A phonetic symbol decomposition and its synthesis method
A synthesis method and technology of phonetic symbols, applied in speech synthesis, speech analysis, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of uncoordinated tones, decreased voice naturalness, high calculation cost, etc., and achieve improved quality, less resource occupation, and simple calculation methods Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
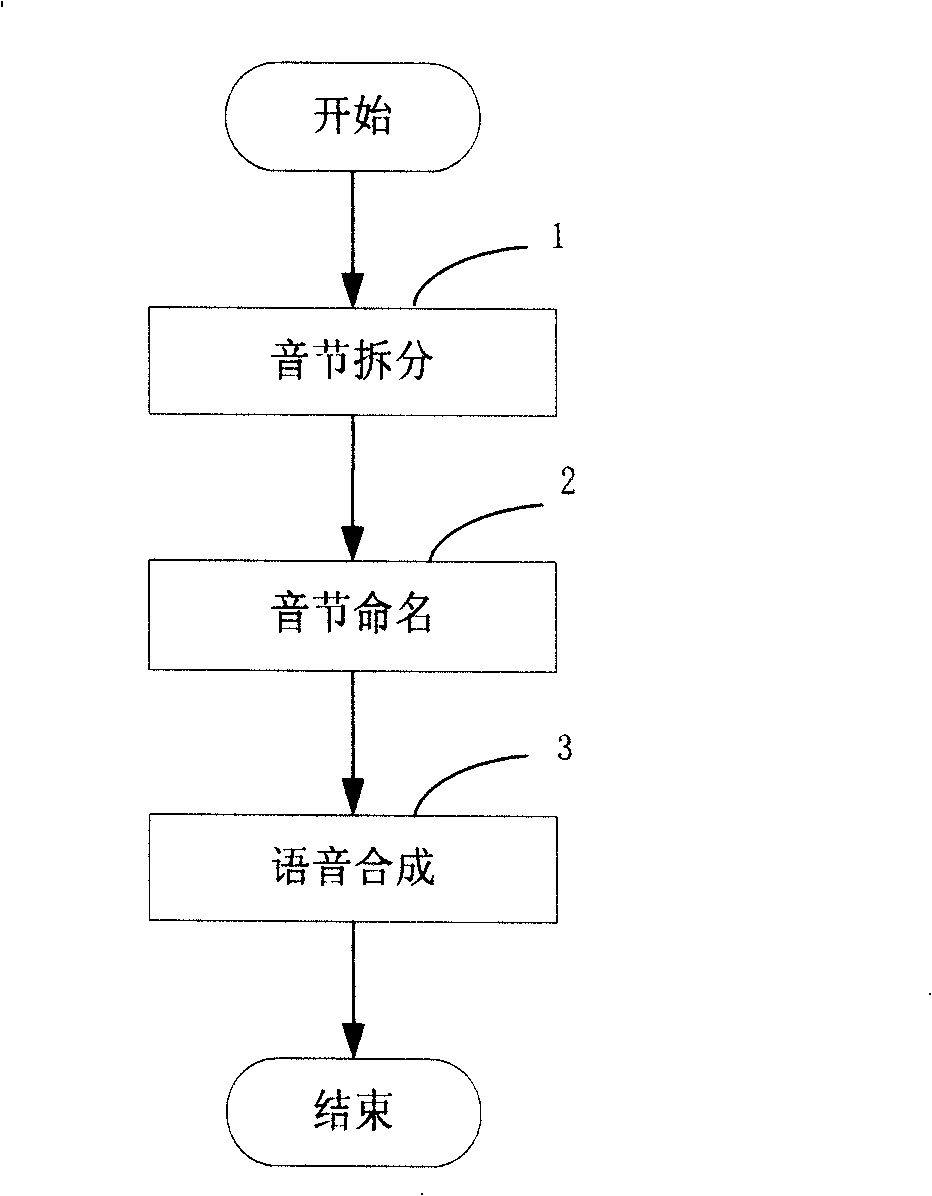
[0079] Embodiment 1 is described by taking English speech as an example. figure 1 It is a flow chart of decomposition and synthesis of phonetic symbols. Such as figure 1 As shown, the phonetic symbol decomposition and synthesis process includes the following steps:
[0080] Step 1 is syllable splitting: convert phonetic phonetic symbols into text phonetic codes, decompose according to waveform characteristics, and form segmentation units;
[0081] Step 2 is naming the syllable: according to the decomposed segmentation unit, name the segmentation unit according to the rules to form a pronunciation pronunciation unit;
[0082] Step 3 is speech synthesis: the phoneme waveforms corresponding to the speech pronunciation units are concatenated for speech synthesis.
