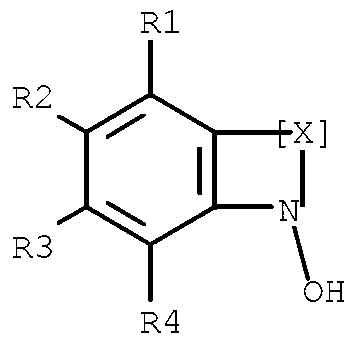
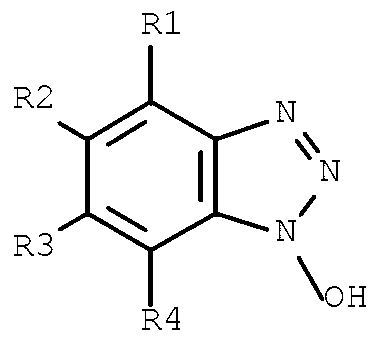
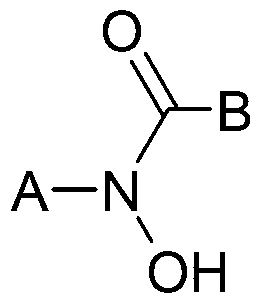
Removal of selenocyanate or selenite from aqueous solutions
A technology of aqueous solution and selenous acid, applied in water/sludge/sewage treatment, biological water/sewage treatment, water pollutants, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0158] Spectrophotometric microassay to quantify SeCN - : starting rate method
[0159] A catalytic spectrophotometric method was used to quantify selenocyanate (ester / salt) in an aqueous matrix. All stock solutions and buffers were prepared according to Table 1. The analytical results from the calibration (Table 2) demonstrate that SeCN- can be quantified by this particular assay as long as its levels are within the range of the calibration standards (0.494-4.935 ppm).
[0160] Table 1: Stock solutions and buffers
[0161]
[0162]
[0163] Calibration standards ranging from 0.494 to 4.935 ppm Se (as SeCN-) in 50 mM sodium acetate (NaAc) buffer were prepared using SeCN-stock 2. Reagents, buffers, standards, and samples were added to the wells of a standard 96-well microplate according to the steps detailed in Table 3. Four wells were allocated for each standard and 8 wells for each sample. An additional four wells were reserved on the plate for a reagent blan...
Embodiment 2
[0169] Enzymatic removal of selenocyanate (esters / salts) from aqueous solutions )
[0170] Prepare a total working volume of 200 ml in four 250 ml flasks using stock buffer, reagents, Millipure water and Myceliophthora thermophila laccase according to Table 4. A Teflon-coated stir bar was placed in each flask, and glass wool was used to stopper the neck of each flask. The flask was then placed on a magnetic stir manifold submerged in a 40°C water bath. Care was taken to ensure that the contents of the flask were below the water level in the water bath. Insertion of tubes into each flask enabled continuous oxygen sparging throughout the incubation period. Oxygen was bubbled through millipure water prior to sample introduction to minimize sample loss over time. While stirring the oxygen sparged samples, Myceliophthora thermophila laccase was added to flasks 3 and 4. After 1 and 300 minutes of incubation, 1 ml aliquots were removed from each flask and immediately centrifuge...
Embodiment 3
[0177] Enzymatic removal of selenocyanate ( ester / salt)
[0178] Prepare a total working volume of 200 ml in five 250 ml flasks using stock buffer, reagents, Millipure water and Myceliophthora thermophila laccase according to Table 6. A Teflon-coated stir bar was placed in each flask, and glass wool was used to stopper the neck of each flask. The flask was then placed on a magnetic stir manifold submerged in a 40°C water bath. Care was taken to ensure that the contents of the flask were below the water level in the water bath. Tubes were inserted into each flask to enable continuous oxygen or nitrogen sparging throughout the incubation period. Oxygen or nitrogen is bubbled through millipure water prior to sample introduction to minimize sample loss over time. Oxygen was bubbled into flasks 1-4 and nitrogen into flask 5. While stirring the sparged samples, Myceliophthora thermophila laccase was added to flasks 3, 4 and 5. After 300 minutes of incubation, two 50 ml aliquo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com