Cell recognition method and device based on stochastic forest classification model
A random forest classification and model technology, applied in the field of image recognition algorithms and machine learning, can solve the problems of feature redundancy, reduced classification accuracy of a single decision tree, and insufficient generalization ability of classifiers, so as to improve classification accuracy and solve feature problems. redundant effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
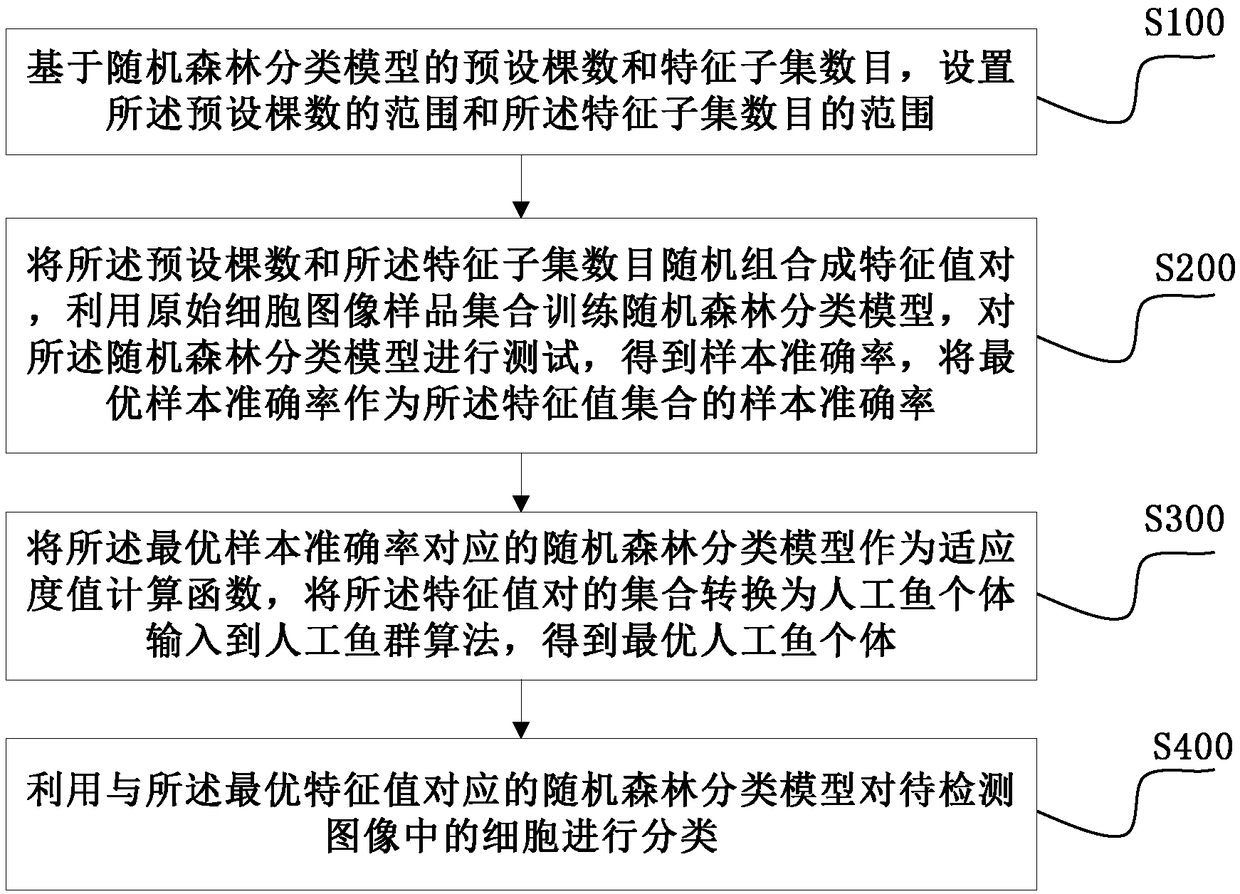
[0051] Based on the following detailed description of the specific embodiments of the present application in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, those skilled in the art will better understand the above and other objectives, advantages and features of the present application.
