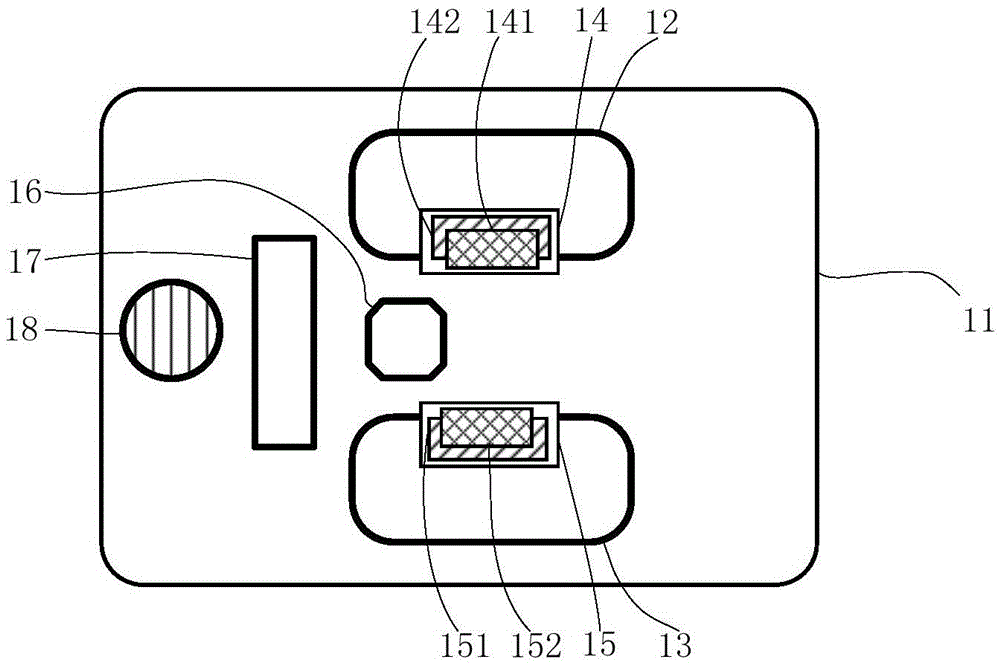
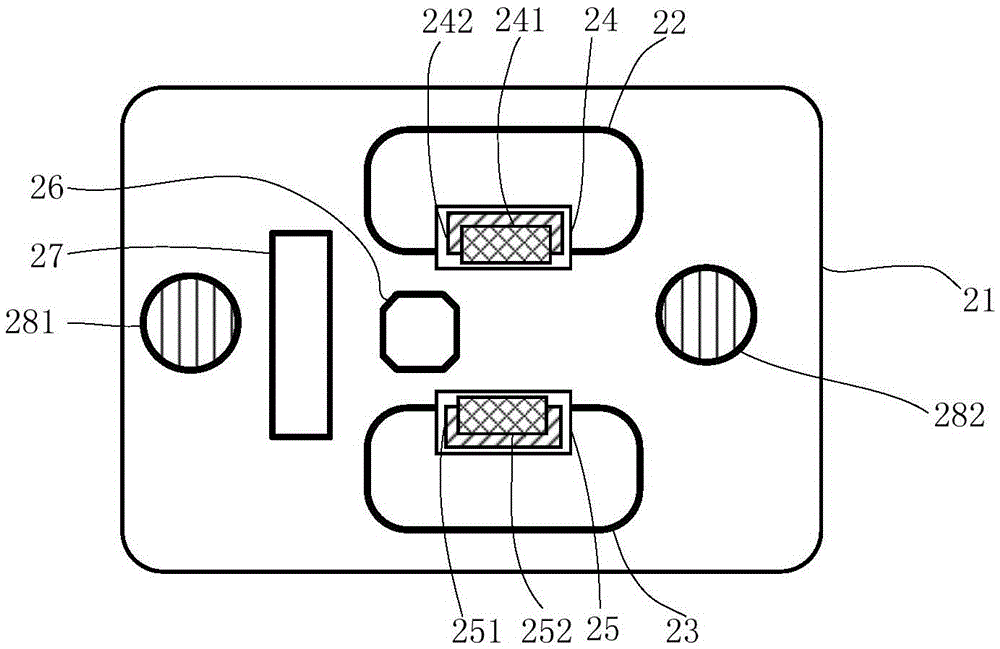
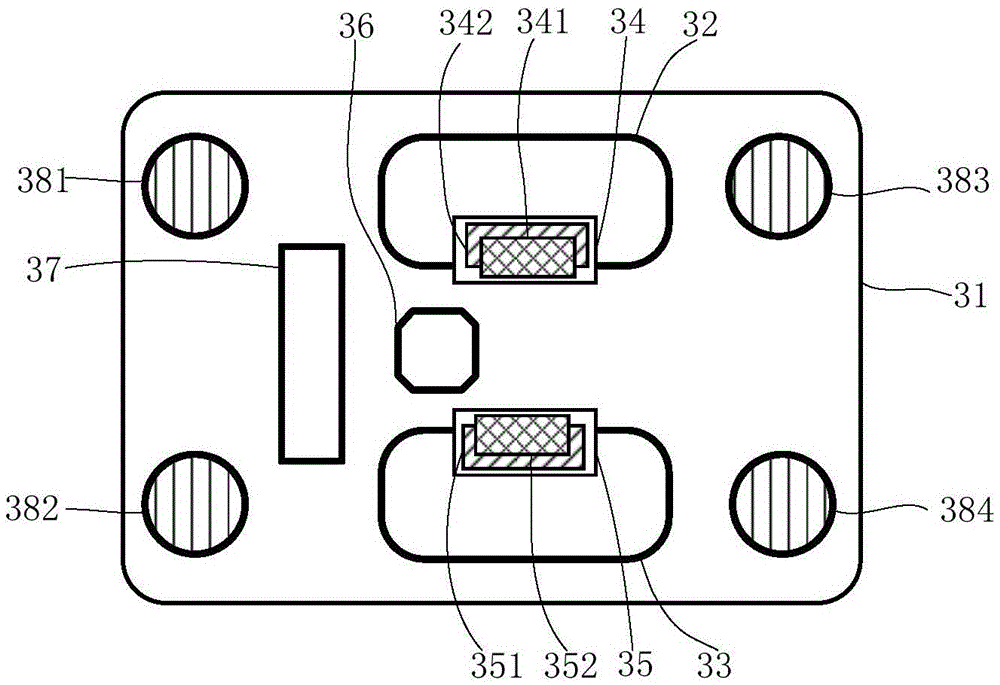
Non-time reference differential drive robot path tracking control method
A non-time reference and tracking control technology, applied in two-dimensional position/lane control, program control manipulator, manipulator, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to determine the structure of the route tracking controller, a large number, and high precision requirements for wheel speed control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] A non-time-referenced differential drive robot route tracking control method proposed by the present invention is described as follows in conjunction with accompanying drawings and implementation examples:
[0040] A non-time-referenced differential drive robot route tracking control method proposed by the present invention and an embodiment for the route tracking control of a two-wheeled robot, the workflow of the two-wheeled robot route tracking controller is as follows Figure 5 shown, including the following steps:
[0041] 1) Analyze the global target route: in the global coordinate system corresponding to the global target route, if the X-axis coordinate value of the global target route changes monotonically (that is, monotonically increasing or monotonically decreasing), the robot controller directly switches to route tracking control state, directly enter step 2), otherwise the global target route is divided into multiple local routes, and the local coordinate s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com