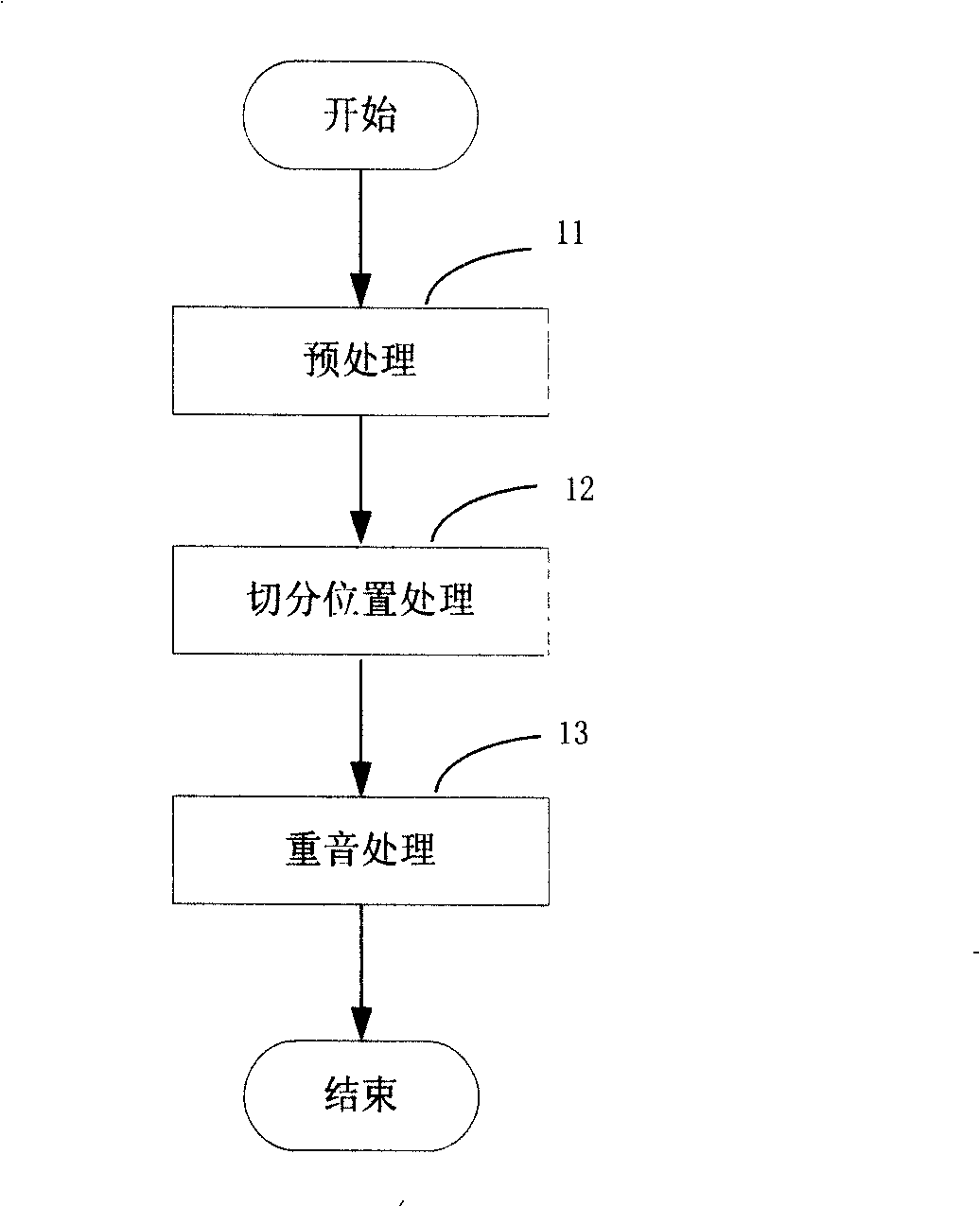
[0083] Such as figure 2 As shown, step 1 syllable splitting further includes three steps:
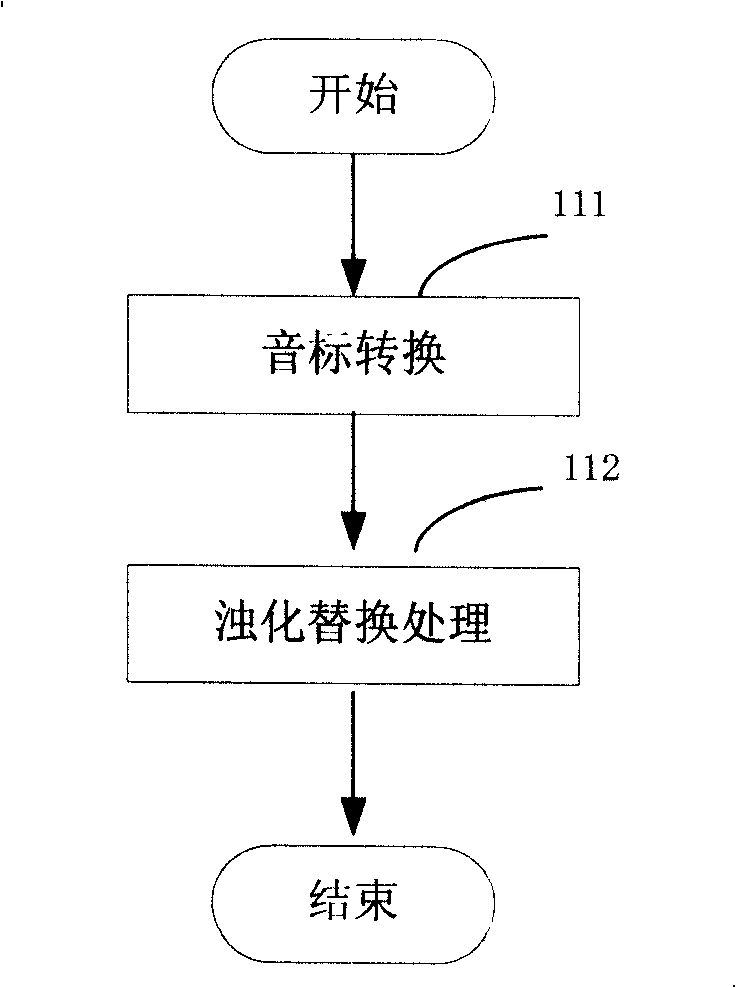
[0084] Step 11 is preprocessing: convert known phonetic symbol symbols into text phonetic symbol code, form text phonetic...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0155] Embodiment 2 is described by taking Chinese speech as an example. The process of decomposing and synthesizing the phonetic symbols of Chinese synthetic vocabulary and short sentences is basically consistent with the process of decomposing and synthesizing the phonetic symbols of English phonetic symbols in the specific embodiment 1, except that:
[0156] The basis for adding the segmentation mark at the corresponding position of the text phonetic symbol code sequence is different. According to the phoneme waveform features, the phonetic codes of Chinese speech can be divided into two categories:
[0157] The first type of collection, non-periodic waveform characteristic consonants, including pinyin are:
[0158] / b / , / p / , / f / , / d / , / t / , / g / , / k / , / h / , / j / , / q / , / x / , / zh / , / ch / , / sh / , / z / , / c / , / s / , a total of 17;
[0159] The second type of collection includes periodic waveform characteristic consonants and periodic waveform characteristic vowels, wherein the period...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0168] Embodiment 3 is described by taking Japanese voice as an example. The process of decomposing and synthesizing the phonetic symbols of Japanese synthetic words, phrases or short sentences is basically consistent with the process of decomposing and synthesizing English phonetic symbols in the specific embodiment 1, except that:
[0169] The basis for adding the segmentation mark at the corresponding position of the text phonetic symbol code sequence is different. According to the phoneme waveform characteristics, the phonetic codes of Japanese speech can be divided into two categories:
[0170] The first type of collection, the head pronunciation is hiragana with non-periodic waveform features, including:
[0171] か(ka) line, さ(sa) line, た(ta) line, ほ(ha) line and their corresponding voiced, semi-voiced and obtrusive lines, totaling 72;
[0172] The second type of collection, the head pronunciation is hiragana with periodic waveform features, including:
[0173] な(na) li...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com