A common mode method and system for GSM and LTE/LTE-A
An LTE-A and GSM frequency band technology, applied in wireless communication, electrical components, network planning, etc., can solve the problem of not improving the spectral efficiency of LTE/LTE-A systems, and achieve the effect of improving spectral efficiency and reducing design and manufacturing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] This embodiment takes the GSM and LTE common mode as an example, specifically including:
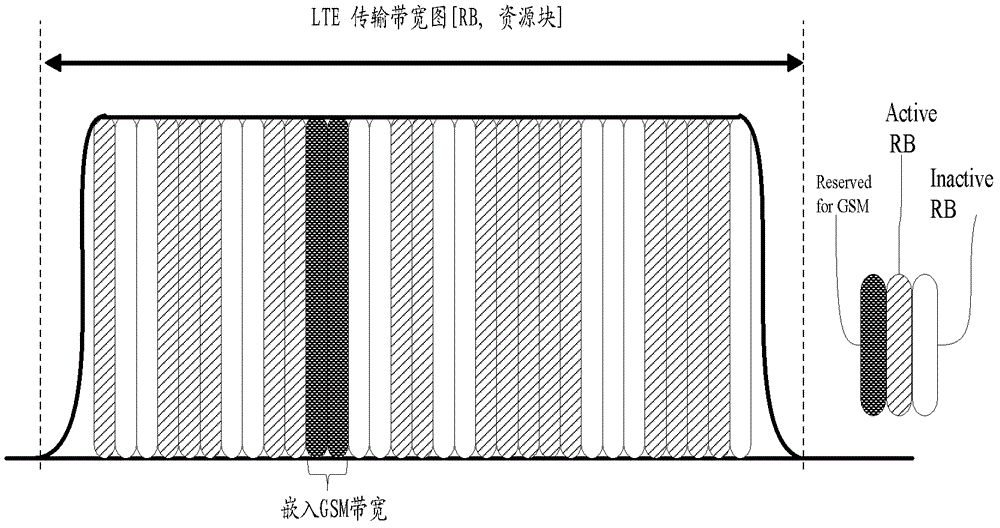
[0049] First, according to the current GSM and LTE / LTE-A bandwidth configuration, determine the position where the GSM bandwidth is embedded in the LTE system bandwidth, and embed the GSM bandwidth as a subband in the determined position;
[0050] Considering that the LTE downlink pilot frequency spreads over the entire LTEDL bandwidth, in order to avoid direct mutual interference between the LTEDL pilot frequency and the GSM signal, the GSM bandwidth embedding position should be selected as much as possible on the LTE uplink system bandwidth;
[0051] The physical uplink control channel (PUCCH, PhysicalUplinkControlChannel) of the LTE uplink is located at both ends of the UL system bandwidth. In order to avoid interference between the GSM signal and the PUCCH, when the GSM bandwidth is embedded in the LTE uplink, the embedding position should avoid the PUCCH dedicated resources, a...
Embodiment 2
[0056] This embodiment takes the GSM and LTE common mode as an example, specifically including:
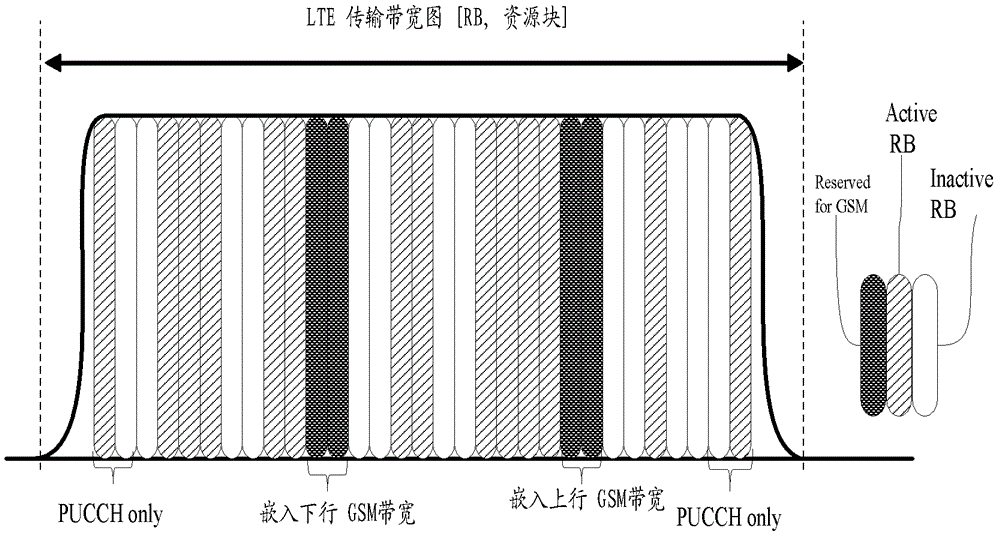
[0057] First, according to the current GSM and LTE / LTE-A bandwidth configuration, determine the position where the GSM bandwidth is embedded in the LTE system bandwidth, and embed the GSM bandwidth as a subband in the determined position;
[0058] In this embodiment, it is assumed that the GSM bandwidth does not meet the condition of being fully inserted into the uplink bandwidth of the LTE system. At this time, half of the GSM bandwidth is embedded in the uplink bandwidth of the LTE system, and the other half is embedded in the downlink bandwidth of the LTE system or placed in the LTE system. system bandwidth.
