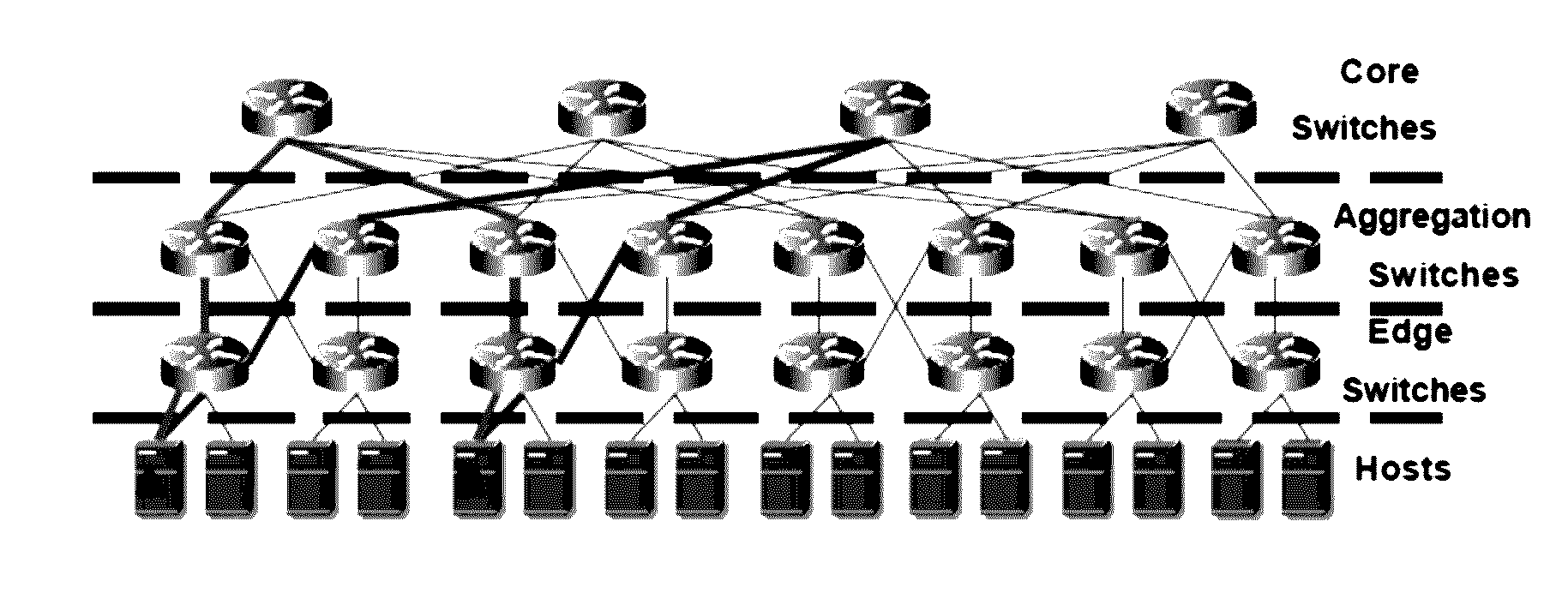
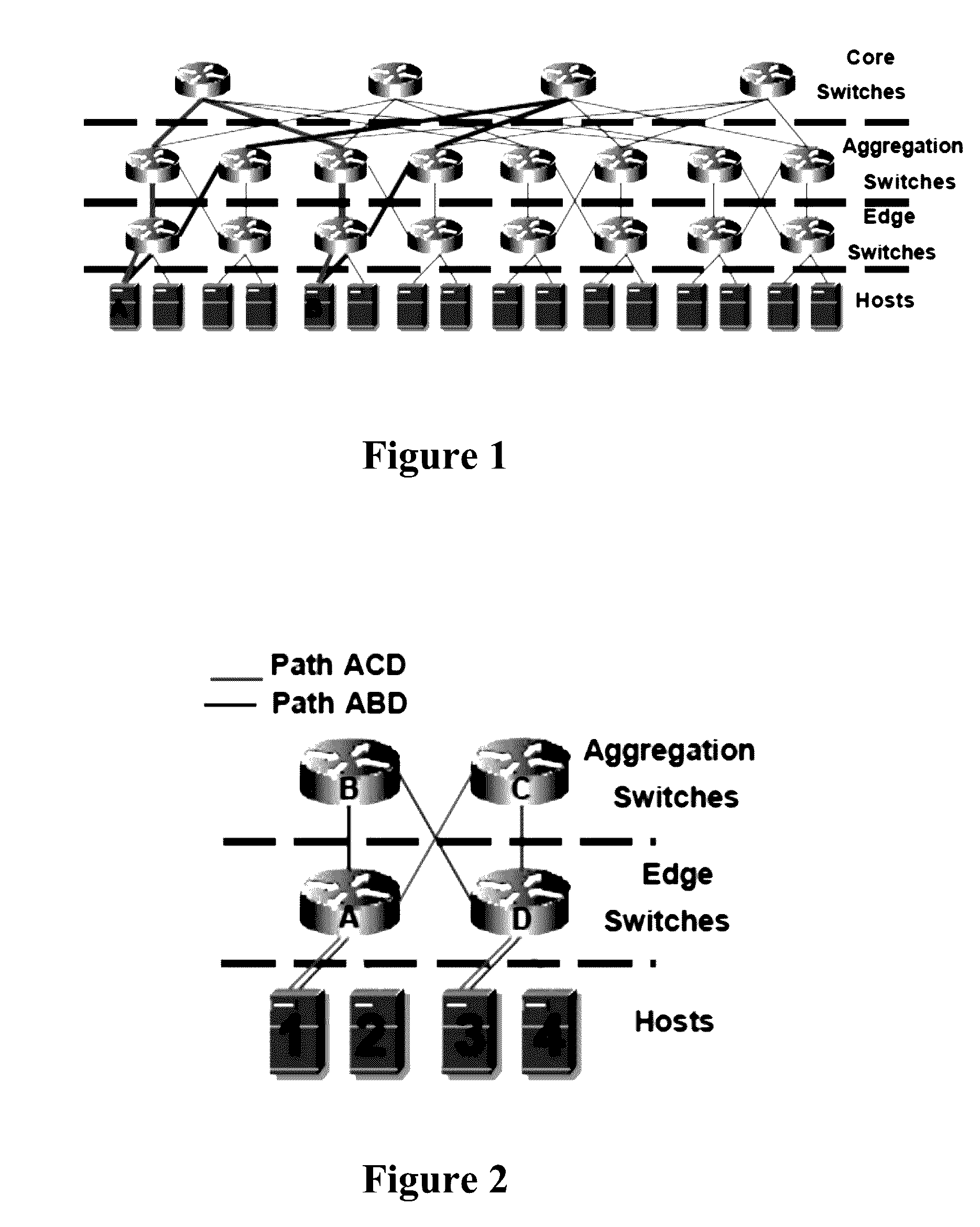
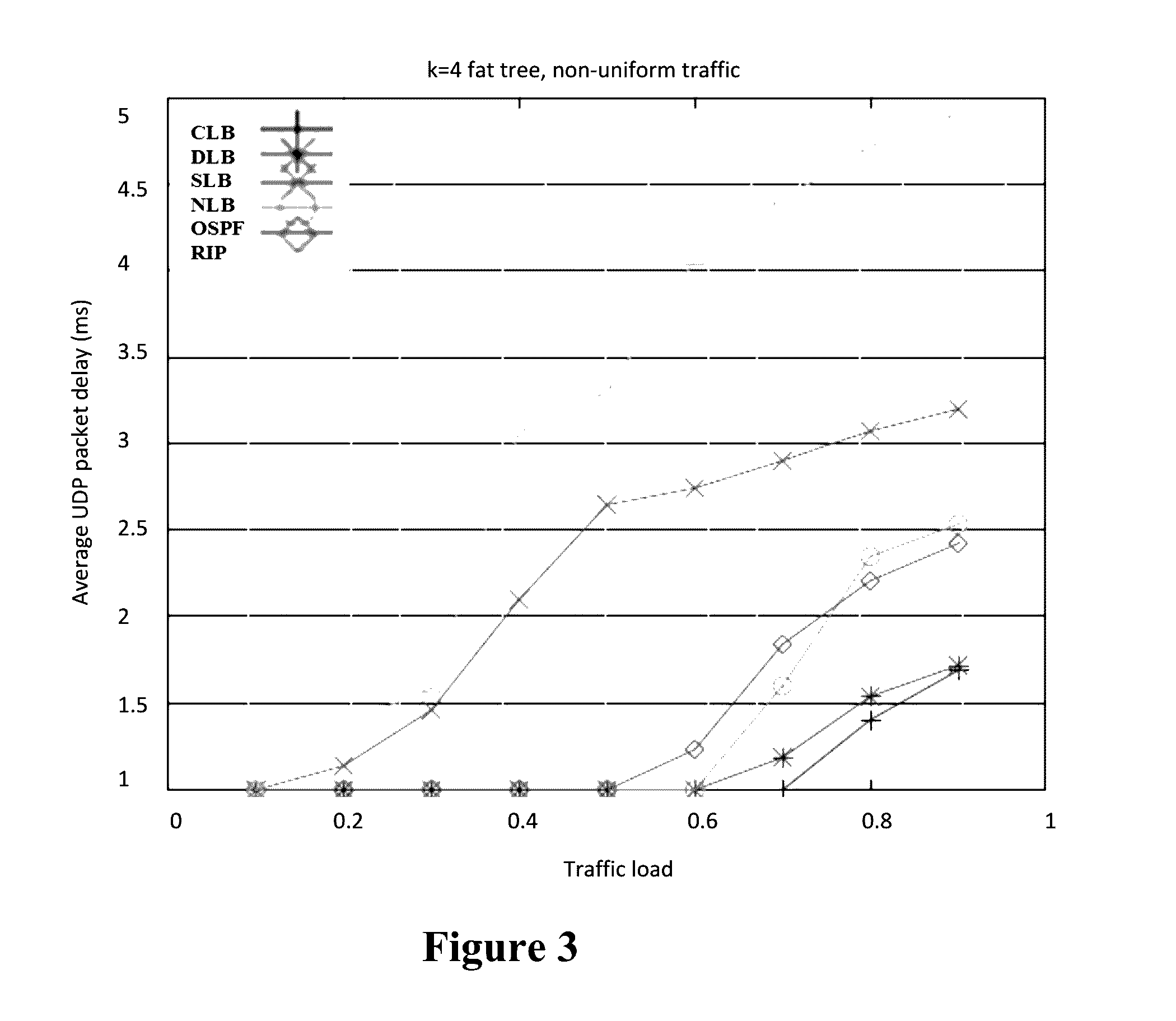
Load-balancing algorithms for data center networks
a data center network and load balance technology, applied in the field of load balance algorithms for data center networks, can solve the problems of insufficiently small number of paths, insufficient and inability to readily utilize the multi-path capability of multi-rooted topologies of traditional link state and distance vector based routing algorithms (e.g., for the internet), and achieve the effect of effective and scalabl
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0051]Experimental performance results were obtained from a real testbed, implemented using the Beacon OpenFlow controller, HP ProCurve OpenFlow switches, VMware vCenter server, and VMware ESXi hypervisor.
[0052]A 4-pod and 16-host fat-tree prototype was built to demonstrate the effectiveness and practicality of the optimization algorithm in real networks. Two OpenFlow-enabled 48-port HP ProCurve 6600 switches running firmware version K.15.06.5008 were utilized, and 20 virtual switches were created. Each virtual switch was assigned with 4 ports, except the first core layer switch had 3 extra ports to allow connections for management nodes, including VMware vCenter server, Network File System (NFS) server, and DHCP server. All switches were managed by Beacon OpenFlow controller version 1.0.0 with a self-developed Equinox framework bundle that implemented the optimization algorithm. Each host was running VMware ESXi hypervisor version 5.0.0 to host VMs running operating system of Ubunt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com