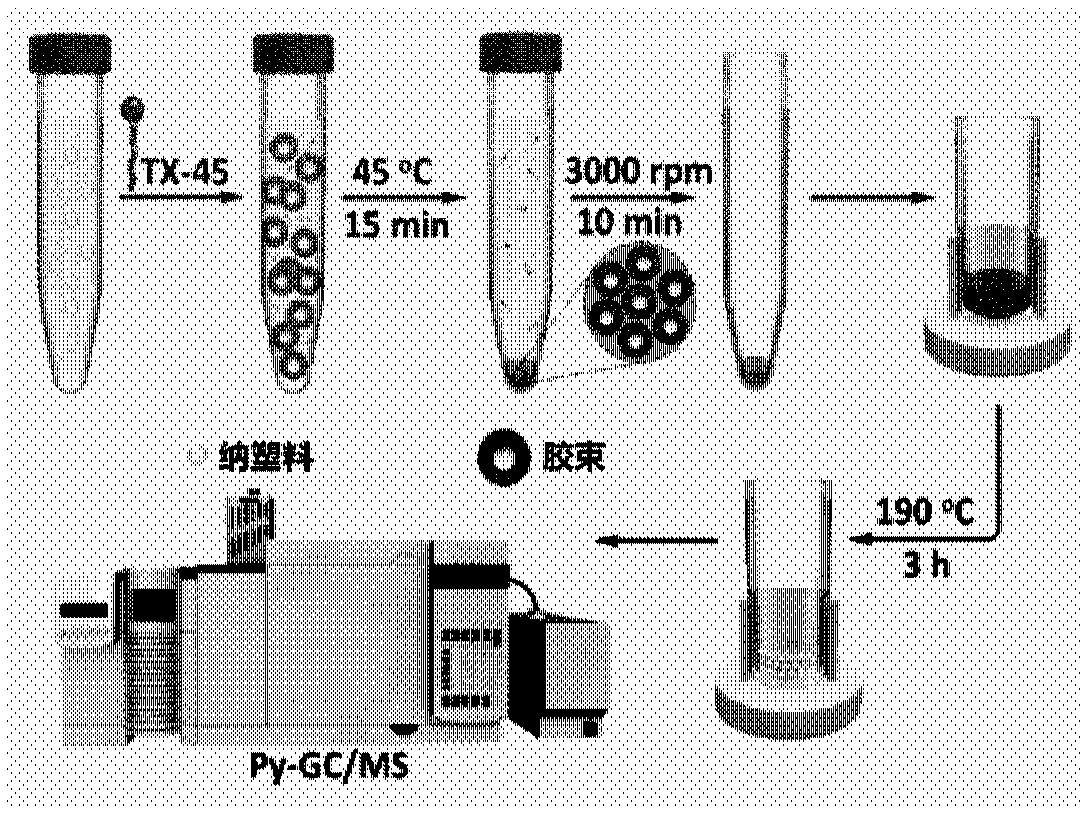
Method for determining nanoplastic based on cloud point extraction-thermal cracking gas chromatography mass spectrometry
A technology of gas chromatography mass spectrometry and thermal cracking, which is applied in the field of determination of nanoplastics based on cloud point extraction-thermal cracking gas chromatography mass spectrometry, can solve the problems of easy mistakes, insufficient reliability, time-consuming, etc., and achieve high sensitivity and stability Good, easy to operate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Optimize cloud point extraction conditions:
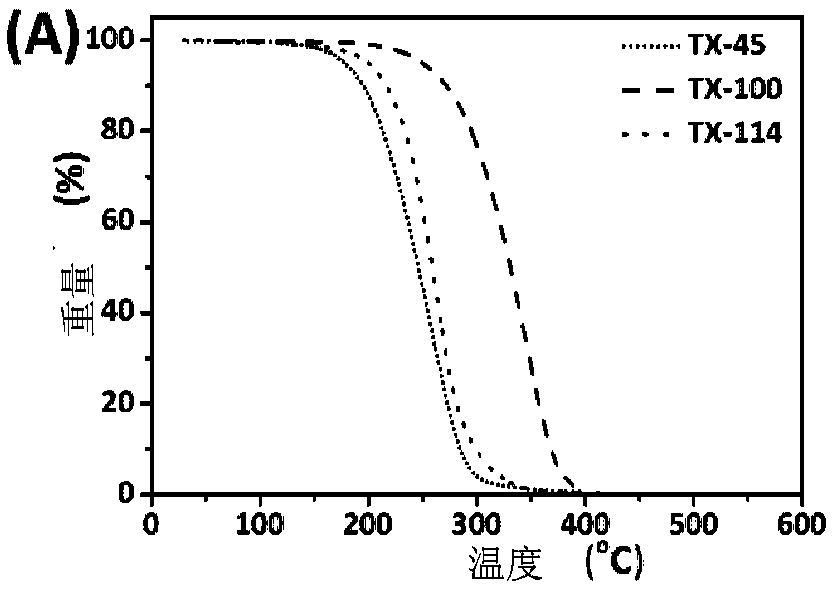
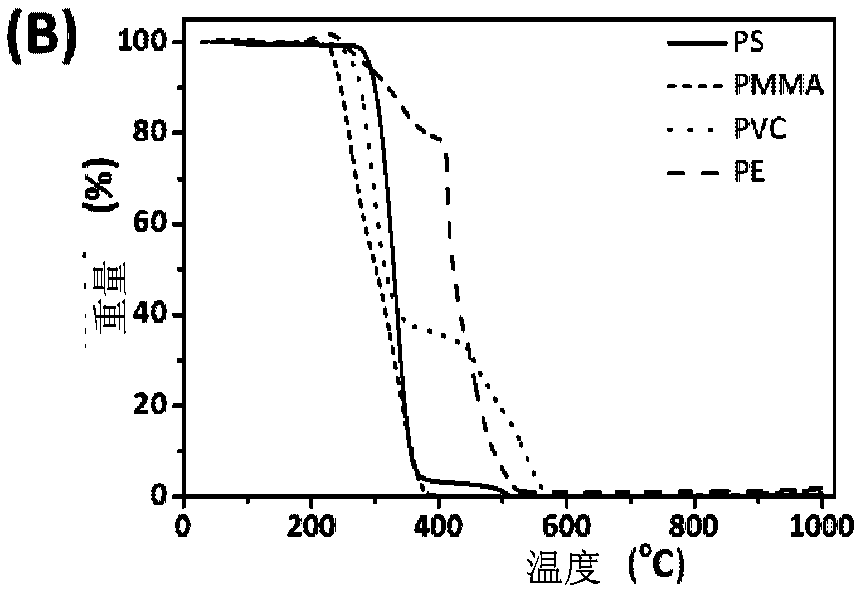
[0030] Such as Figure 2A As shown, the initial thermal decomposition temperatures of surfactants TX-45, TX-100 and TX-114 are about 180 °C, 260 °C and 210 °C, while as Figure 2B As shown, the initial thermal decomposition temperature of polystyrene (PS), polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyethylene (PE) nanoplastics is 210 ° C ~ 260 ° C, thus, it can be TX-45 with a lower thermal decomposition temperature was selected as the cloud point extraction agent, and the subsequent heating temperature was determined to be 190°C, and the heating time was 3h, so that TX-45 could be removed before Py-GC / MS detection without affecting the detection of nanoplastics analyze.
[0031] In this embodiment, taking 60nm polystyrene nanoplastics as an example, select MgSO 4 Additional extraction conditions were optimized for ionic strength modifiers. For other extraction conditions such as surfactant concentrati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com