Method for measuring distance between star and earth
A measurement method and distance technology, applied in the field of measurement of planetary distance, can solve problems that are not the actual distance of the planet
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
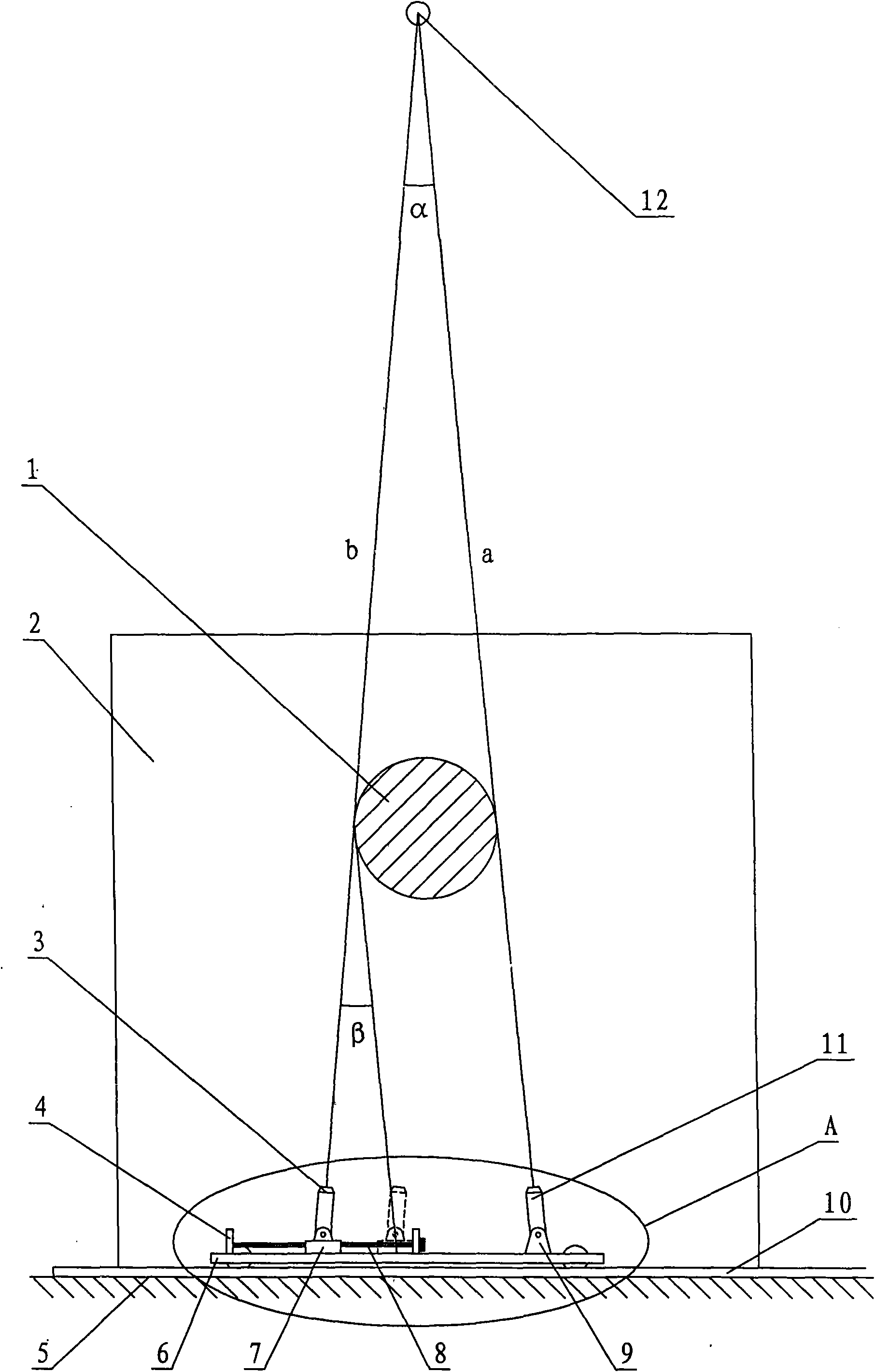
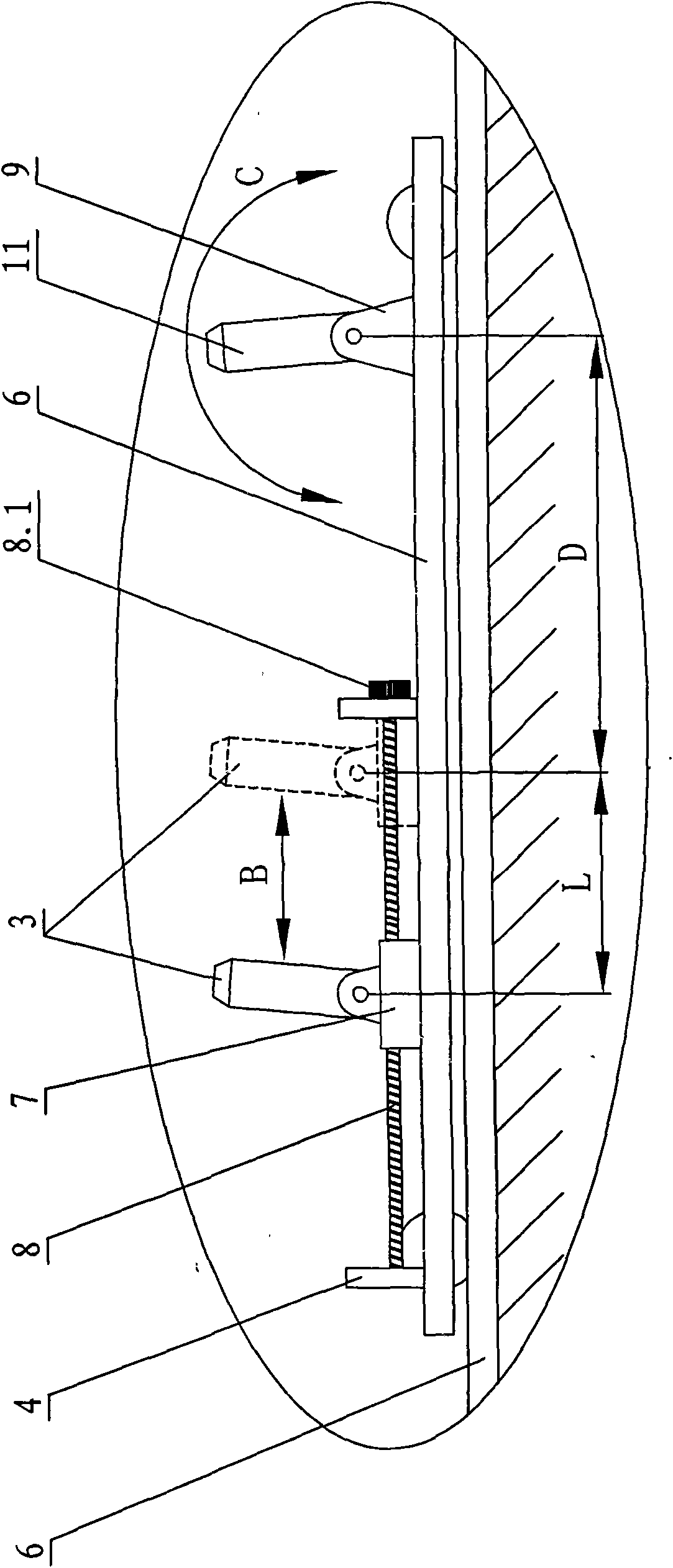
[0018] A method of measuring the distance of a planet, including a fixed obstacle in the sky, through two viewing points on the ground on the same north-south pointing line, and viewing from both sides of the obstacle and the star to be measured in a straight line, the two The straight lines intersect at the star to be measured, and the angle formed is the angle of view difference of the star to be measured; taking the radius of the earth as the base, it is calculated that the angular difference of 1 second = 360*60*60 / 6.2832*6350 km = 1.309.778.457 km ≈8.732 astronomical units, and finally divide the angular difference of 1 second by the viewing angle difference to get the distance from the measured star to the center of the earth. The obstacle is a horizontal bar with a circular cross section. The straight line formed by one viewing point and the star...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com