Bhattacharyya-distance-algorithm-based excitation inrush current and fault differential current identification method of transformer
A Babbitt distance and excitation inrush current technology, applied in electrical components, emergency protection circuit devices, etc., can solve the problems of easy CT saturation, difficulty in setting the threshold value of the second harmonic braking method, and disappearance of the discontinuity angle.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
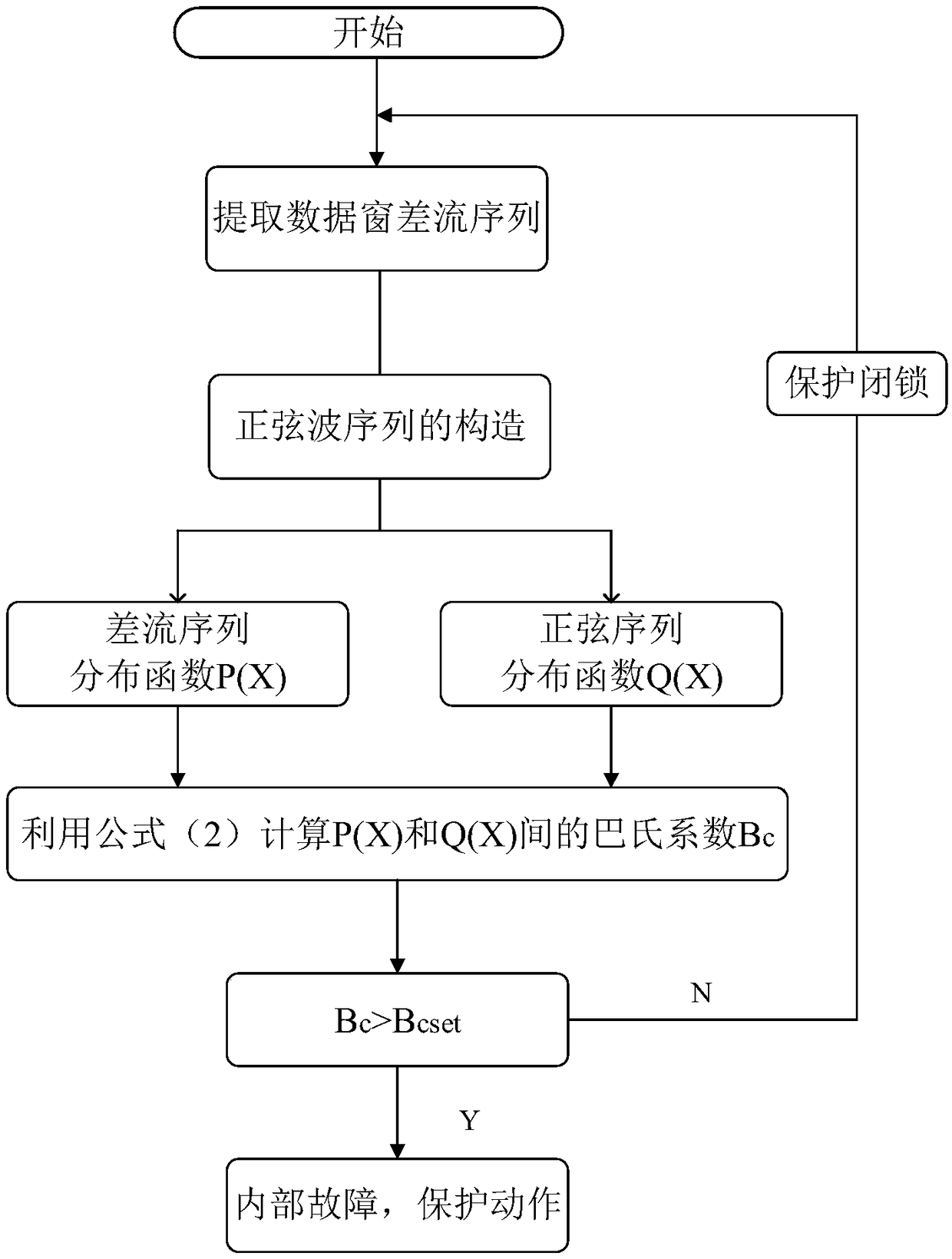
[0040] The identification method of transformer excitation inrush current and fault differential current based on Bhattacharyachian distance algorithm includes the following steps:
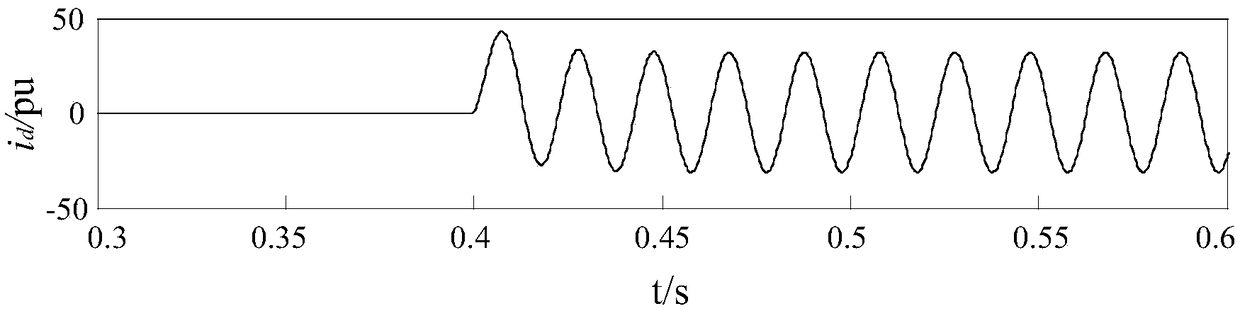
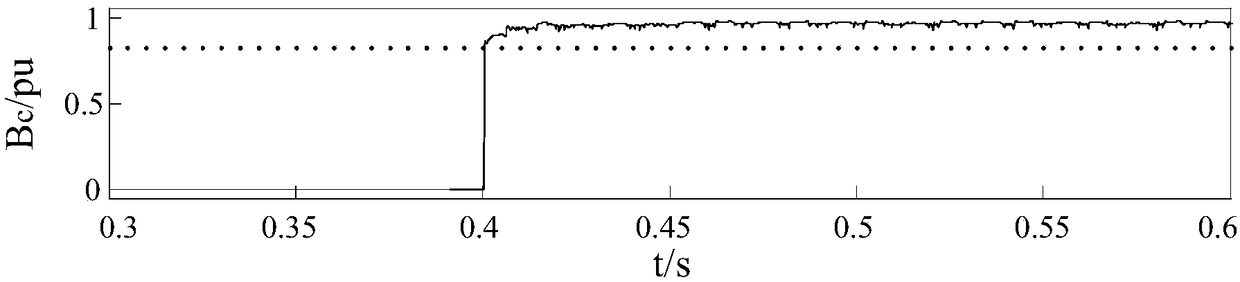
[0041] Step 1: At a certain sampling rate, collect the secondary current of the current transformers on both sides of the differential protection of the transformer, and form a differential current signal sequence I, according to N points per cycle, then the differential current signal sequence I={I( 1), I(2),...I(i),...I(N)}, i=1, 2,...N; Step 2: Judging the extreme value of the differential current signal in the 1 / 2 cycle data window, If the extreme value is less than the threshold value, the protection will be blocked; if it is greater than the threshold value, the criterion will be activated to distinguish the fault differential current and the excitation inrush current.
[0042] Step 3: Construct the sine wave sequence B;
[0043] Let I 1 and I 2 are the start and end points of a data wind...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com