Frequency domain correlation analysis method for cardiac mapping signals
A technology of cardiac mapping and analysis methods, which is applied in the directions of diagnostic recording/measurement, medical science, sensors, etc., and can solve the problems of inability to reflect the degree of correlation between two signals in the frequency domain, low coherence coefficient, and large limitations.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1: The F correlation method of the present invention is used for sinus rhythm mapping signals (consistent rhythms in different parts) and atrial fibrillation signals (multiple rhythms exist, and rhythms in different parts may be inconsistent), and the traditional correlation analysis and Correlation analysis for comparison. In this embodiment, epicardial mapping signals are used, and the workflow is as follows:
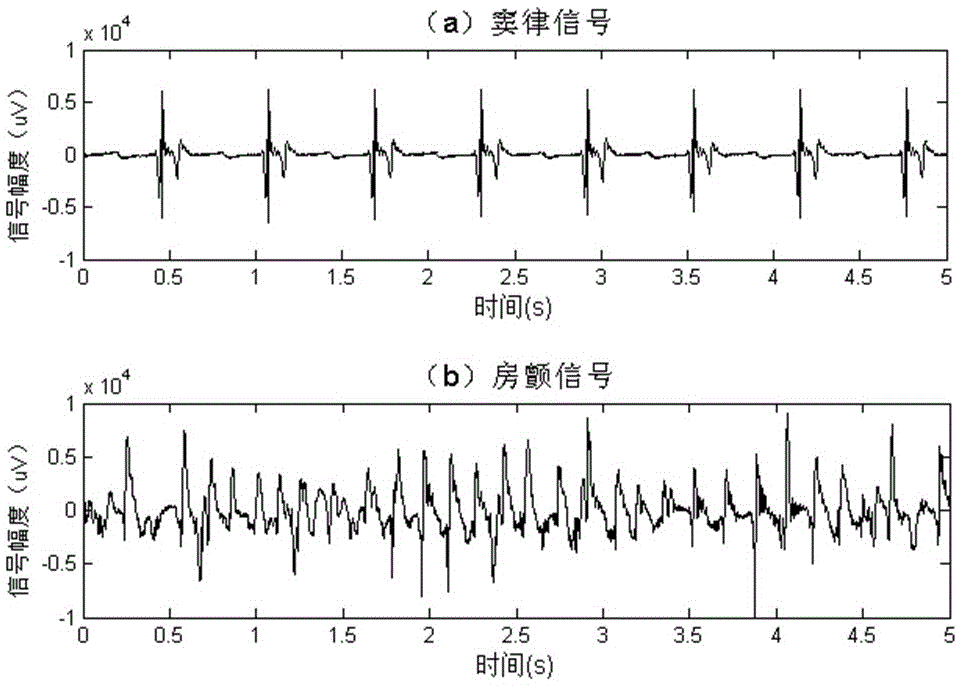
[0041] (1). Using epicardial mapping technology to collect epicardial mapping signals (digital signals) of dogs. Such as figure 1 as shown, figure 1 (a) is the sinus rhythm signal at a certain mapping point, figure 1 (b) is the atrial fibrillation signal at another mapping site. figure 1 (a) with figure 1 (b) Not collected at the same time.
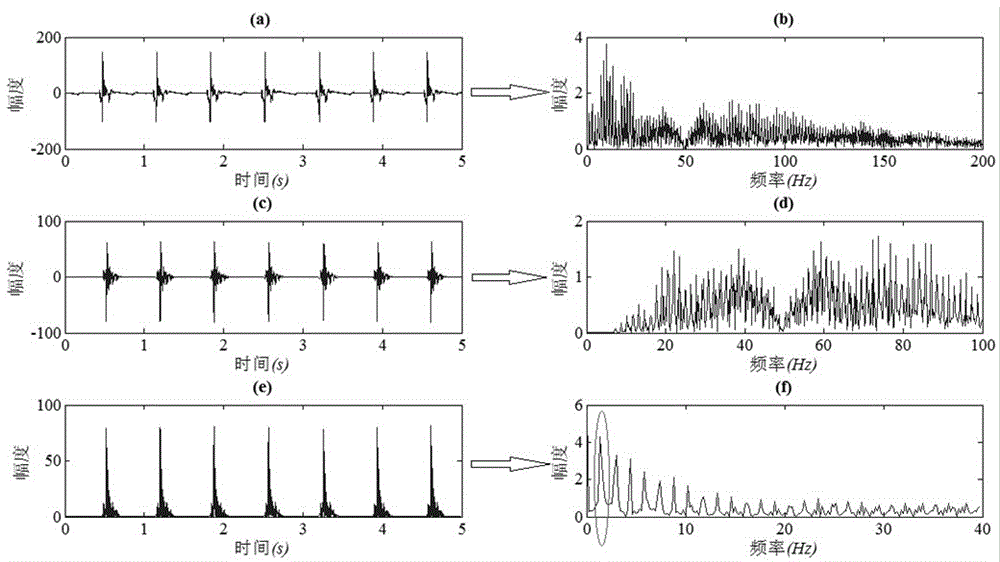
[0042] (2). Perform 20-100Hz band-pass filtering on the sinus rhythm signal collected in step (1). Such as figure 2 as shown, figure 2 (a) is a period of 5s sinus rhythm signal at a certain mapping ...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2: Figure 8 It is an embodiment in which the F-correlation of the present invention (calculation steps are the same as in Embodiment 1) is applied to the time dimension of 128-way mapping signals. In this example, the electrical signals of 128 points on the outer surface of the atrium are collected simultaneously and continuously collected at a certain sampling frequency. will t 1 The signal collected at time and t 1 Each corresponding channel of the signal that starts to be collected at +Δt moment implements the F correlation of the present invention (such as taking Δt=10s, the signal duration is 5s, that is, No. 1 channel t 1 A period of 5s long signal collected from time to time is related to channel 1 t 1 Another 5s long signal collected at +10s is subjected to F-correlation; all 128 signals are implemented sequentially), and two indicators F-C of F-correlation are obtained max and F-f max . Figure 8 It is a schematic diagram of the result when Δt=10...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Embodiment 3: FIG. 9 is an embodiment in which the F-correlation of the present invention (calculation steps are the same as in Embodiment 1) is applied to the spatial dimension of 128-way mapping signals. This example is taken from 128 channels of atrial epicardial signals collected synchronously when atrial fibrillation occurs, with a duration of 5 s. Implement the F-correlation of the present invention for each two-way signal, and obtain two corresponding indexes F-C respectively max and F-f max . In this way, F-C max and F-f max The results of the two F correlations form a 128*128 matrix, and the matrix is represented by an image, as shown in Figure 9. Comparative analysis of multiple images at different times or videos composed of multiple continuous images can help analyze and study the occurrence and maintenance mechanism of arrhythmia.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com