Method for detecting transmission line fault direction
A technology for transmission lines and fault directions, applied in directions such as fault locations, can solve the problems that current fault transient traveling wave fault direction detection and direction protection cannot be realized, and voltage fault transient traveling wave wave head transmission cannot be changed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
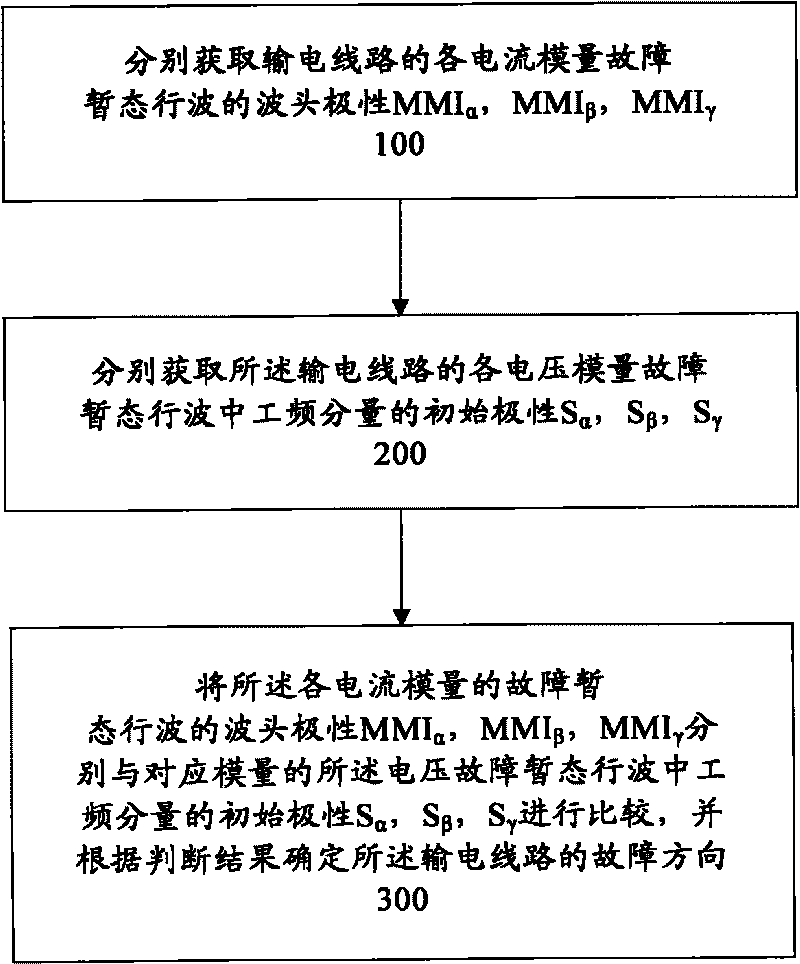
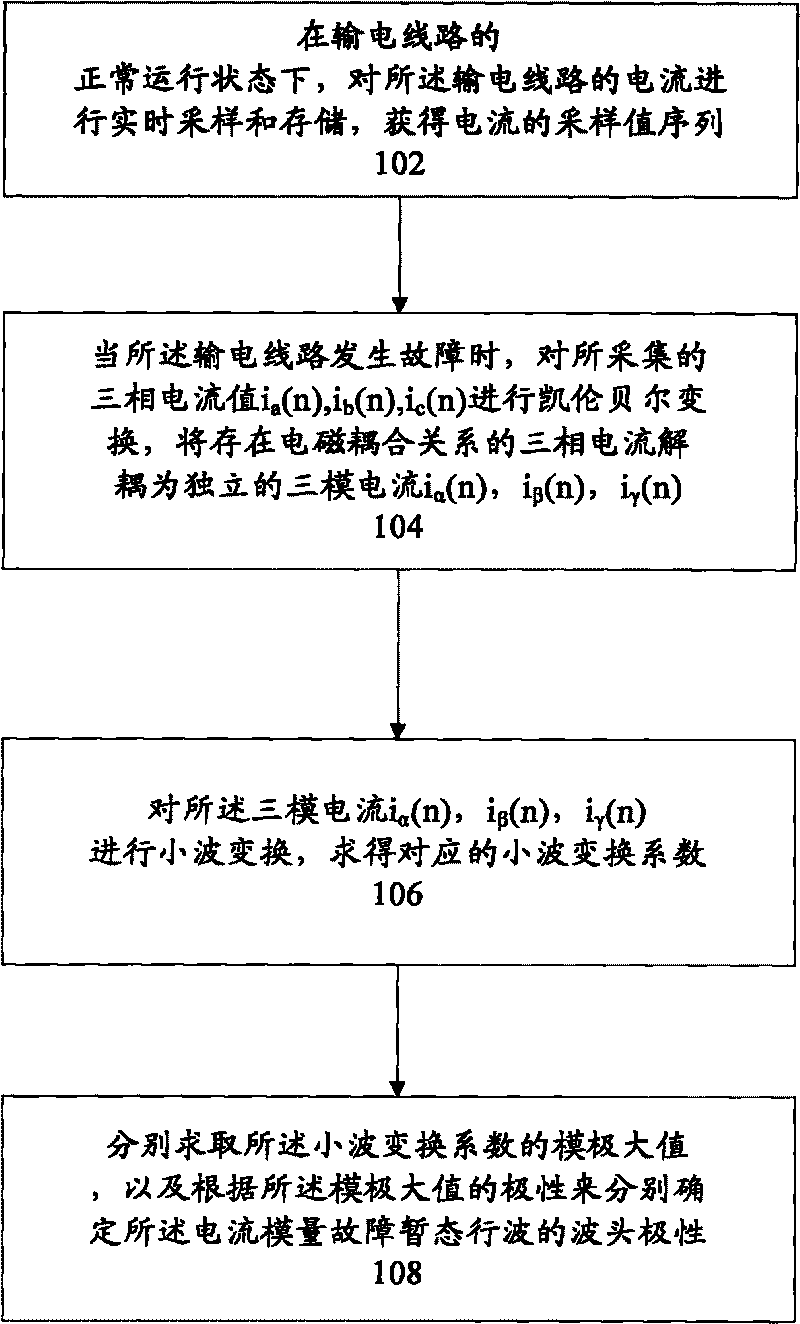
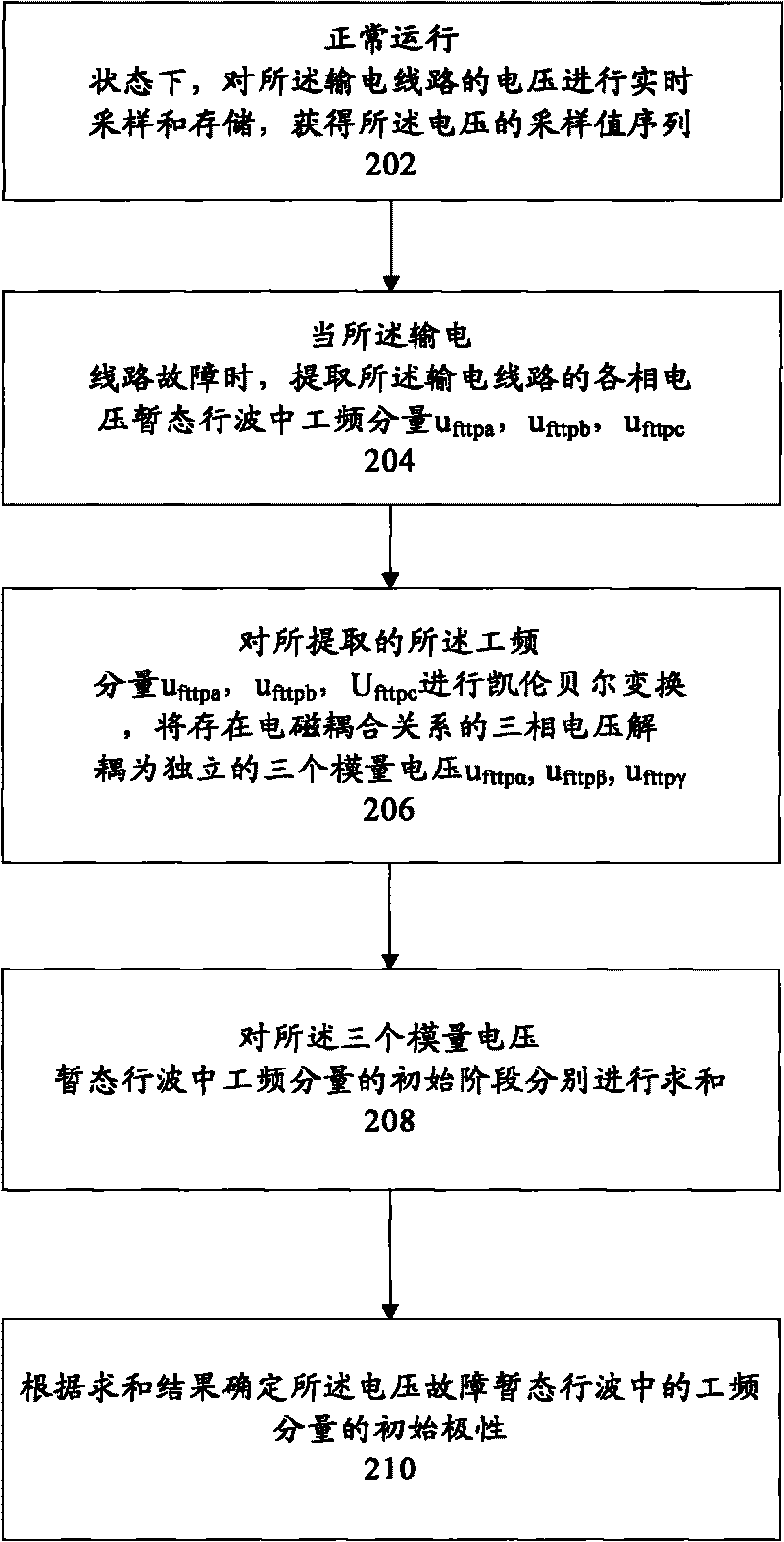
[0027] figure 1 A flow chart of a method for detecting a fault direction of a transmission line according to an embodiment of the present invention is shown. The method for detecting the fault direction of the transmission line includes: step 100, respectively obtaining the wave head polarity MMI of the three current modulus fault transient traveling waves of the transmission line α , MMI β , MMI γ ; Step 200, respectively obtain the initial polarity S of the power frequency component in the three voltage modulus fault transient traveling waves of the transmission line α , S β , S γ ; Step 300, the wave head polarity MMI of each current modulus fault transient traveling wave α , MMI β , MMI γ Respectively with the initial polarity S of the power frequency component in the voltage fault transient traveling wave corresponding to the modulus α , S β , S γ making a comparison, and determining the fault direction of the transmission line according to the judgment result. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com