Data splicing technology for measuring flatness of super large plane
A technology of data splicing and flatness, which is applied in the field of data splicing technology for measuring the flatness of super large planes, and can solve the problems that the laser beam energy cannot be too large, the flatness of the inclined plane cannot be measured, and the measurement time is long.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
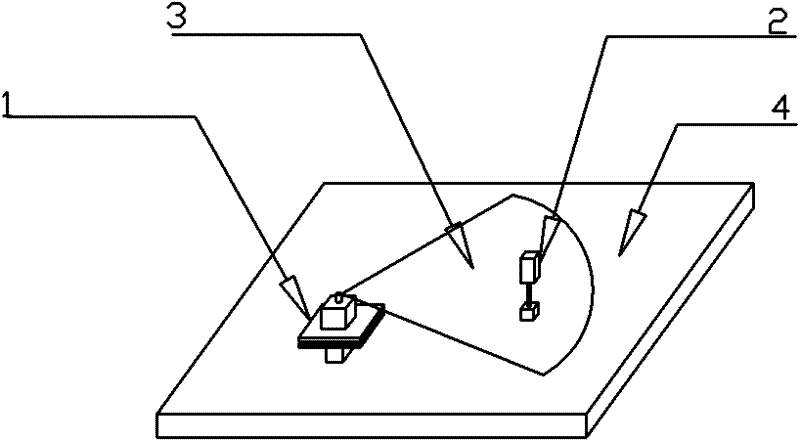
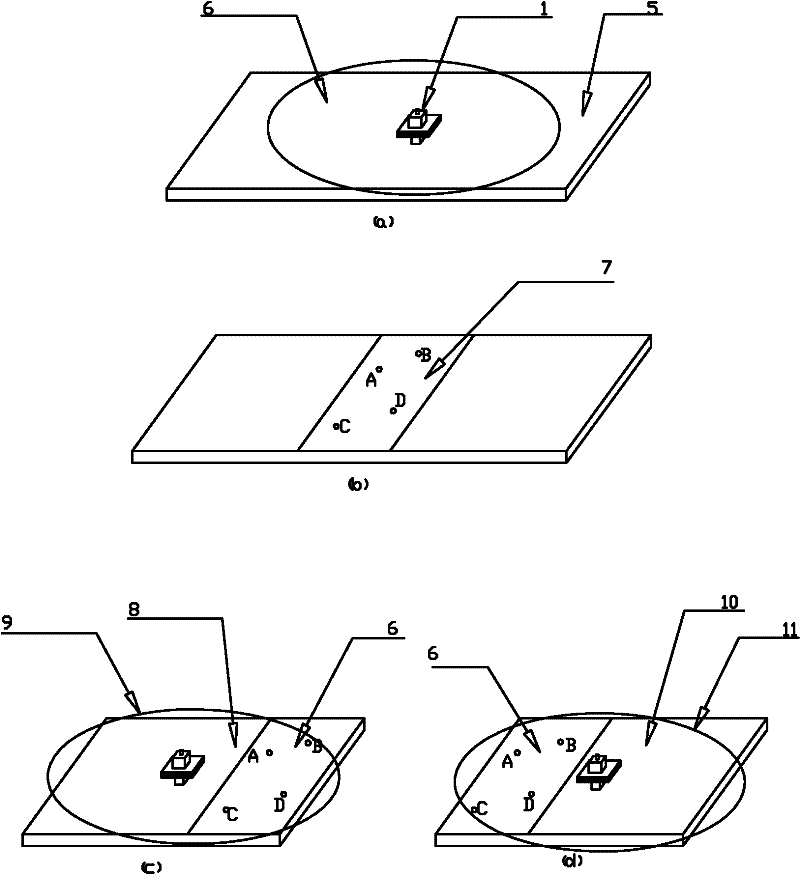
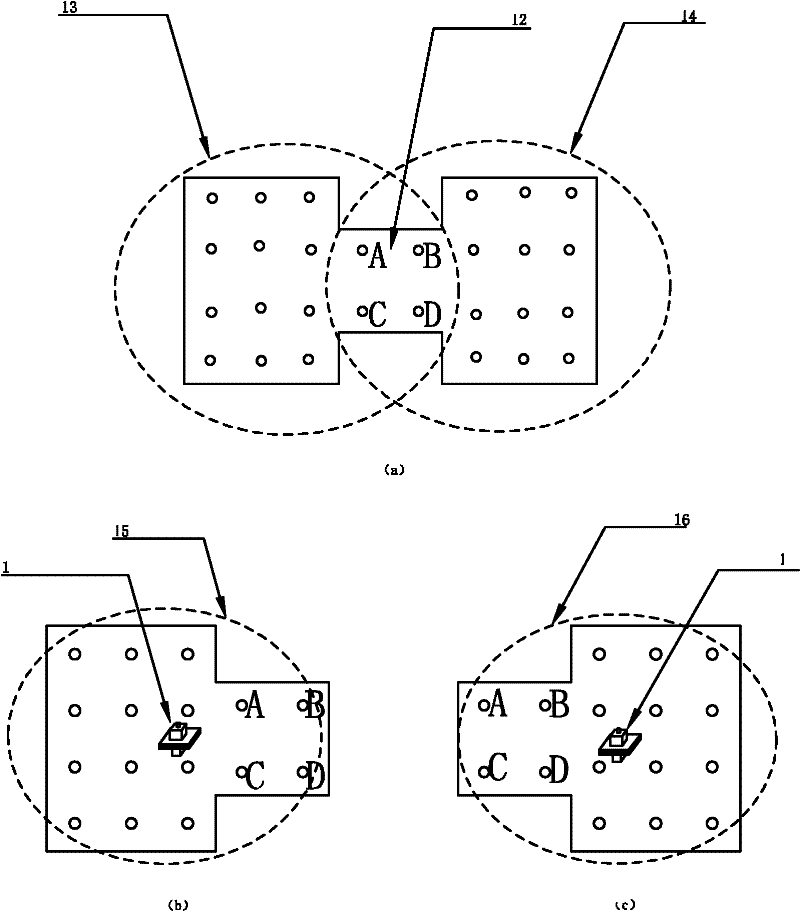
[0054] The specific embodiments of the present invention are shown in the drawings, and the laser collimation scanning method measures flatness as figure 1 As shown, first arrange appropriate sampling points on the measured plane (4), place the laser emitting device laser (1) on the measured plane (4), and place the photoelectric receiving device laser target (2) in sequence on the measured plane (4). On the measured sampling point, within the laser beam effective scanning area of the laser beam surface h(3), the height difference of the measurement point relative to the laser beam surface h(3) can be obtained. The coordinates of each point are recorded during the measurement, where the x-axis and y-axis coordinates are the position coordinates of the measuring point on the measured plane (4), and the z-axis coordinate is the height difference of the measuring point relative to the laser beam surface h(3). Finally, the flatness evaluation algorithm is used to process the measu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com