Large scale publishing and subscribing pipelined matching method based on noumenon
A publish-subscribe and matching method technology, applied in the computer field, can solve problems such as time-consuming, difficulty in merging RDF subscription graph modes, failure to meet the performance requirements of large-scale publish-subscribe middleware systems, etc., to eliminate redundant matching and improve matching efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
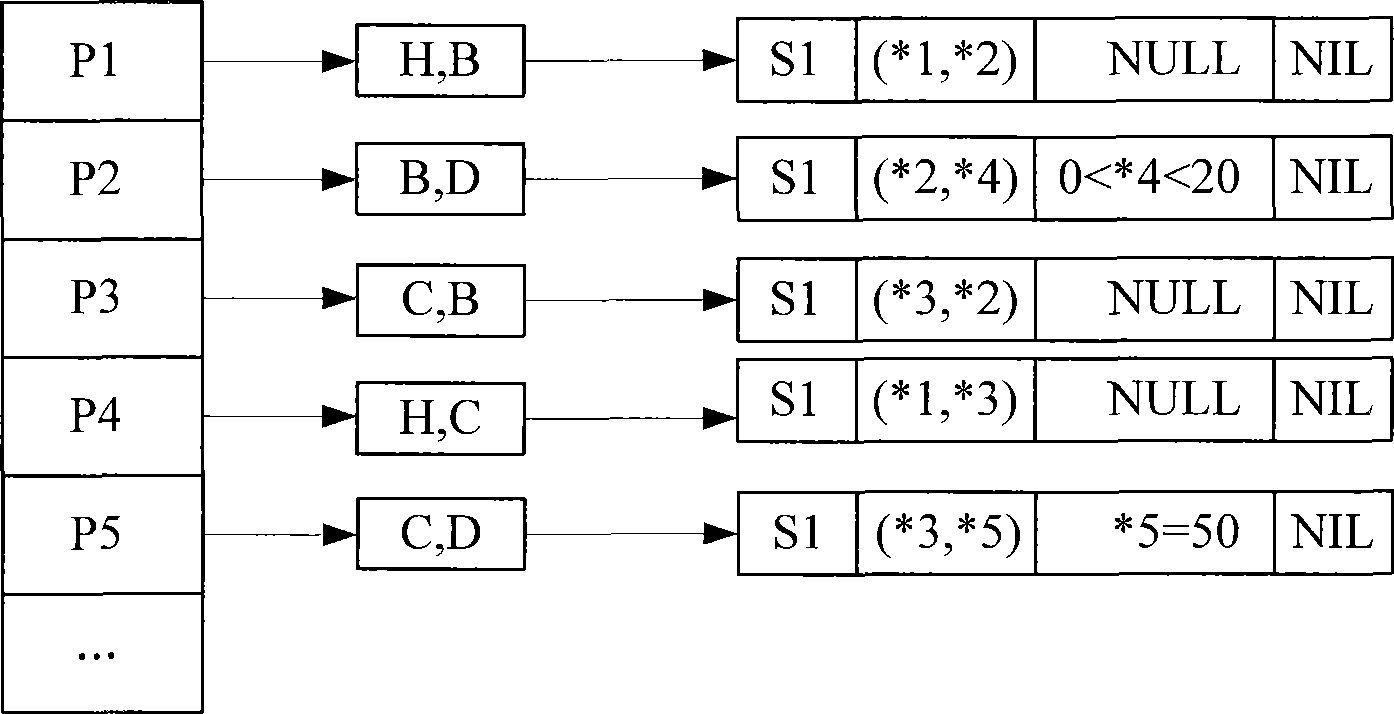
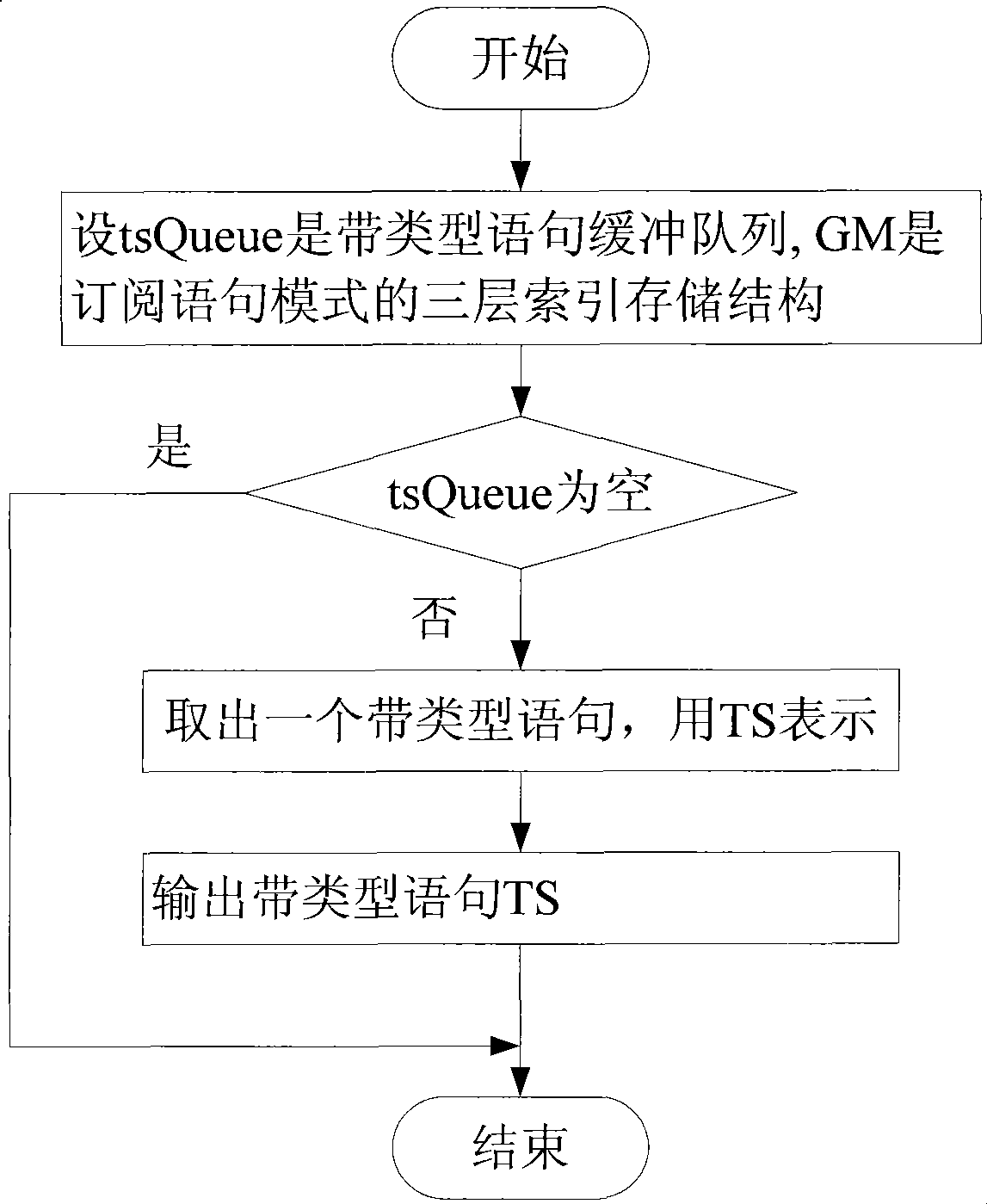
[0027] A large-scale publish-subscribe pipeline matching method based on ontology includes the following steps:
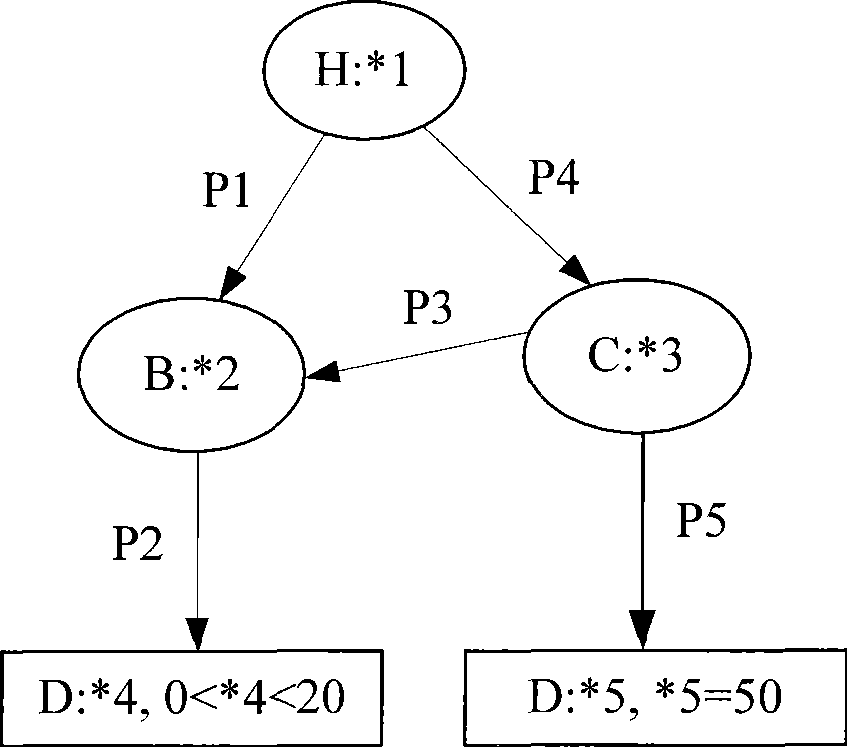
[0028] Step (1) Establish the event / subscription ontology model: use the RDF ontology description language to express the event / subscription in the form of RDF event graph or RDF subscription graph mode, specifically:
[0029] ① RDF event graph: RDF language expresses objective facts in the form of triples (Subject, property, Object), and each triple is called an RDF statement. Among them, the subject (Subject) is the URI reference of the described resource, the predicate (property) is the URI reference of a property, and the object (Object) is the value of the property, which can be a URI reference or text. If the subject and object are represented by nodes, and the predicates are represented by directed arcs, one or more RDF statements can be represented as a directed labeled graph, called an RDF graph. In the method of the present invention, each event is repre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com