Food magnagementregerator utilizing RFID
A food management and refrigerator technology, applied in household refrigerators, applications, household appliances, etc., can solve the problems of increased refrigerator manufacturing cost, consumption, long input time, etc., and achieve the effect of easy food management
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the embodiments of the present invention and the accompanying drawings. However, the scope of the present invention is not limited to the following examples and drawings. The scope of the invention is limited only by the claims.
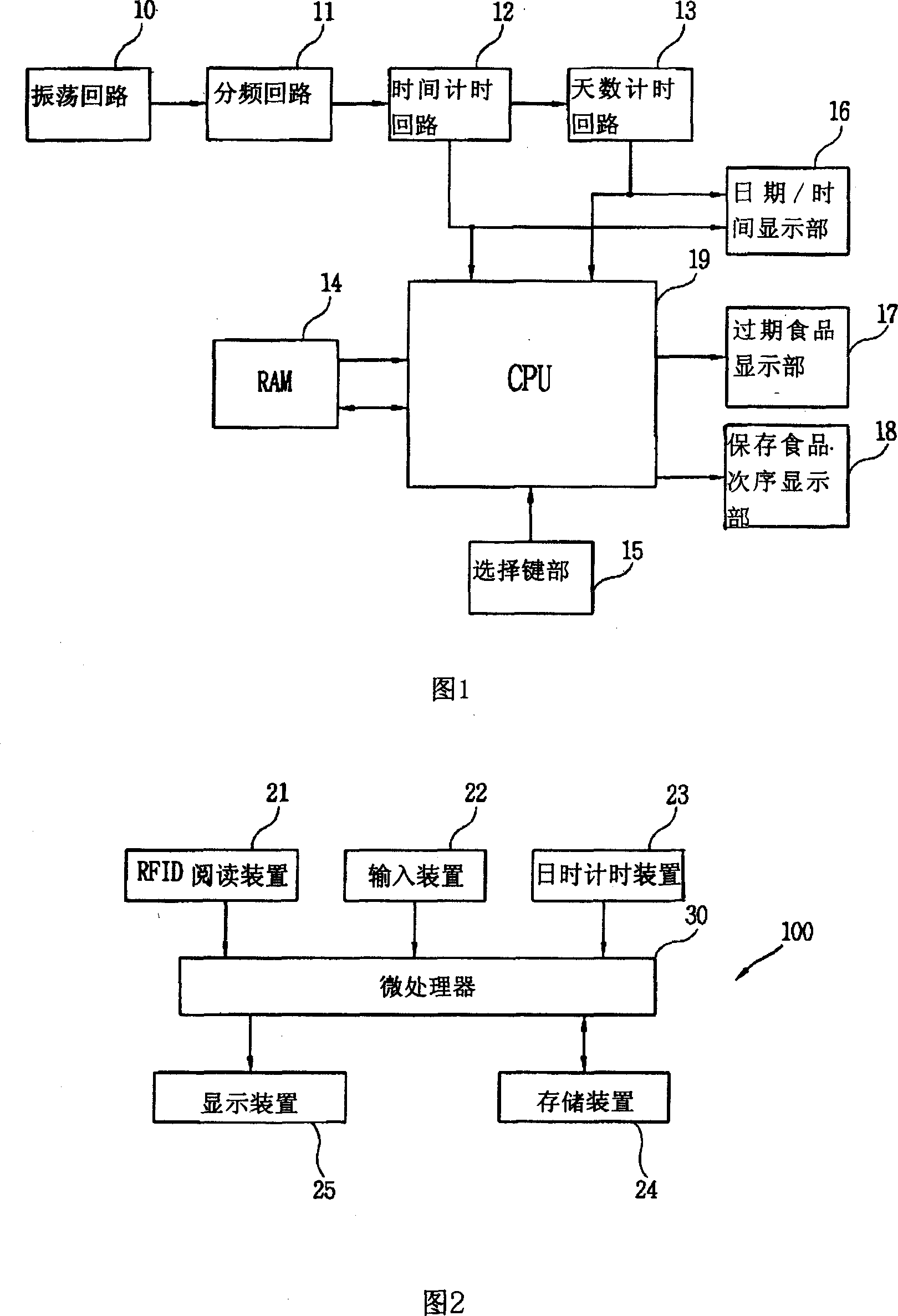
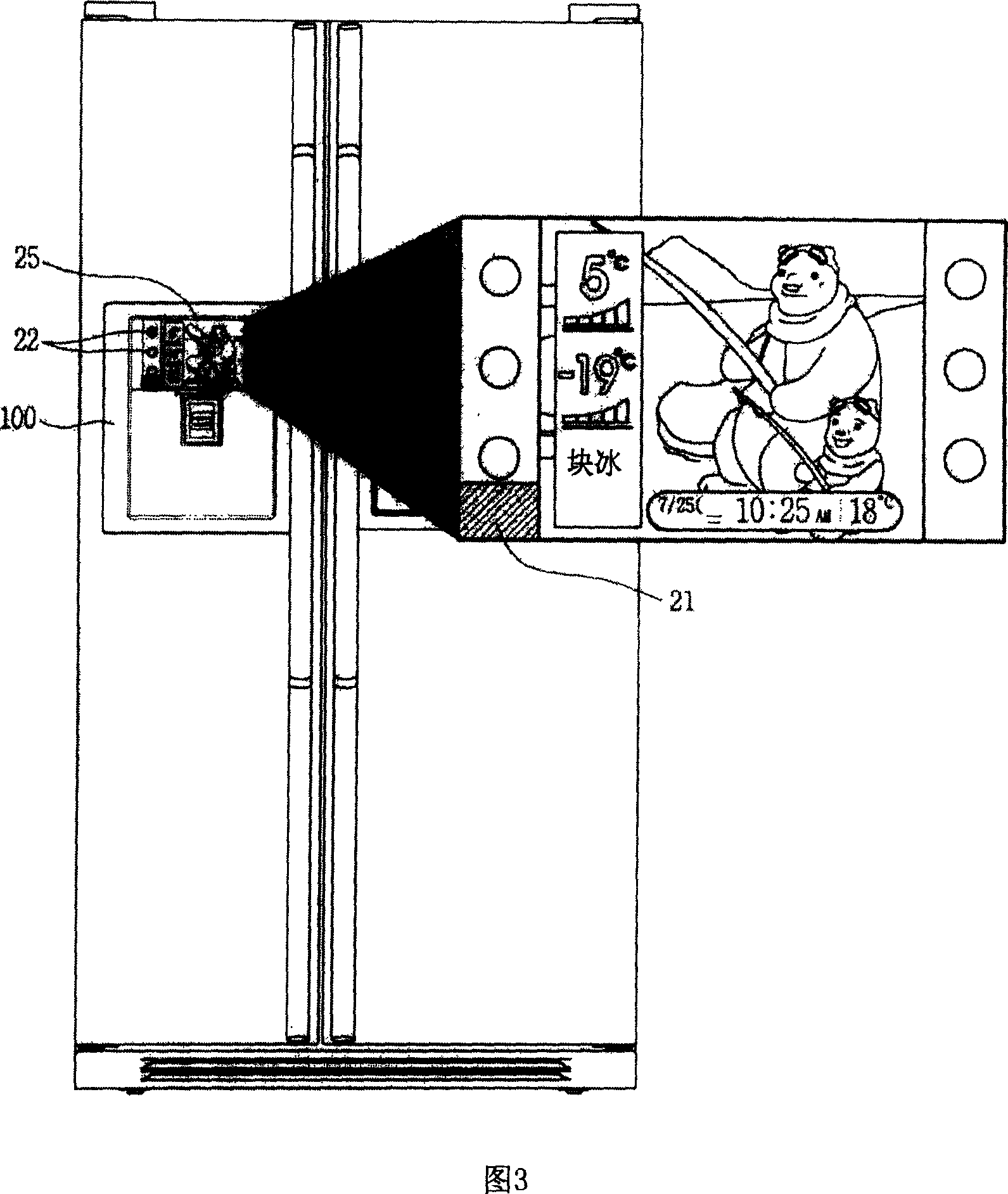
[0034] Fig. 2 is a block diagram of the food management refrigerator utilizing RFID of the present invention. Fig. 3 is a front view and a partially enlarged schematic view of the food management refrigerator utilizing RFID of the present invention.
