Positioning method for modal subspace reconstruction steady target in uncertain marine environment
A modal subspace and marine environment technology, applied in the field of target positioning, can solve the problems of difficulty in sonar target positioning, low radiated sound source level of the target to be located, and loss of positioning performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments, and the present invention includes but not limited to the following embodiments.
[0041] Main content of the present invention has:
[0042] 1. The present invention proposes for the first time the method of using the predictable modal subspace to reconstruct the copy field vector to realize robust positioning, and provides its Bartlett and Capon forms respectively.
[0043] 2. The method of determining the predictable mode subspace is given.
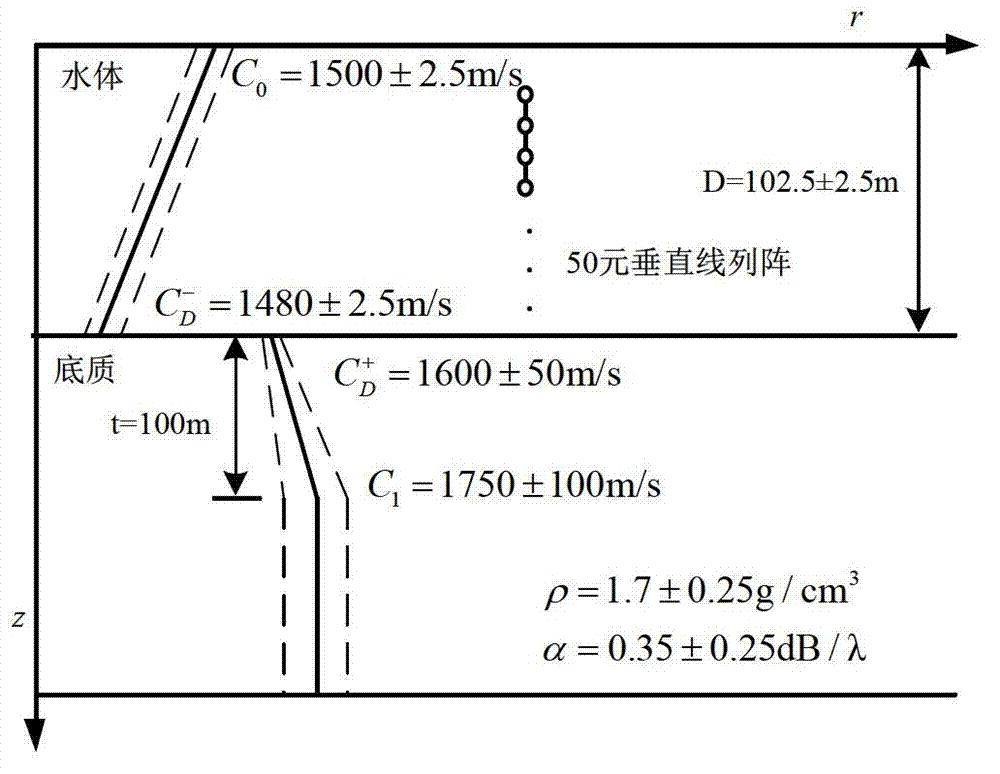
[0044] 3. Using the computer simulation analysis of the standard mismatch test model, the positioning performance of the modal subspace positioning method, the robust maximum likelihood positioning method and the conventional matching field positioning method are compared.
[0045] Technical scheme of the present invention can be divided into following steps:
[0046] 1) Establish an uncertain marine environment...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com