Method for measuring distance of celestial bodies
A measurement method and technology for stellar objects, which are applied in the directions of line-of-sight measurement, measurement device, measurement distance, etc., and can solve problems such as the inability to accurately record the distance of stars
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0015] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
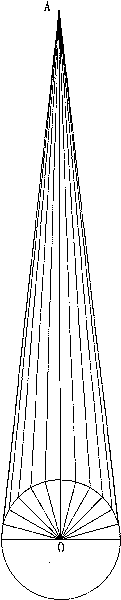
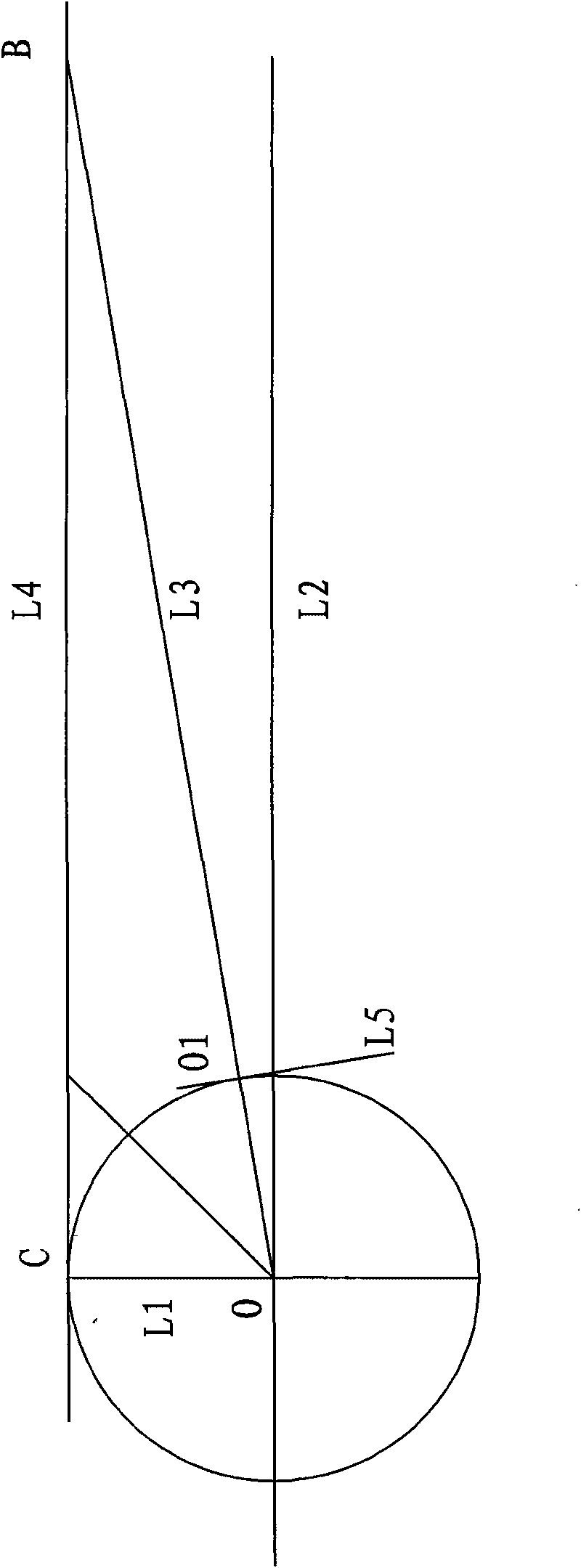
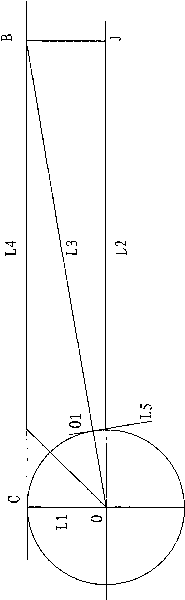
[0016] see figure 1 , to accurately measure the distance of the planet, it is necessary to analyze the transmission of starlight A. The transmission of light is emitted from the luminous point to all directions, forming a radiation angle. The position where the starlight can be seen on the earth forms a line with the starlight. In a straight line, the light of every star in the sky radiates to the range of the hemisphere of the earth, and radiates the whole earth with the rotation of the earth. The angles of starlight measured at different locations are different. When the starlight radiates to the hemisphere of the earth, there must be one point on the earth perpendicular to the stars, and two points on the horizontal line. This is the radiation angle of the starlight. The earth itself also has a radiation angle, which is radiated from the center poin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com