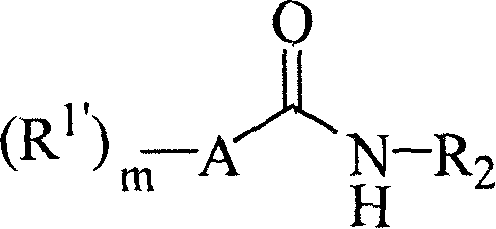
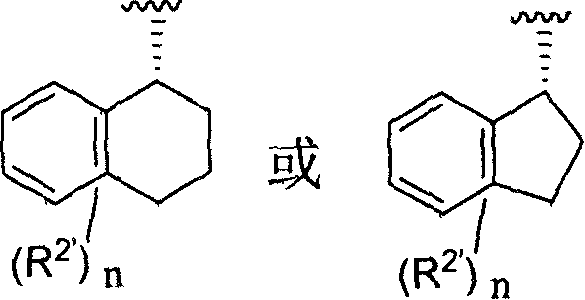
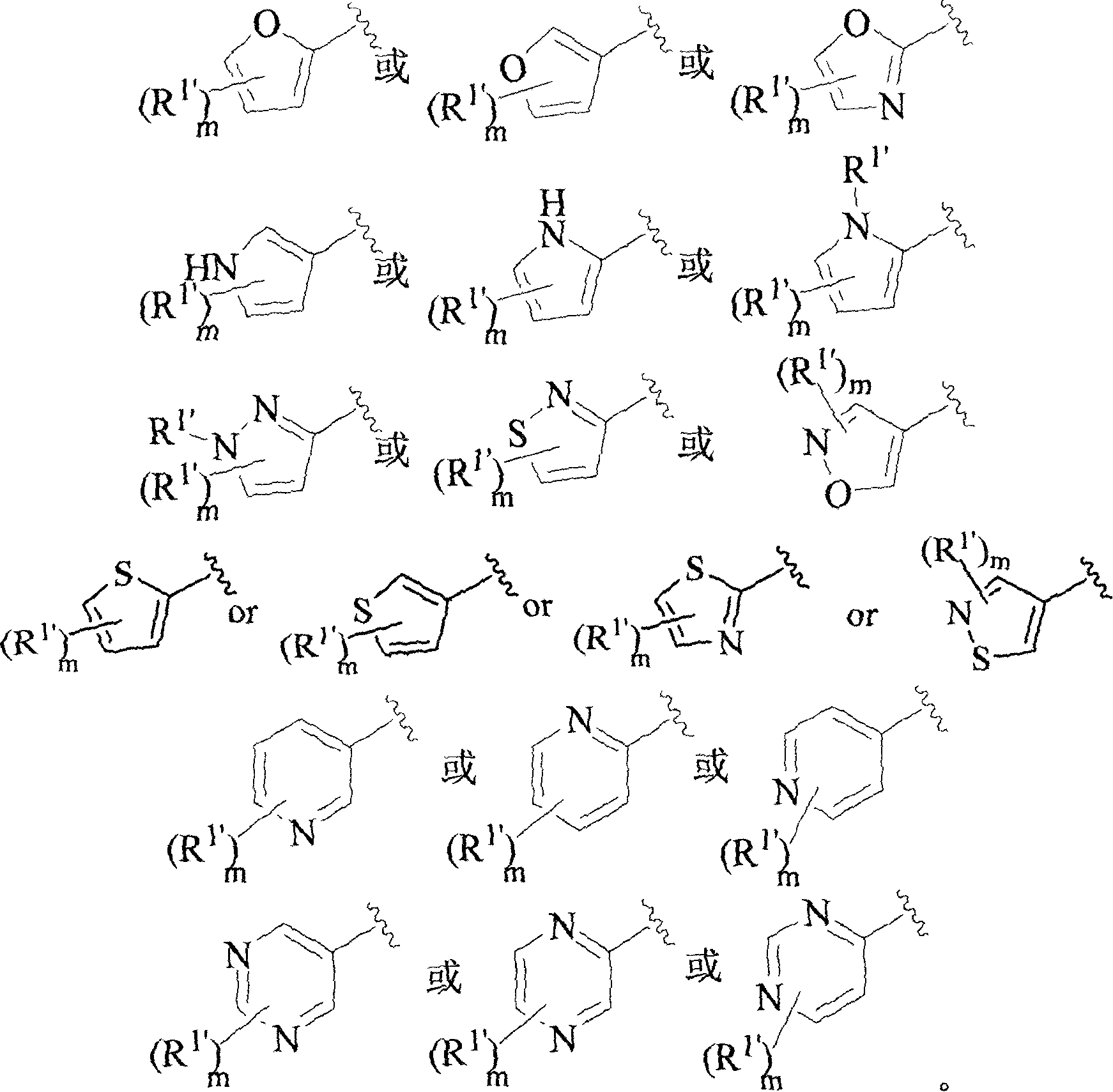
Aromatic amides and ureas and their uses as sweet and/or delicate flavor modifiers, flavouring agents and taste enhancers
A flavoring and sweetening technology, applied in the fields of savory or sweet flavorings and savory or sweet flavor enhancers, can solve the problems of expensive, difficult separation and purification of natural sources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0555] Reaction formula 1c. Preparation of oxalamide
[0556]
[0557] As a general procedure, react an amine with ethyloxalyl chloride in the presence of a tertiary amine in an organic solvent such as dioxane, acetonitrile, tetrahydrofuran, tetrahydropyran, and dimethylformamide at room temperature for 0.5 to 2 hours. The second amine was then added and the suspension was heated at 80°C overnight using an oil bath, or at 160°C for 5 minutes in a microwave reactor. The reaction mixture can be subjected to preparative HPLC, or subjected to aqueous work-up (aqueous work-up), and the crude product can usually be easily purified by recrystallization, flash column chromatography, or other methods well known to those of ordinary skill in the art to give pure ethyl diamide. The yields reported below were not optimized.
[0558] Reaction formula 1d. Preparation of urea
[0559]
[0560] x 1 、X 2 and x 3 Each is independently an alkyl or alkoxy group.
[0561]Scheme 2 des...
Embodiment 1
[0635] N-(hept-4-yl)benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-carboxamide
[0636]
[0637] To a solution of heptane-4-amine (8.06 mL, 54 mmol) in triethylamine (15.3 mL, 108 mmol) and dichloromethane (135 mL) was added dropwise dissolved in dichloromethane (135 mL) at 0°C. A solution of benzo[1,3]dioxol-5-carbonyl chloride (10 g, 54 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred for 1 hour. