Hearing aid battery alarm method, circuit for monitoring battery and hearing aid having the same
A technology for hearing aids and circuits, applied in hearing aids, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as user annoyance and increased frequency of alarms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
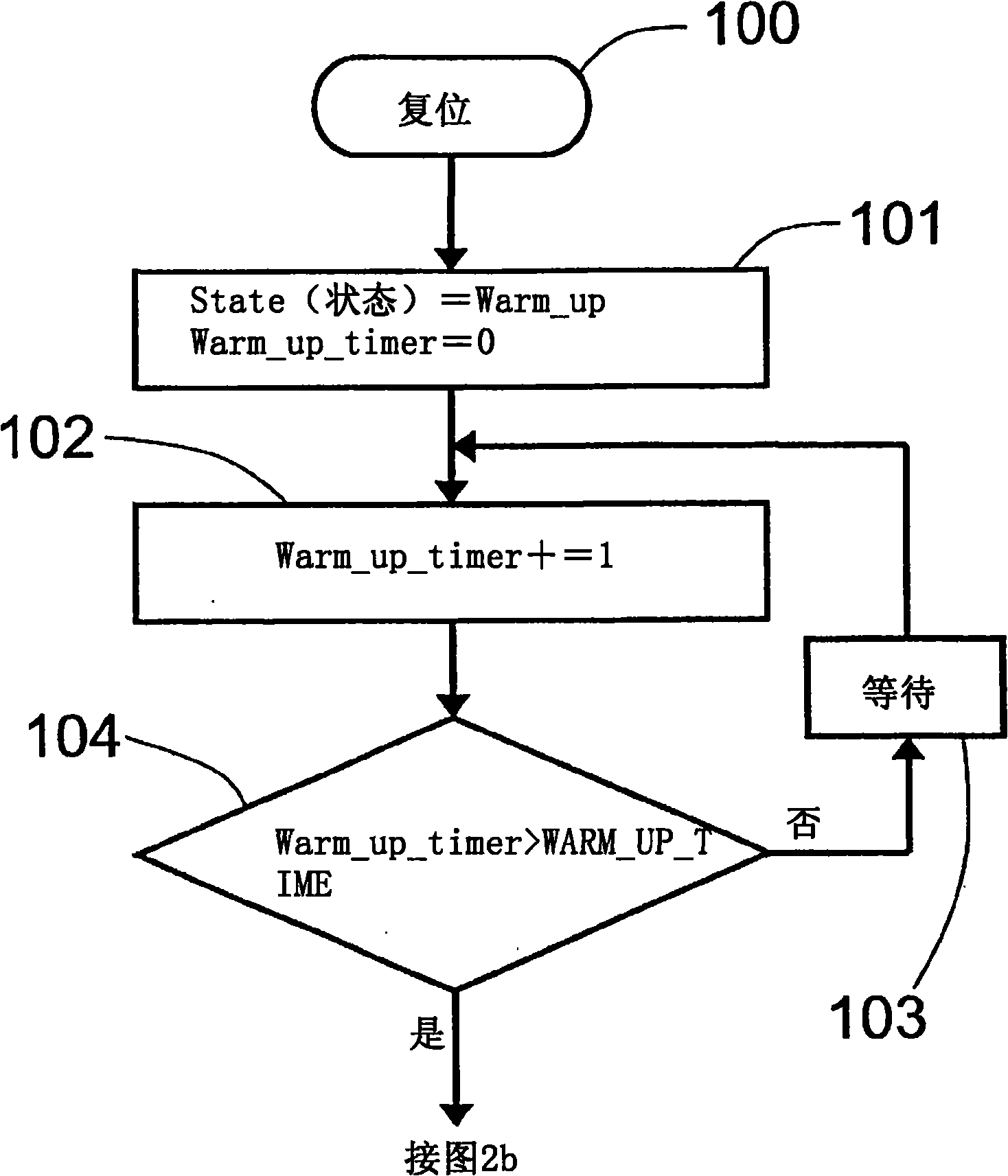
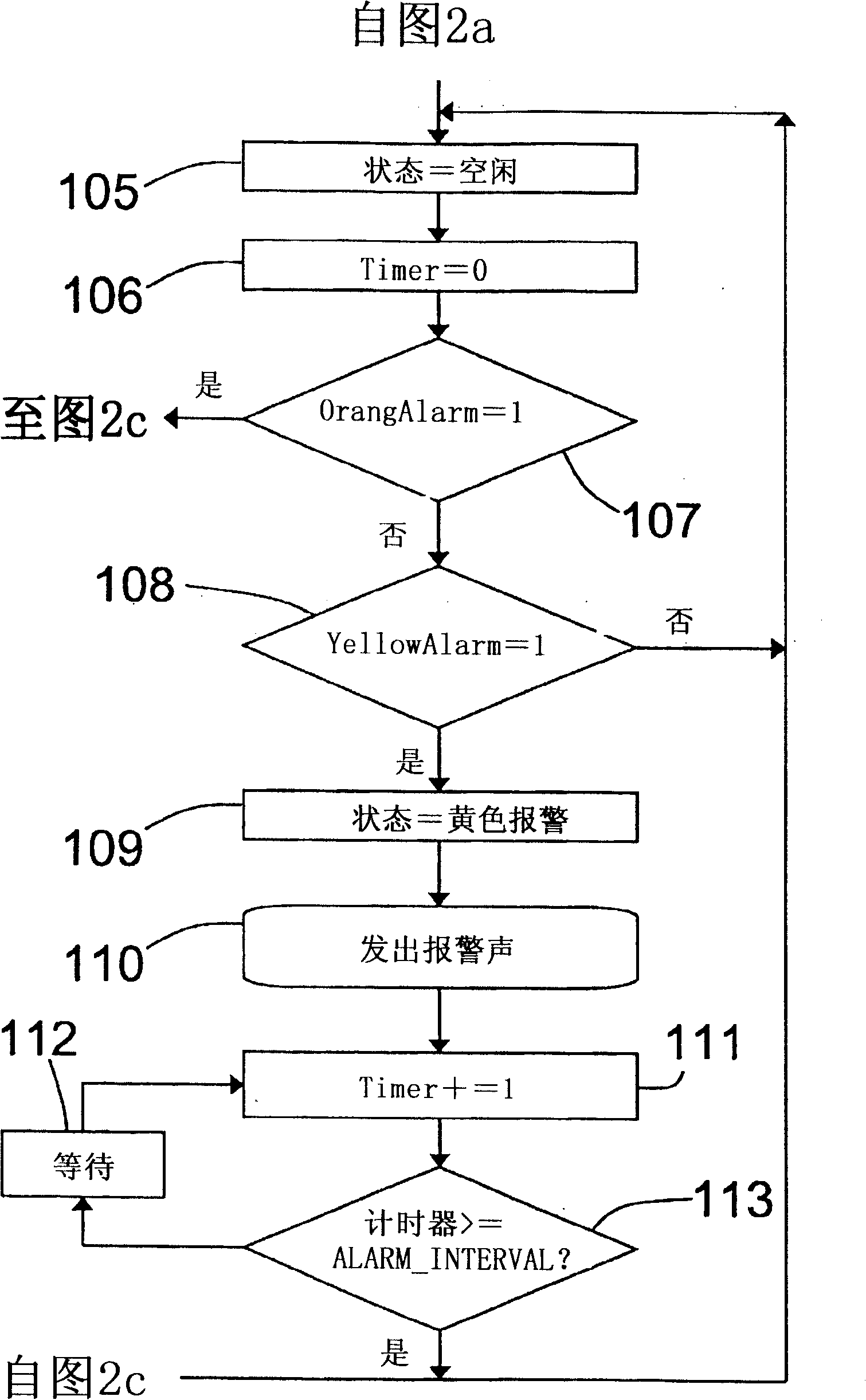
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
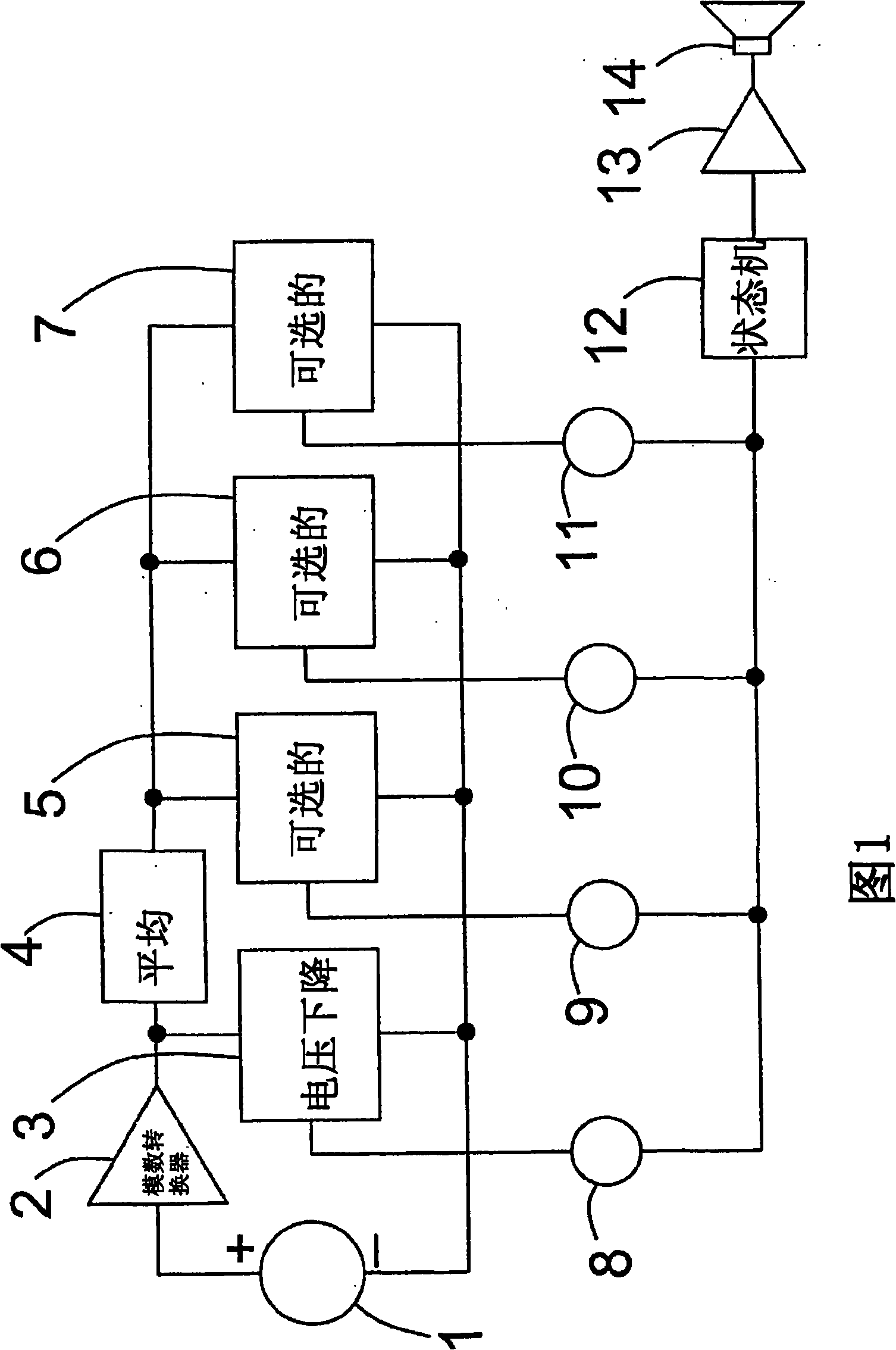
[0039] [0040] FIG. 1 is a block diagram schematically illustrating circuitry for performing the method of the present invention. The circuit includes a power supply. In the following examples, this power source is assumed to be a primary battery 1 , but the skilled person will understand that it could equally be an accumulator (secondary battery), a battery pack 1 or in principle any type of power source subject to a voltage drop. In the following it is also assumed that the method is implemented in a digital hearing aid, but obviously it can be used anywhere a battery warning is required.
[0040] [0041] The voltage of the battery is measured using an analog-to-digital converter 2, which converts the instantaneous voltage into a corresponding digital value for use in the digital circuitry of the hearing aid.
[0041] [0042] The instantaneous battery voltage value is fed to a brownout module 3, which will be described in further detail below. The digital values correspondi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com