A PUSCH retransmission indication method
A retransmission indication and indication technology, which is applied in the direction of error prevention/detection using the return channel, can solve problems such as PHICH occupation and physical resource collision, and achieve the effect of avoiding PHICH resource collision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
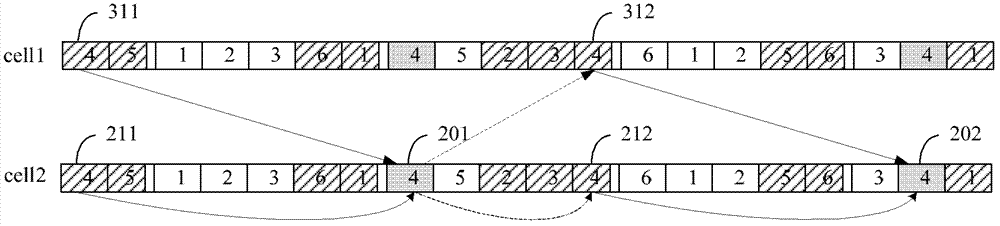
[0062] ① Regarding the timing relationship of PUSCH, if either the calling Cell or the called Cell has an uplink and downlink configuration of 0 or 6, and the calling Cell and the called Cell have different uplink and downlink configurations, the cross-carrier scheduling of the called Cell’s retransmission PUSCH , the corresponding PHICH is ignored, and the UL Grant is used to trigger retransmission if necessary.
[0063] ② Regarding the timing relationship of PUSCH, if the PUSCH loopback time of the uplink and downlink configurations of the calling Cell and the adjusted Cell are different, for the retransmission PUSCH of the adjusted Cell with cross-carrier scheduling, the corresponding PHICH is ignored. If retransmission is required, use UL Grant triggered.
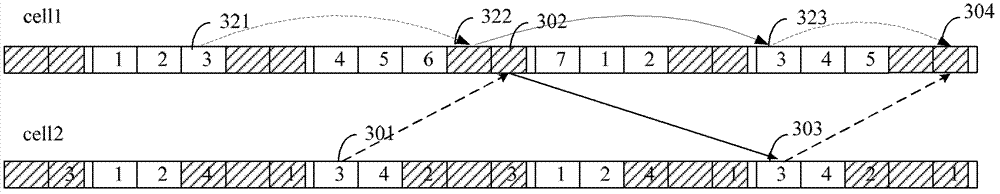
[0064] (2) Implementation Method 2
[0065]For the PUSCH transmitted by the adjusted Cell for the first time, the terminal detects the PHICH channel, the enhanced PHICH channel or the UL Grant to obtain the indication ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com