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue was dissolved in EtOAc. The organic layer was washed sequentially with 1N aqueous HCl, 1N aqueous NaOH, water, brine, and dried (MgSO 4 ) and concentrate. The residue was recrystallized from EtOAc and hexanes to afford 6.9 g of N-(heptyl-4-yl)benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-carboxamide (48.3%) as a white solid. 1 H NMR (500MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ0.92(t, 6H), 1.38(m, 6H), 1.53(m, 2H), 4.11(m, 1H), 5.63(m, 1H), 6.01(s, 2H), 7.98(d, 1H), 7.27 (s, d, 2H). MS (M+H, 264).
[0638] The compound activates the EC of hT1R1 / hT1R3 umami taste receptors expressed in HEK293...
Embodiment 2
[0640] N-(2-Methylhept-4-yl)benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-carboxamide
[0641]
[0642] Prepared in a similar manner to Example 1 using benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-carbonyl chloride and 2-methylheptan-4-amine (Example 2a). 1 H NMR (500MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ0.93(m, 9H), 1.38(m, 5H), 1.53(m, 1H), 1.66(m, 1H), 4.21(m, 1H), 5.61(d, 1H), 6.01(s, 2H), 6.82 (d, 1H), 7.26 (m, 2H). MS (278, M+H).
[0643] a. Preparation of 2-methylheptan-4-amine
[0644] To a solution of 2-methylheptan-4-one (4.24 g, 33.07 mmol) in methanol (60 mL) was added ammonium acetate (25.50 g, 330.71 mmol) and sodium cyanoborohydride (2.08 g, 33.07 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for about 24 hours. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure, the residue was diluted with water and basified with 15% aqueous NaOH, and extracted with ether. The extract was washed with brine, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered and evaporated to give 3.3 g of 2-methylheptan-4-amine (77%). MS (M+H,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com