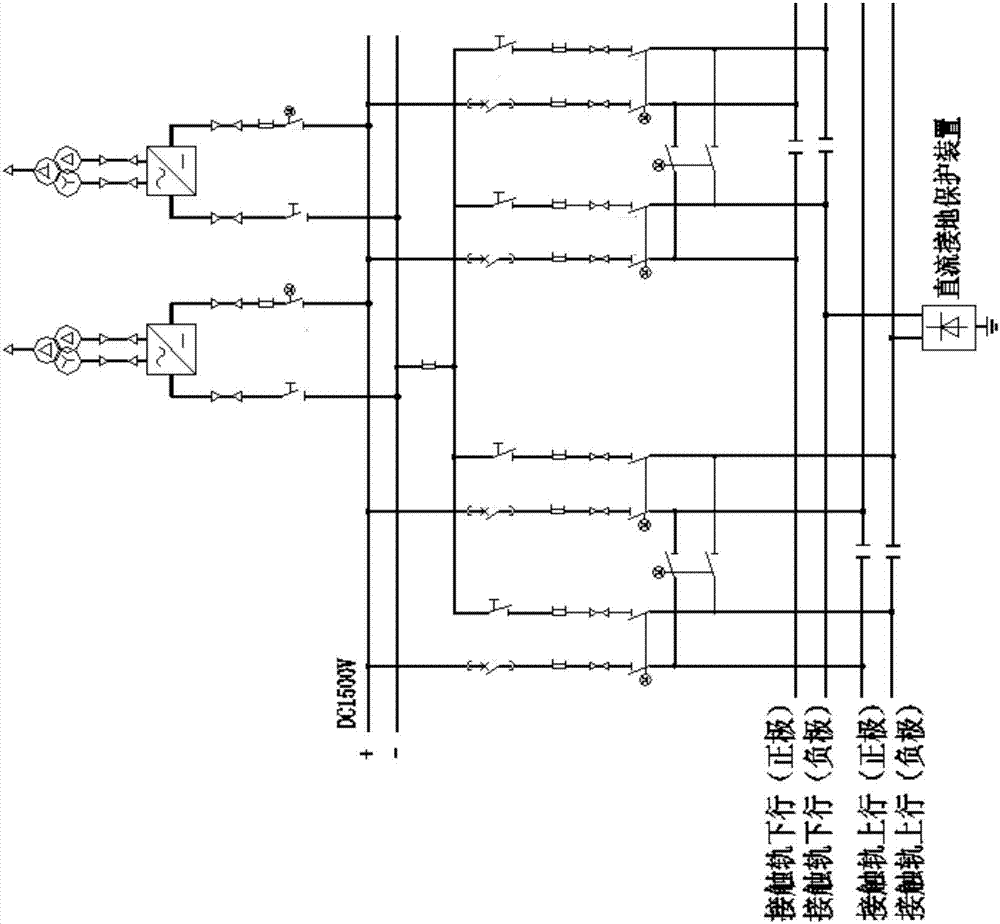
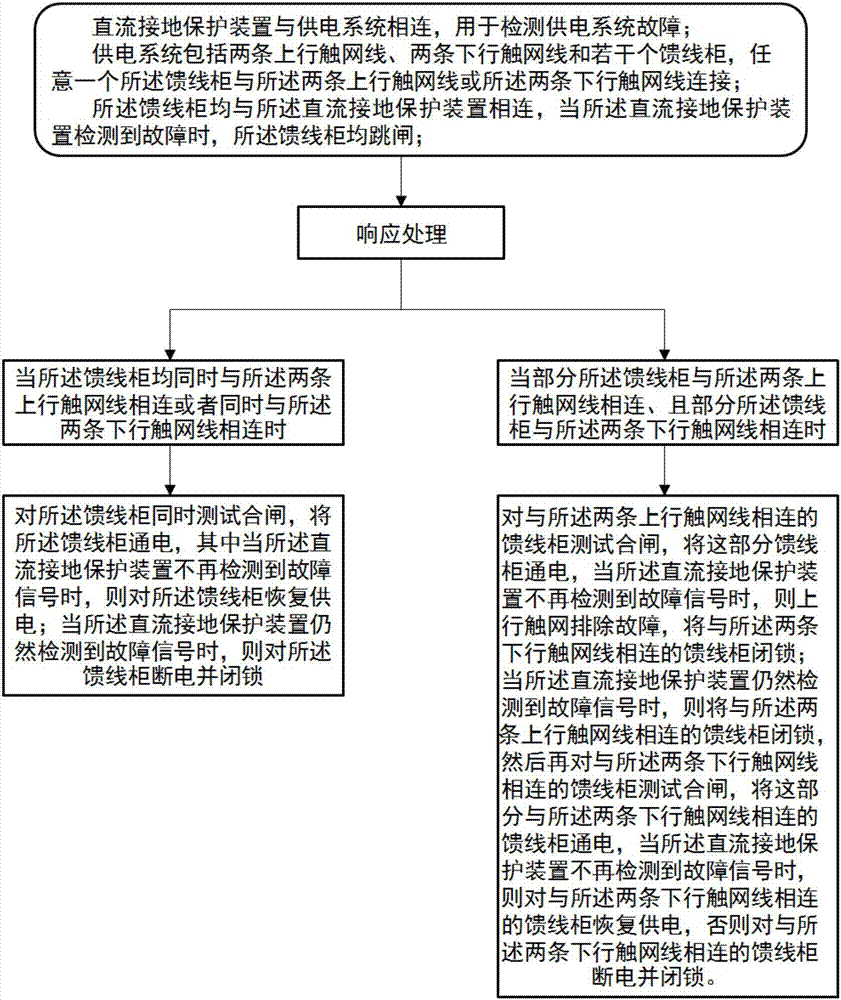
A method for restoring power supply after DC grounding protection starts tripping
A DC grounding and power restoration technology, applied in the field of maglev systems, can solve the problem of high fault identification efficiency, achieve the effects of high fault identification efficiency, fast power restoration, overcoming fault identification and power restoration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] The working condition of this embodiment is: when any one feeder cabinet is running, the DC grounding protection device detects a fault.
[0021] Response processing consists of the following steps:
[0022] (1) The feeder cabinet trips immediately, and then performs a test switch-on;
[0023] (2) If the test is closed successfully and the DC protection trip signal is no longer received, it will operate normally;
[0024] (3) If the DC ground protection trip signal is received immediately after the test is closed, the feeder cabinet will trip and be locked.
Embodiment 2
[0026] The working condition of this embodiment is: when any two feeder cabinets (named A and B respectively) are running, the DC grounding protection device detects a fault.
[0027] Response processing is divided into the following two cases:
[0028] Situation 1: If A and B are both uplink or downlink at the same time, when the DC ground protection trip signal is received for the first time, they all trip, and at the same time, they are tested and closed together. If the DC ground protection trip signal is received again after closing, then trip and lockout;
[0029] Case 2: If A and B are not in the uplink or downlink at the same time, follow the steps below:
[0030] (1) All feeder cabinets A and B trip, and then send a test closing signal to feeder cabinet A;
[0031] (2) If no DC grounding protection trip signal is received after the A feeder cabinet is successfully tested and closed, it is considered that the line is faultless, and no test closing signal is sent to t...
Embodiment 3
[0036] The working condition of this embodiment is: when any three feeder cabinets (named A, B, and C respectively) are running, the DC grounding protection device detects a fault.
[0037] Response processing is divided into the following two cases:
[0038] Case 1: Two upstream feeder cabinets (named A and B respectively) and one downstream feeder cabinet (named C), follow the steps below:
[0039] (1) The three feeder cabinets are running normally, and a DC grounding protection fault occurs. The three feeder cabinets trip immediately, and then send a test closing signal to the upstream, and the two upstream feeder cabinets A and B are tested to close. If A and B are closed If the DC grounding protection trip signal is not received after that, it is considered that there is no fault in the uplink, and no test closing command will be issued to the downlink;
[0040] (2) If the DC grounding protection trip signal is received again after the upstream test is closed, the A and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com