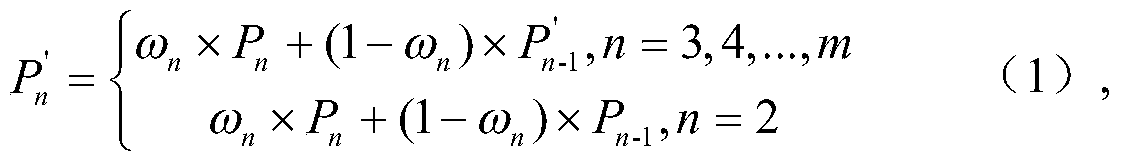An Iterative Method for Core-Heat Coupling of Supercritical Water Reactor
A supercritical water reactor, nuclear thermal coupling technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing and other directions, can solve the problem of iterative calculation difficult to converge, to solve the iterative convergence problem, improve computational efficiency, ensure Effects of Numerical Stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
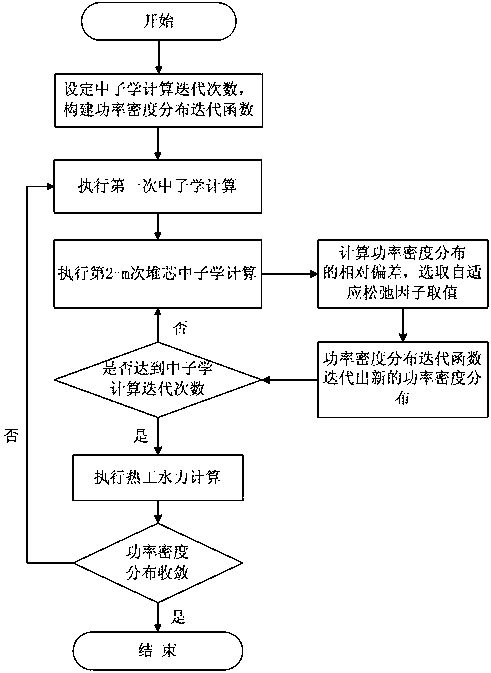
[0035] like figure 1 As shown, a supercritical water reactor core-nuclear thermal coupling iterative method includes the following steps S1-S7:
[0036] S1. Set the neutronics calculation iteration number m, construct the power density distribution iterative function; initialize and execute the neutronics calculation number n, and set the value of n to 0 when initializing n in this embodiment;
[0037] S2. Perform the first neutronics calculation, and jump to step S3 after counting the number of neutronics calculations; in this embodiment, the method of counting the number of neutronics calculations is: add 1 to the number of neutronics calculations, That is, the value of n+1 is assigned to n, and in this step, the value of n is 1 after the number of neutronics calculations is increased by 1;
[0038] S3. Using the power density distribution P obtained by performing the first neutronics calculation 1 Execute the second neutronics calculation, and count the number of neutroni...
Embodiment 2
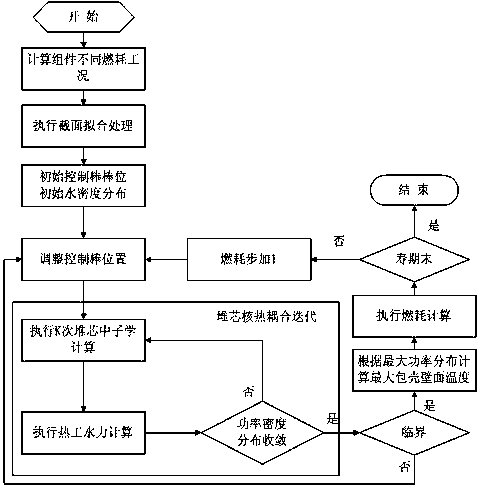
[0064]In this embodiment, a supercritical water reactor core thermal coupling calculation method based on the iterative method in embodiment 1 or embodiment 2 is provided, such as figure 2 shown, including the following steps:
[0065] (1) Calculation of different fuel consumption conditions of components;
[0066] (2) Perform section fitting processing;
[0067] (3) Initial control rod position and water density distribution;
[0068] (4) Adjust the position of the control rod;
[0069] (5) Core-nuclear thermal coupling iterations until the power density distribution obtained after performing thermal-hydraulic calculations converges;
[0070] (6), judge whether to critical state, then jump to step (7), otherwise jump to step (4);
[0071] (7) Calculate the maximum cladding wall temperature according to the maximum power density distribution;
[0072] (8) Execute fuel consumption calculation;
[0073] (9) Determine whether the fuel has reached the end of its life, if so...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com