[0059] Among them, when some parts are embedded in the LTE system downlink bandwidth, there may be interference between the GSM signal and the LTE downlink pilot because the LTE downlink pilot frequency is throughout the entire LTE DL bandwidth; and when part is placed in...
Embodiment 3
[0064] This embodiment takes GSM and LTE-A common mode as an example, specifically including:
[0065] First, according to the current GSM and LTE / LTE-A bandwidth configuration, determine the position where the GSM bandwidth is embedded in the LTE-A system bandwidth, and embed the GSM bandwidth as a subband in the determined position;
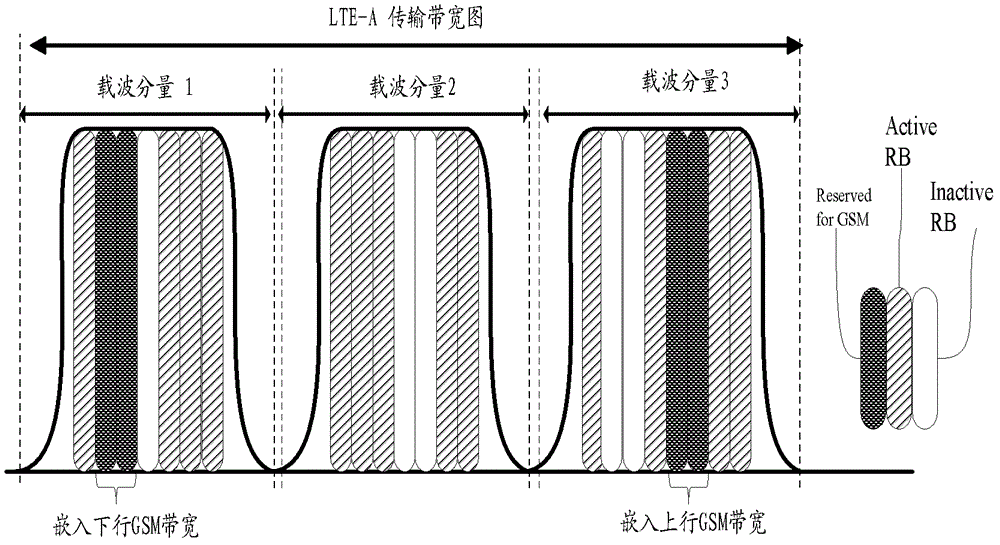
[0066] Based on the principle of avoiding interference between LTE-A and GSM, this embodiment embeds the GSM bandwidth into the LTE-A uplink bandwidth; and the GSM bandwidth embedding position avoids the physical uplink control channel, such as image 3 shown.
[0067] It should be noted that the GSM system bandwidth is usually 1M to 2M wide, the LTE system bandwidth is usually 1.4M to 20M, and the LTE-A system bandwidth is usually 100M. It can be seen that the narrowband GSM bandwidth can usually be embedded in LTE-A In the uplink bandwidth of system A. Since the LTE-A system bandwidth is composed of multiple carrier components (CC, Componen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com