Polypeptides for inhibiting complement activation
An inhibitory and complement system technology, applied in complement proteins, fusion polypeptides, targeting specific cell fusion, etc., can solve problems such as unstudied long-term effects of deposition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
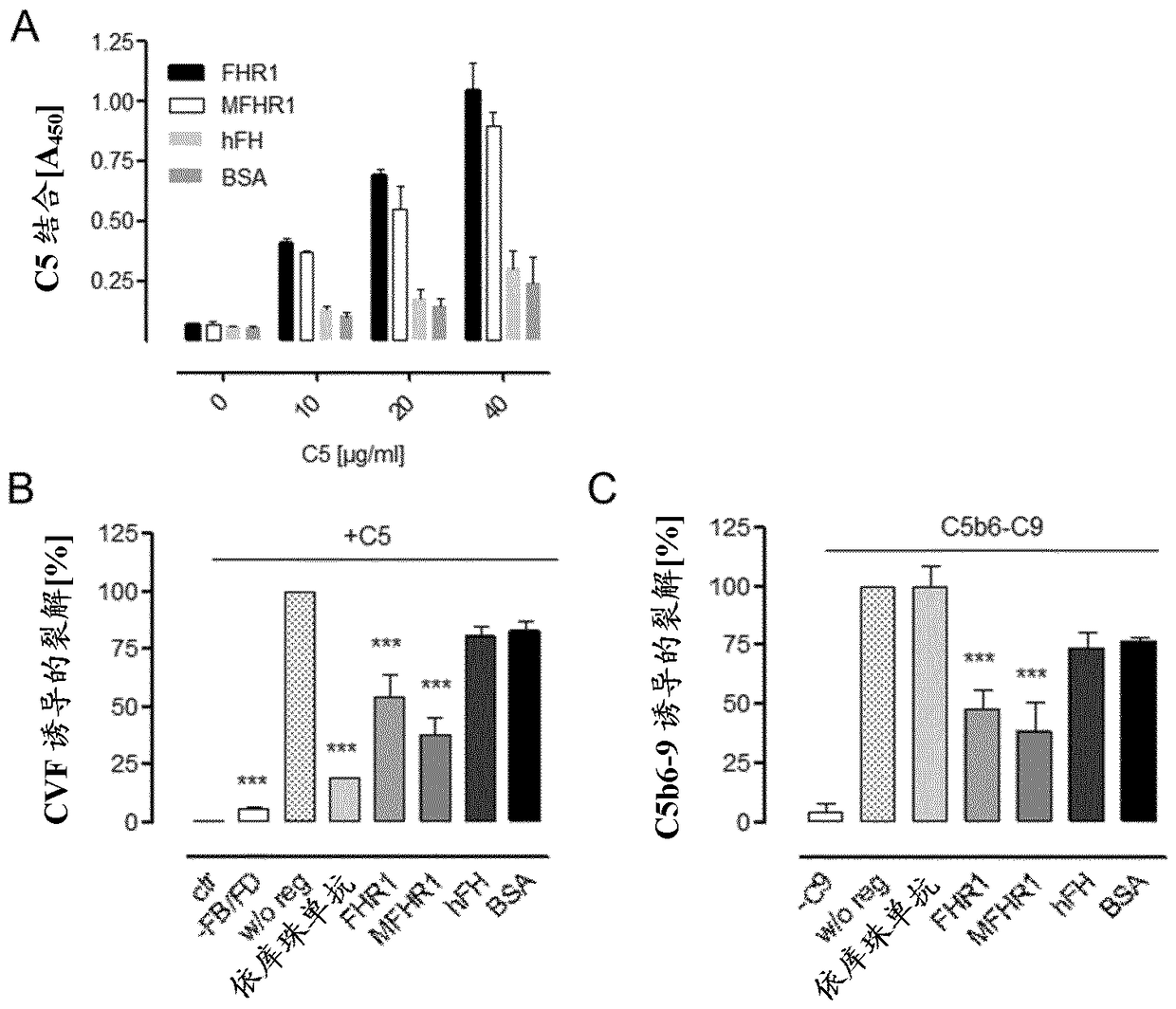
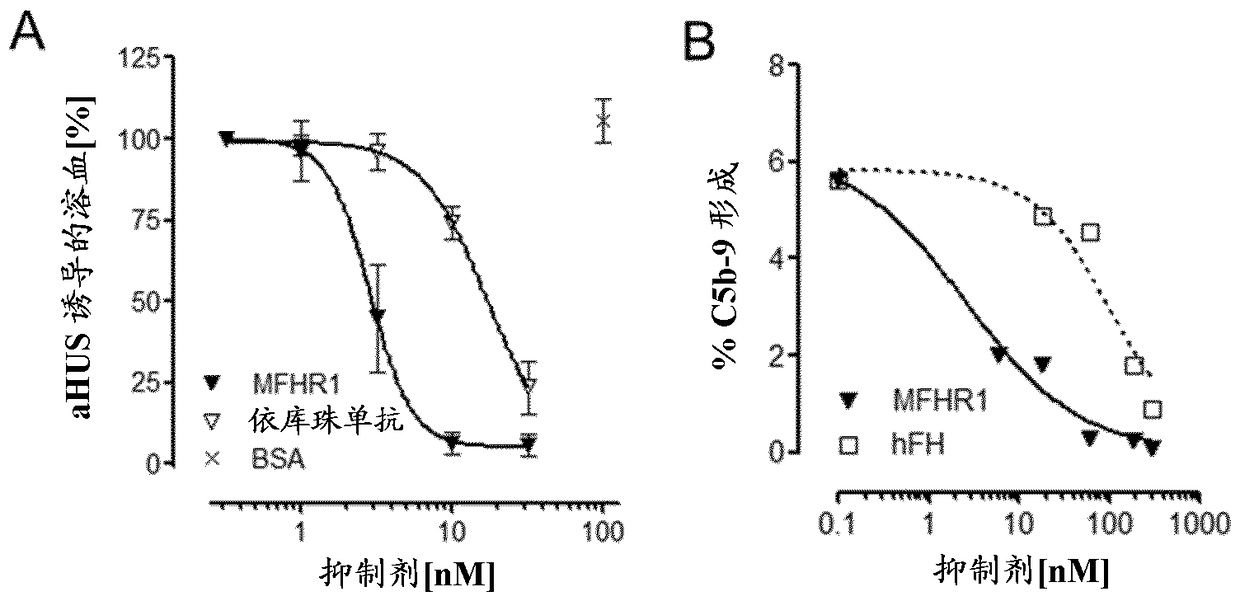
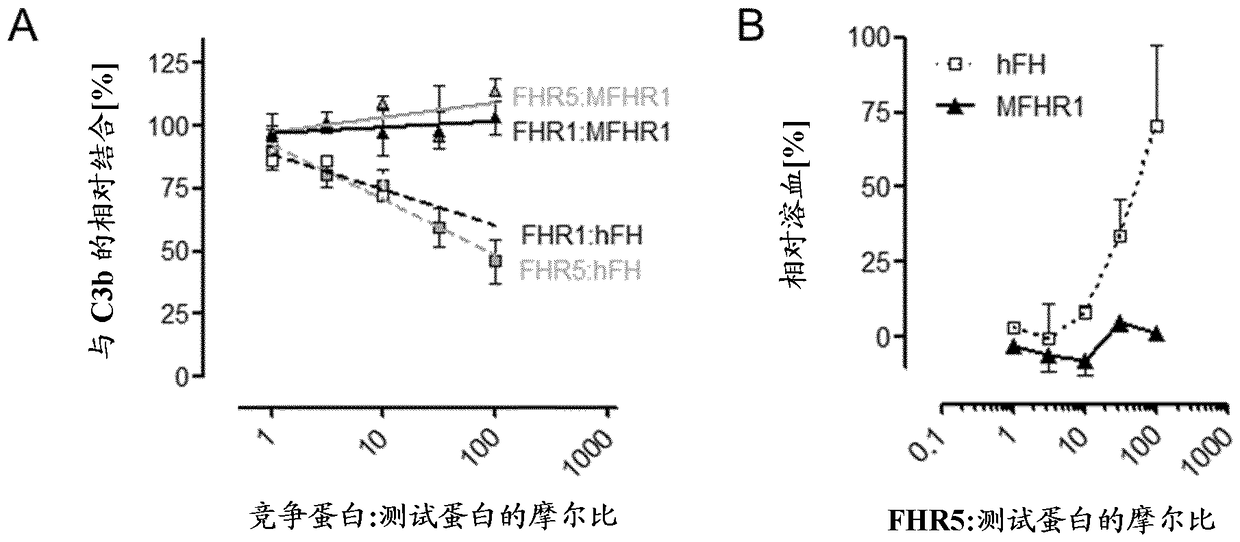
[0092] MFHR1 consists of the N-terminal FH regulatory activity domain SCR1-4 (C3 / C5 convertase decay acceleration and cofactor activity) and the C-terminal surface recognition domain of FH (SCR19-20) and the N-terminal domain of FHR1 ( SCR1-2) consists of [ figure 1 ]. FHR1 is the only known endogenous complement regulator of the C5 convertase. FHR1 SCR1-2 binds C5 and thereby inhibits the cleavage of C5 into C5a and C5b. Additionally, FHR1 SCR1-2 inhibits the terminal complement pathway by binding to C5b6. Through the combination of these domains, complement activation is inhibited at multiple effector sites of the cascade (C3b degradation, inhibition of C3 / C5 convertase, inhibition of C5 cleavage and C5b-9 formation). This also leads to the inhibition and formation of anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a, which are thought to promote disease progression in AP-associated diseases.
[0093] To prepare MFHR1, a cDNA fragment containing the requested sequence of the above-mentioned F...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com