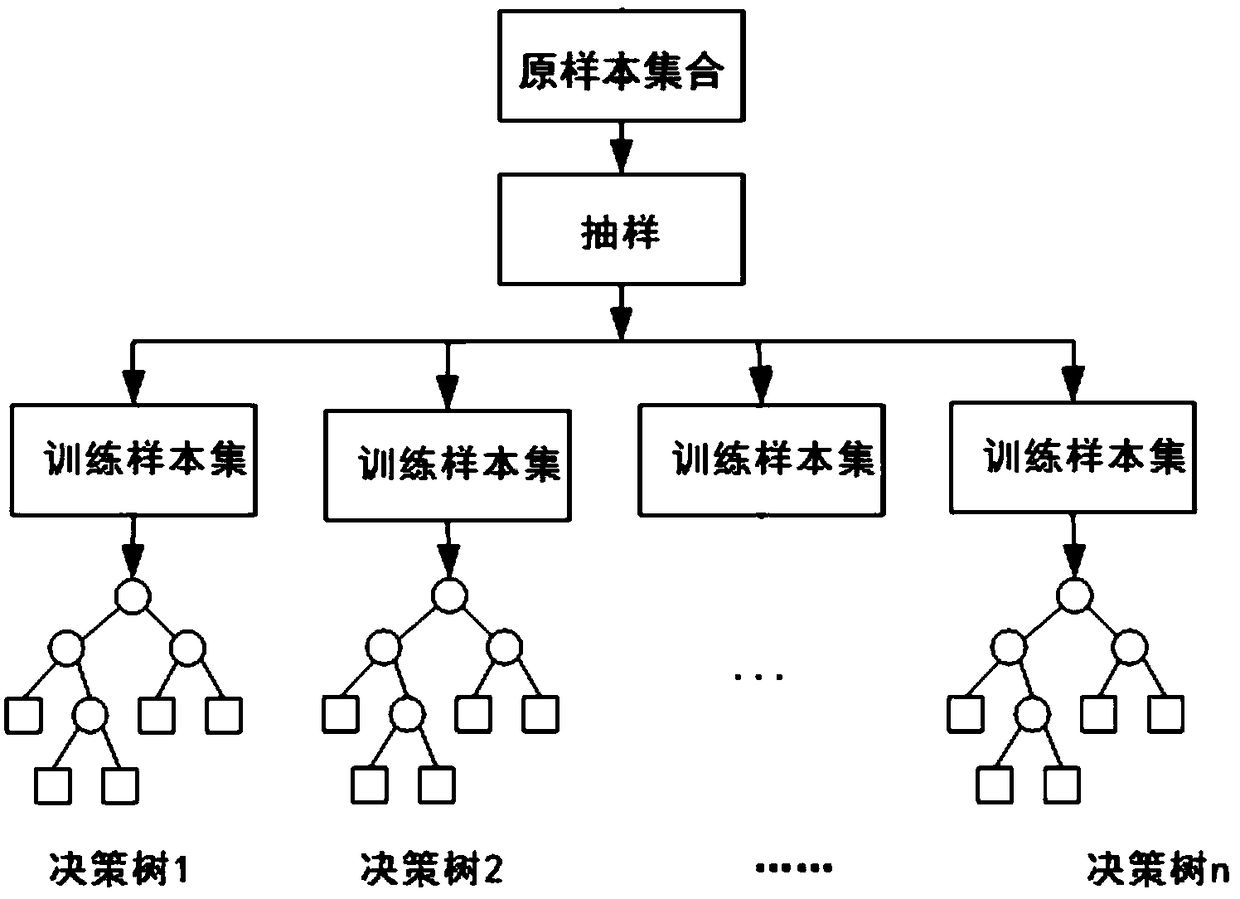
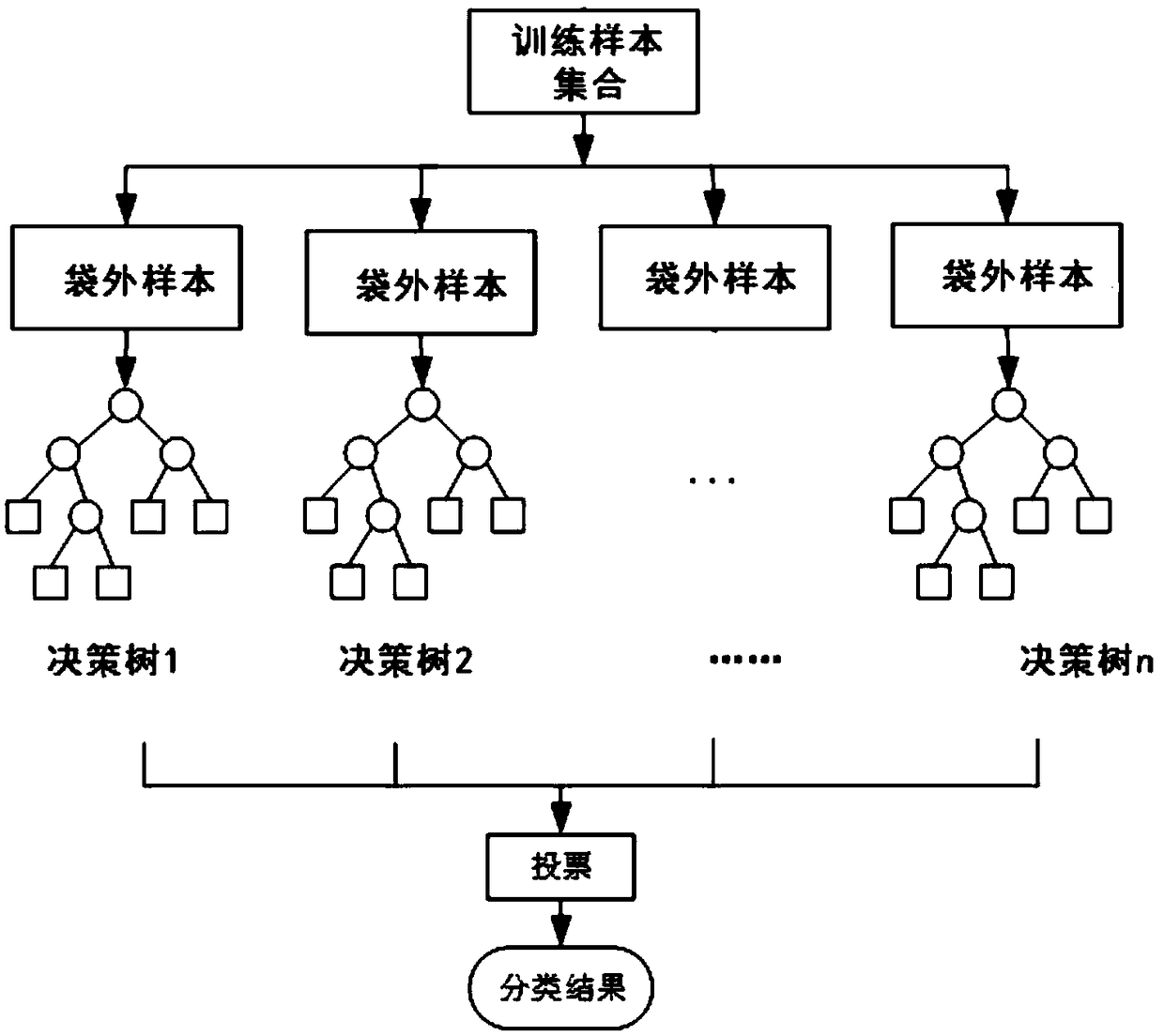
[0052] As a single classifier, the decision tree has high classification efficiency, but its classification results often show a local optimal solution instead of a global optimal solution; during the training process of the decision tree, overfitting is prone to occur. The random forest algorithm is composed of a series of mutually independent decision trees, and each decision tree constitutes the smallest composition of the entire random forest algorithm. Its expression can be written as R={h(x,θ k ),k=1,2,...K}, where {θ k } Is the randomness vector, subject to independent and identical distribution, and K is the number of individual decision trees in the entire classifier. When the random fores...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com