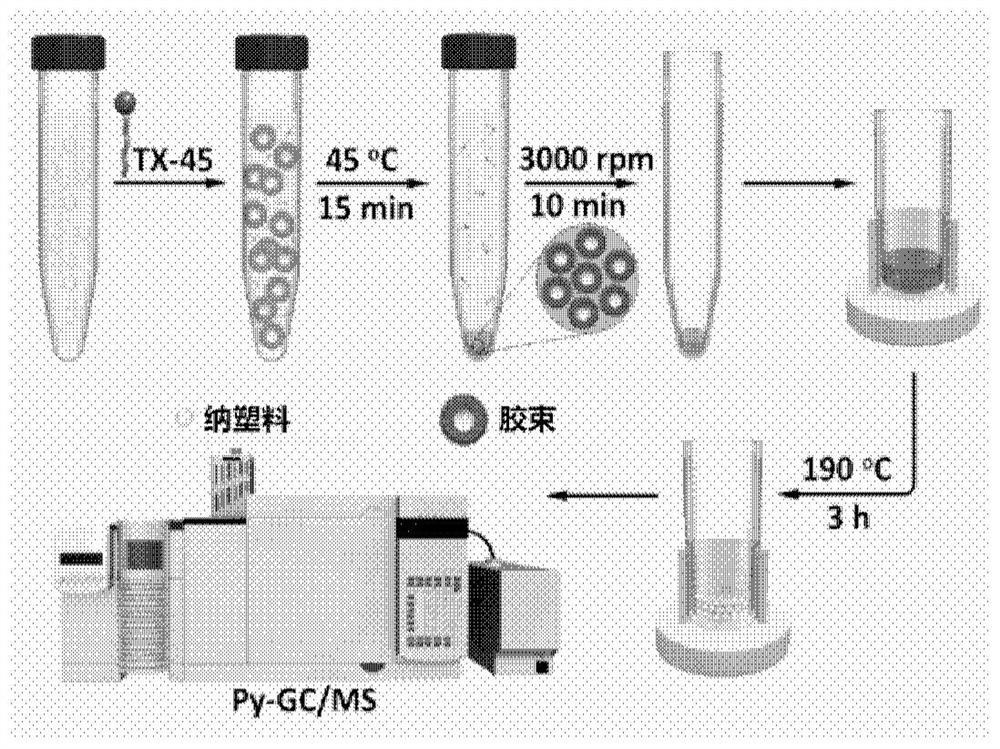
Method for Determination of Nanoplastics Based on Cloud Point Extraction-Pyrolysis Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
A gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and thermal cracking technology, applied in the field of determination of nanoplastics based on cloud point extraction-thermal cracking gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, can solve the problems of insufficient reliability, time-consuming, laborious and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Optimize cloud point extraction conditions:
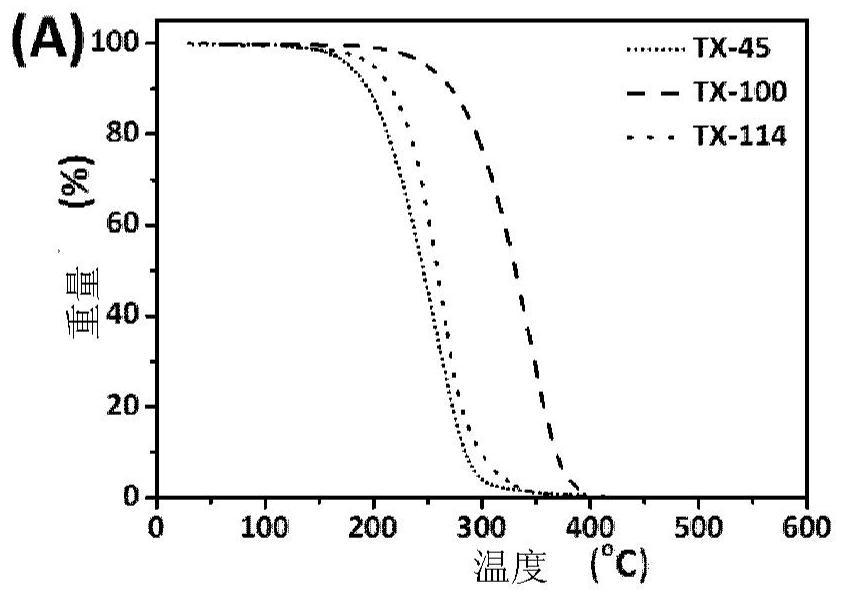
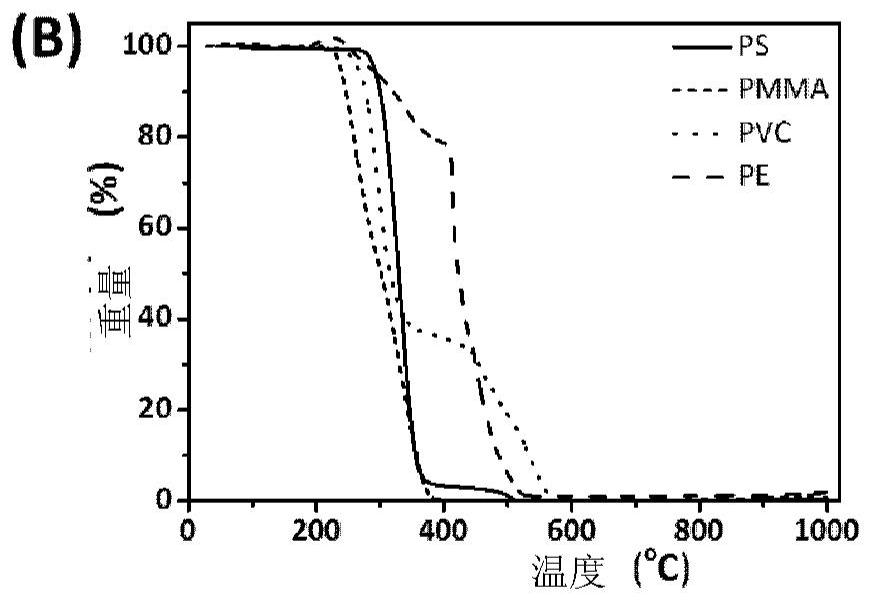
[0030] Such as Figure 2A As shown, the initial thermal decomposition temperatures of surfactants TX-45, TX-100 and TX-114 are about 180 °C, 260 °C and 210 °C, while as Figure 2B As shown, the initial thermal decomposition temperature of polystyrene (PS), polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyethylene (PE) nanoplastics is 210 ° C ~ 260 ° C, thus, it can be TX-45 with a lower thermal decomposition temperature was selected as the cloud point extraction agent, and the subsequent heating temperature was determined to be 190°C, and the heating time was 3h, so that TX-45 could be removed before Py-GC / MS detection without affecting the detection of nanoplastics analyze.
[0031] In this embodiment, taking 60nm polystyrene nanoplastics as an example, select MgSO 4 Additional extraction conditions were optimized for ionic strength modifiers. For other extraction conditions such as surfactant concentrati...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com