A method for simulating material damage of headlight lampshades using efgm in car crashes
A technology for simulating cars and headlights, applied in the field of automobile collision modeling, can solve problems such as insufficient accuracy of strength evaluation, and achieve the effects of avoiding grid dependency defects, ensuring calculation accuracy, and ensuring calculation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
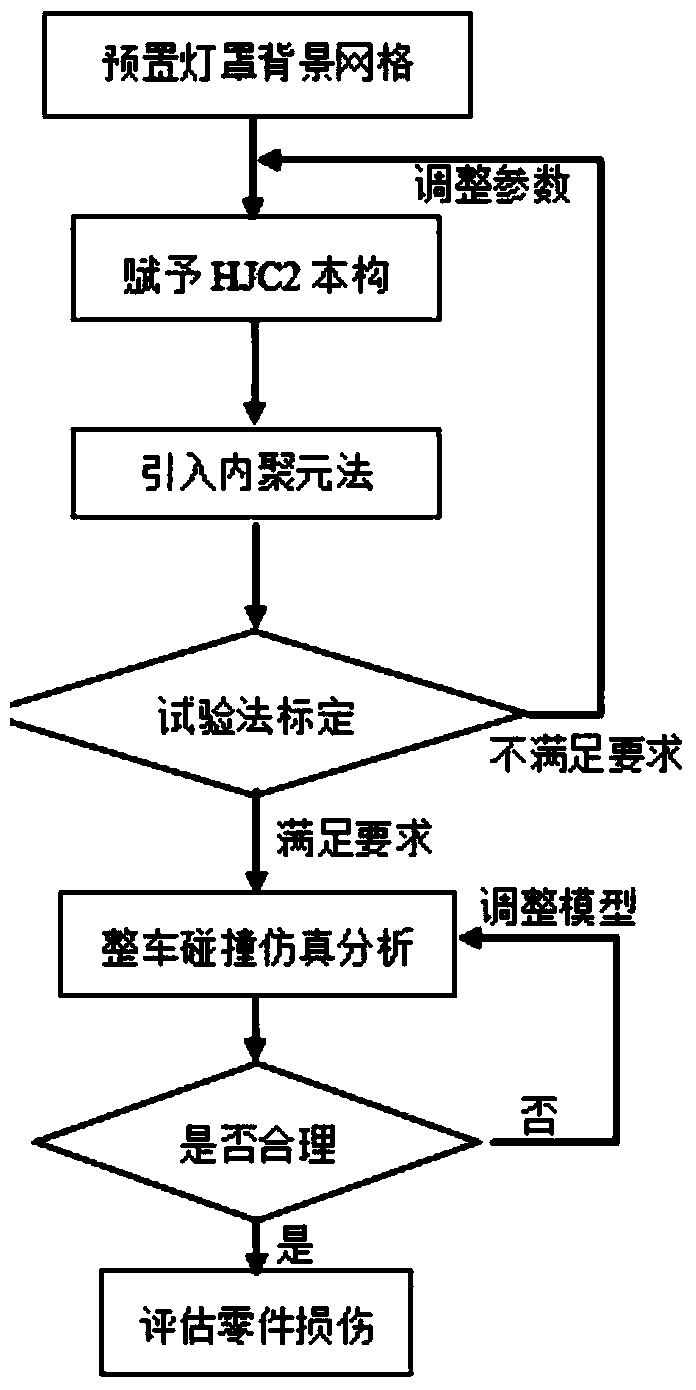
[0028] In a car collision, EFGM is used to simulate the damage of the headlight lampshade material. The specific steps are as follows:
[0029] S1. Use tetrahedron unit (4-node tetrahedron) as discrete element for lampshade, and preset background grid;
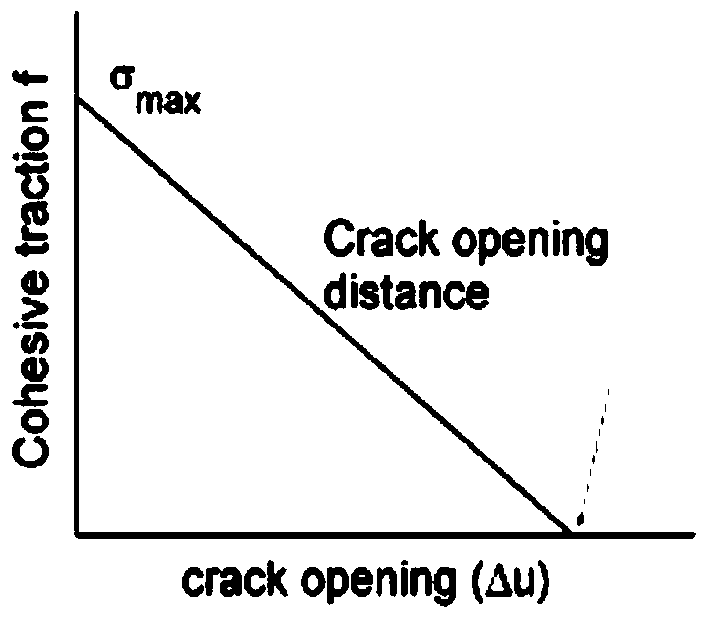
[0030] S2. Endow the lampshade with plastic damage HJC2 constitutive material, and use the cohesive element fracture method to determine how much force the discrete points bear, when the separation occurs, that is, the effect of fracture is expressed;
[0031] S3. Use the calibration test for the constitutive parameters of the lampshade of the corresponding model and the parameters of the EFGM algorithm itself: if the simulation result is consistent with the calibration test, proceed to step S4; if the simulation result is inconsistent with the calibration test, adjust the constitutive parameters of the lampshade and the parameters of the EFGM algorithm itself ;
[0032] In order to keep the benchmarking simulation consistent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com