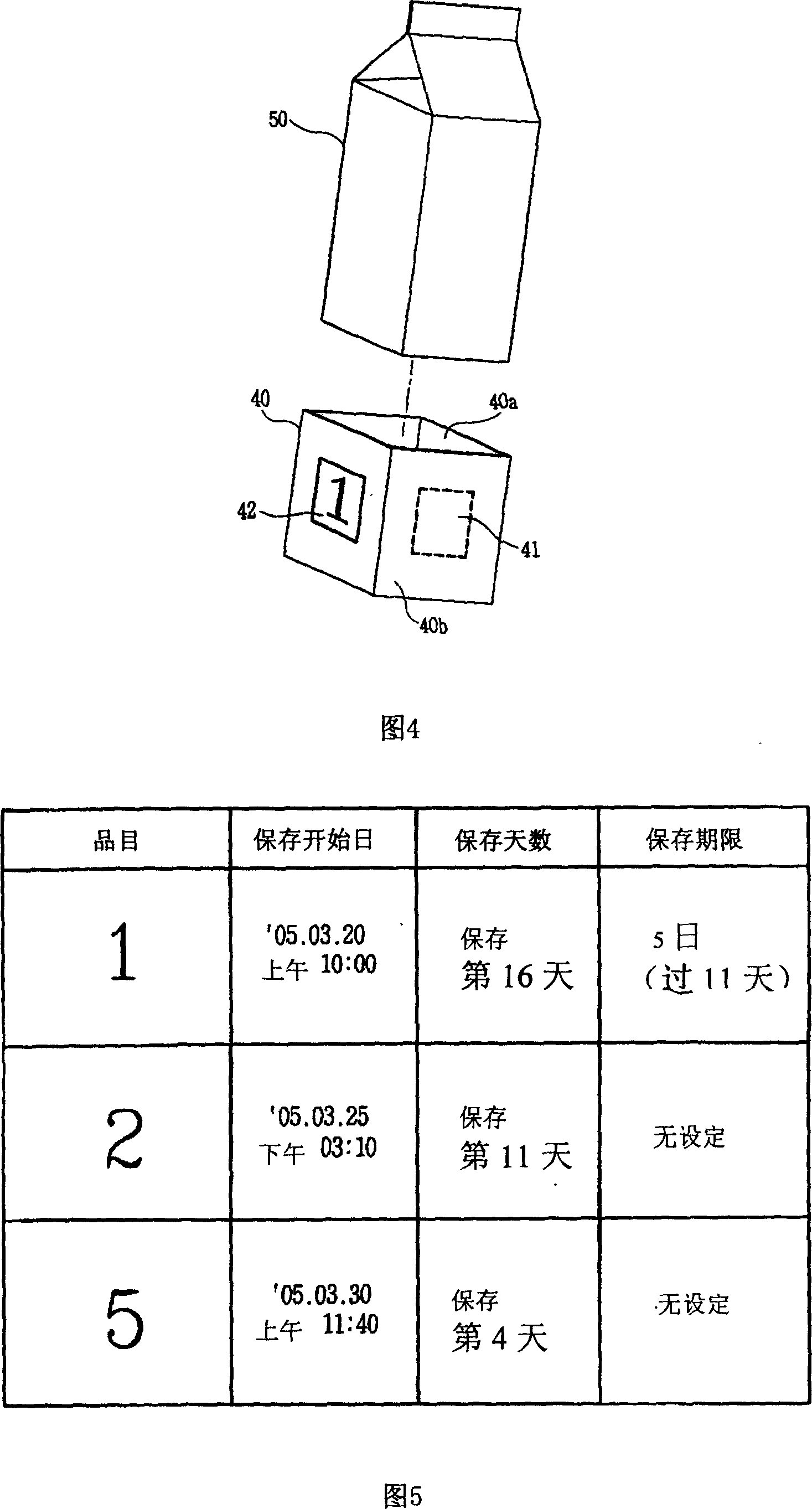
[0035] As shown in Figure 2, the food management refrigerator 100 includes an RFID reading device 21 for obtaining container information from an RFID special container (not shown) that will store food inside the refrigerator; an input device 22 for the user to input some commands Calculating the date and time timing device 23 of the year, month, day and time; storing various screens (frame: user interface, etc.) an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com