Personal security device in traffic accidents
A protection device and personnel technology, which is applied in the field of safety protection devices for people in car accidents, can solve problems such as moving backwards and reducing the possibility of people being stuck
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
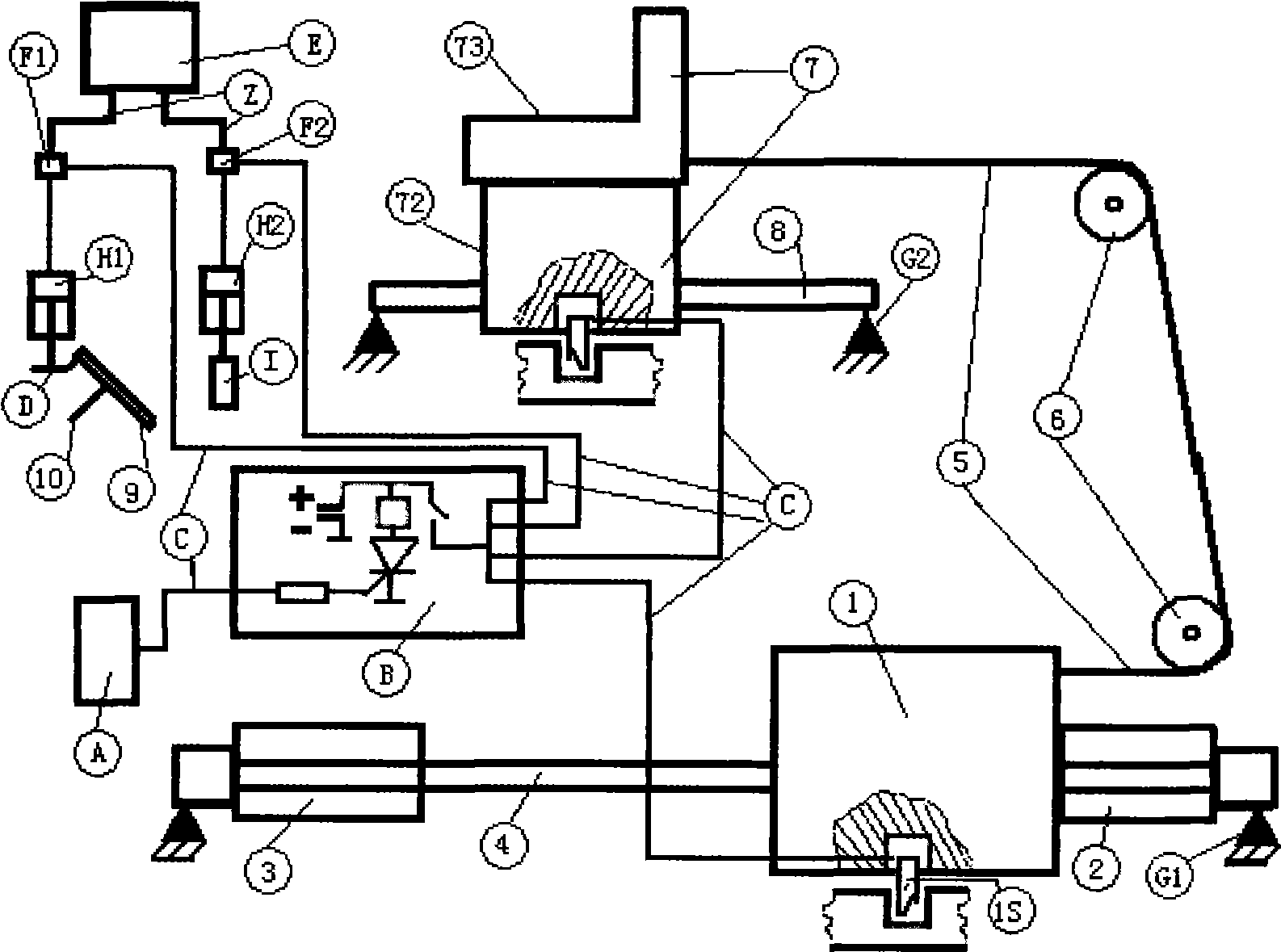
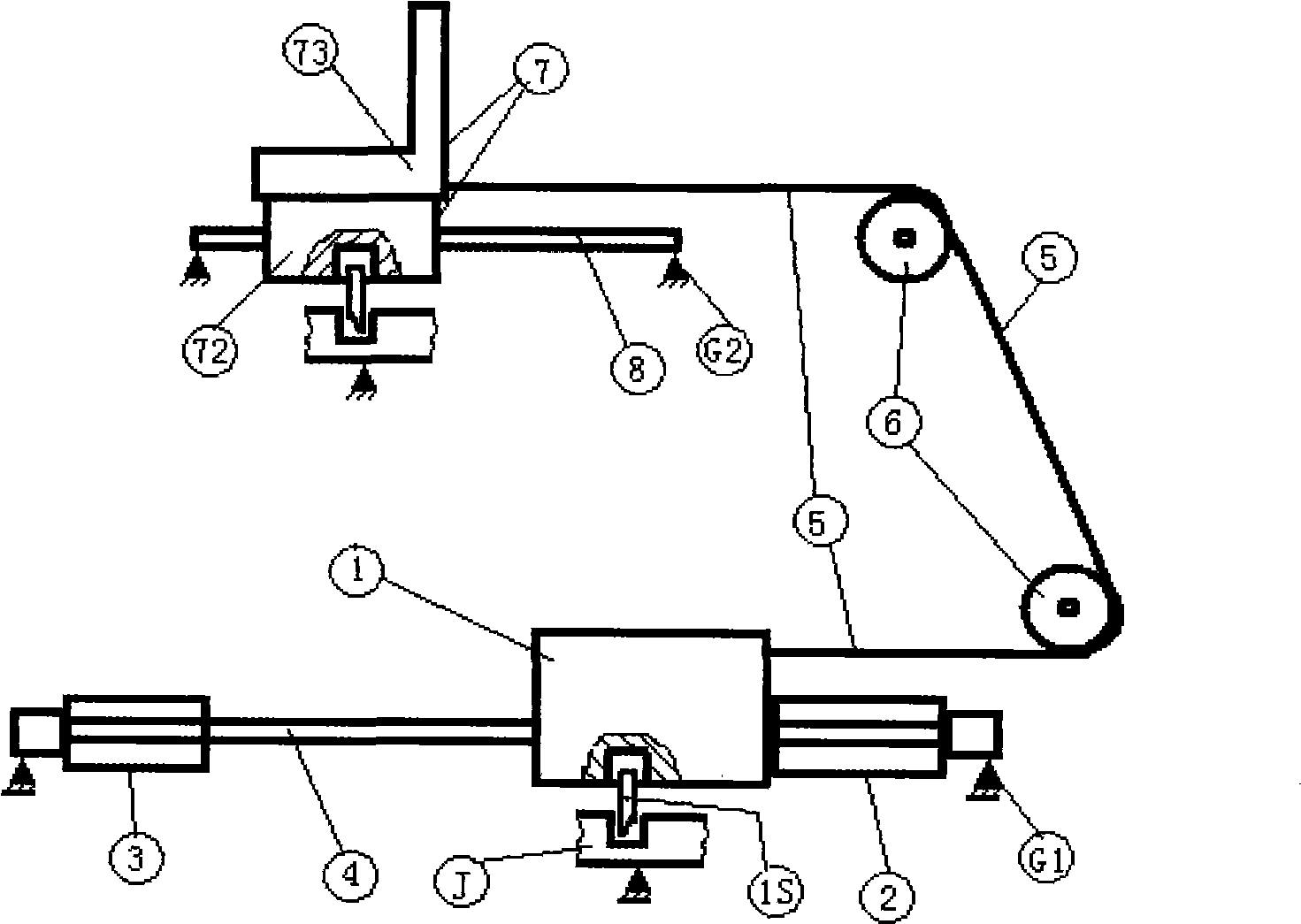
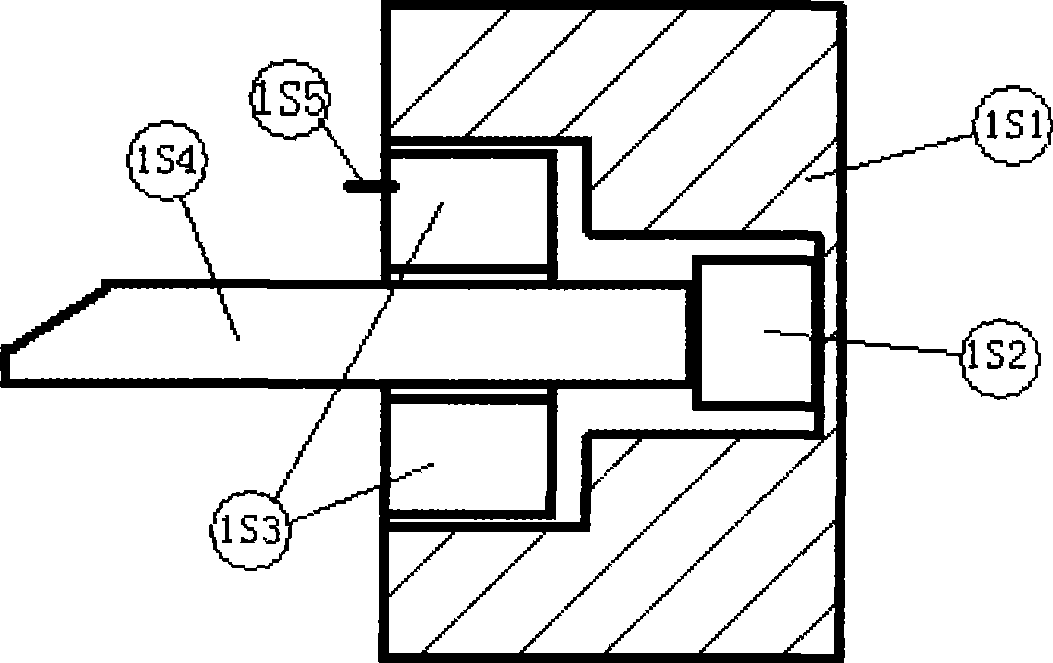
[0038]The device is composed of the vehicle front seat back moving system, automatic braking system, automatic power off system, control circuit system, collision degree detection system and connecting wires. The current-limiting starting resistor BR of system B is electrically connected, and the output connecting wire C of the intermediate relay BMK of control circuit system B is respectively connected to the electromagnetic coil package 1S3 and electromagnetic coil package 1S3 of the electromagnetic control lock in the inertial kinetic energy weight block 1 of the vehicle front seat rearward movement system. The electromagnetic coil package 7S3 of the electromagnetic control lock in the seat 7 that can be moved backward is electrically connected. The output connection wire C of the intermediate relay BMK of the control circuit system B is electrically connected with the electromagnetic coil F1 of the electromagnetic air pressure valve in the automatic braking system. The out...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com